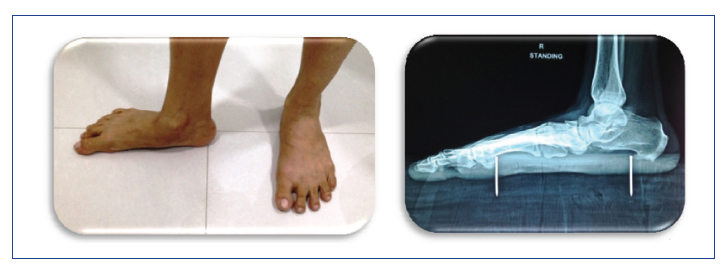
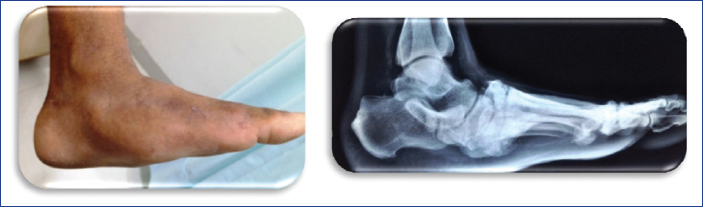
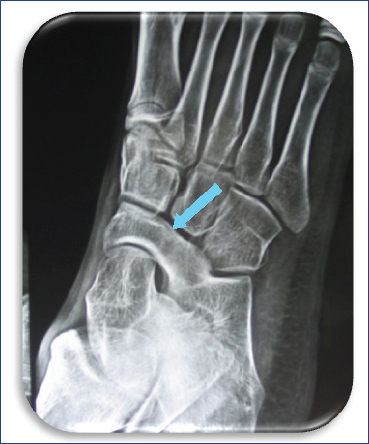
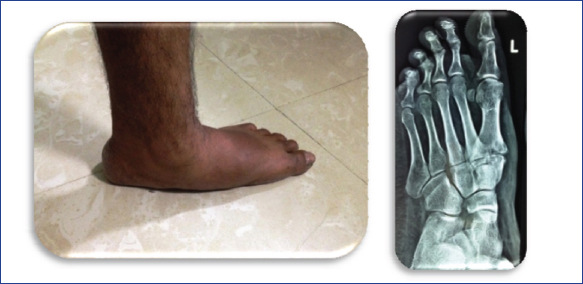
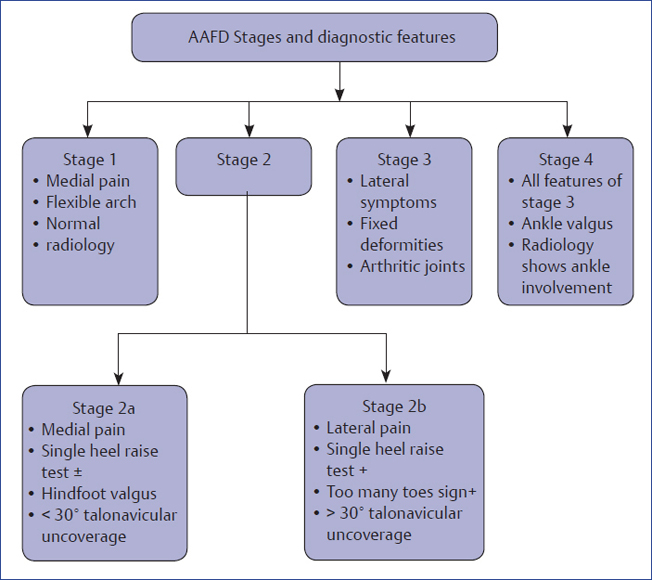
11 Replace ignorance with aggression for treatment of adult flat foot! Replace aggression with reassurance for treatment of paediatric flat foot! Every adult flat foot is not due to tibialis posterior insufficiency! Insufficiency of tibialis posterior (TP) is the most common cause of flat feet in adults! To reach at a correct diagnosis, the examiner needs to have answers for the following questions: Question 1: Is there a flat foot? Answer: History, clinical examination, and radiology would help in answering this question. Question 2: What is the cause of flat feet? Answer: Six basic sets of causes are found for adult flat feet. 1. Adult flexible flat foot 2. Adult acquired flat foot deformity (AAFD) or posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) (Fig. 11.1) 3. Tarsal coalition (Fig. 11.2) Fig. 11.2 X-ray picture of calcaneonavicular coalition. 4. Posttraumatic, arthritic, or iatrogenic flat foot (Fig. 11.3) Fig. 11.3 Clinical and X-ray picture of flat foot due to arthritis of midfoot. 5. Charcot flat foot (Fig. 11.4) 6. Neuromuscular flat foot Table 11.1 Cause-specific diagnostic features of flat foot • Tender TP • Flat arch • Forefoot deformity • Hindfoot deformity • Too many toes sign +ve • Single heel raise test +ve • Radiological signs • Postural complaints • Arch pain • Heel pain • Symptomatic weight bearing • TP intact • Foot flexible • Angle changes in radiology • History of trauma or • prior surgery • RA or seronegative arthritides • Joint pain along with effusion • Radiology shows implant, arthrosis, malalignment • Adolescent age • Symptoms ± • Reduced motion of hindfoot • Peroneal spasm • Rigid flat foot • Radiology • CT Scan • History of swelling and deformity • Neuropathy • Radiology shows joint destruction, osteolysis, fractures, and vascular calcifications • History of trauma, or prior surgery • Pain on ambulation • Gait abnormalities • Neuromuscular dysfunction • Radiology shows anomalies and malalignment Question 3: Which is the stage of adult acquired flat feet (AAFD)? Answer: Stage-specific diagnostic algorithm is displayed in Flowchart 11.1. Flowchart 11.1 Adult acquired flat feet Stages and diagnostic features.
Growing with Flat Feet: Childhood to Adulthood
Adult Flat Foot
Diagnostic Algorithm
Cause-specific diagnostic features of flat foot are displayed in Table 11.1.
S. No.
Specific-cause of flat foot
Cause-specific diagnostic features
1
TP tendon dysfunction
2
Non-PTTD flat feet
3
Arthritic, posttraumatic, and iatrogenic flat foot
4
Tarsal coalition
5
Charcot foot
6
Adult neuromuscular flat foot
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree