Arthroscopic Lateral Retinacular Release
Patient Presentation and Symptoms
- Lateral patellar dislocation
- Patellar catching or giving way
- Anteromedial knee pain
Indications
Malalignment with recurrent subluxation or dislocation of the patella that has been refractory to nonoperative management
Physical Examination
- Apprehension
- Medial retinacular tenderness
- Abnormal patellar tracking through a range of motion
Patient and Equipment Positions
- Supine on the operating table
- No leg holder
- Thigh tourniquet applied but not inflated
Surgical Procedure
Surgical Approach
Arthroscopic Portals
- Superomedial inflow portal
- Inferolateral arthroscopy portal
- Inferomedial portal
Surgical Technique
- Arthroscopic examination through the inferolateral portal, paying close attention to patellofemoral tracking, lateral facet compression, and chondromalacia
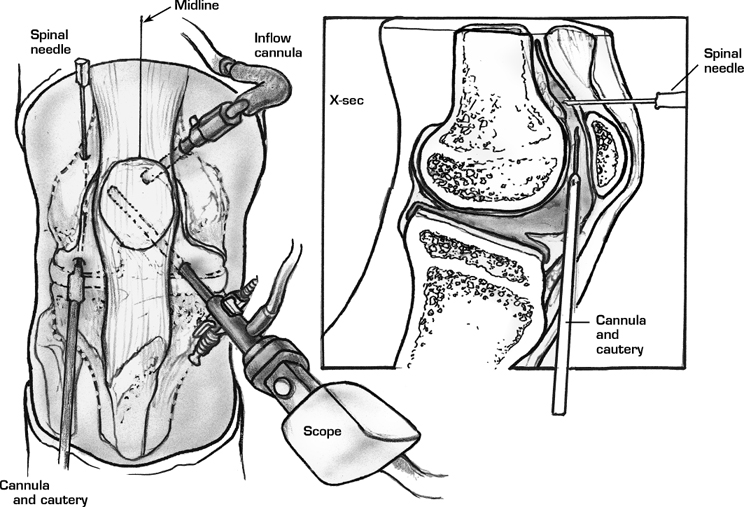
- Transfer the arthroscope to the inferomedial portal (Fig. 49–1)
- Insert a spinal needle approximately 2 cm proximal to the superolateral margin of the patella. This helps in orientation during the release.
- Insert the arthroscopic electrocautery unit or ultrasound wand through the inferolateral portal.
- Begin the lateral release at the musculotendinous junction of the vastus lateralis near the superolateral border of the patella.
- Transect the synovium and capsular ligaments sequentially (Fig. 49–2).
- Progress with the release distally, staying approximately 1 cm from the patella.
- Adequate release is confirmed by manually everting the patella 90 degrees.
Dressings, Braces, Splints, and Casts
Standard postoperative dressings including an Ace bandage
Postoperative Care
- Immediate range of motion exercises
- Weight bearing as tolerated, initially with crutches
- Reestablish the dynamic equilibrium between the hamstrings and quadriceps.
Tips and Pearls
- Maintain the layer of subcutaneous fat as this layer acts as an insulator against cutaneous burns from the cautery unit.
- To ensure an adequate release, the lateral patellotibial ligament and capsular tissue must be released.
- The inferolateral arthroscopy portal may be enlarged as a small arthrotomy to complete the distal release.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








