Hemivertebra Resection
Examination/Imaging
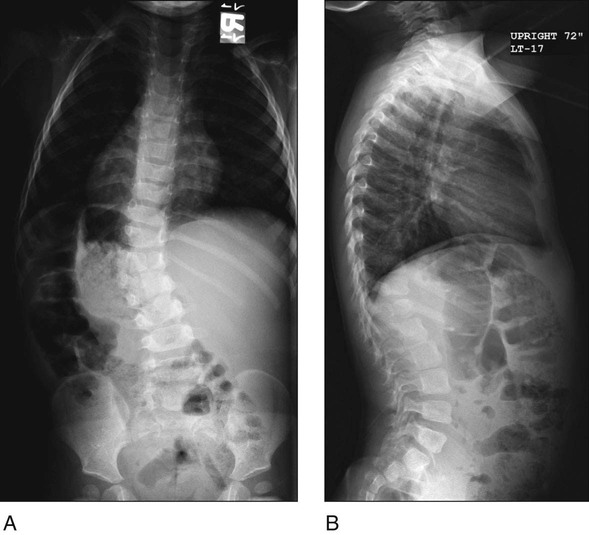
 Standing posteroanterior (PA) and lateral 36-inch spine radiographs are obtained. Figure 1 shows standing radiographs of a patient with a thoracolumbar hemivertebra in PA (Fig. 1A) and lateral (Fig. 1B) views.
Standing posteroanterior (PA) and lateral 36-inch spine radiographs are obtained. Figure 1 shows standing radiographs of a patient with a thoracolumbar hemivertebra in PA (Fig. 1A) and lateral (Fig. 1B) views.
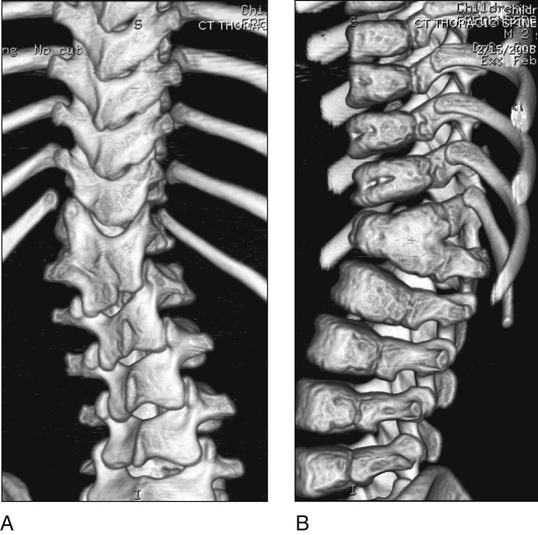
 Three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) scan will reveal the posterior elements (Fig. 2A) and the partial anterior fusion (Fig. 2B).
Three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) scan will reveal the posterior elements (Fig. 2A) and the partial anterior fusion (Fig. 2B).
 Screening examinations should be done for additional morbidities:
Screening examinations should be done for additional morbidities:
Surgical Anatomy
 The relevant surgical anatomy for hemivertebra excision relies on a thorough understanding of the posterior spinal elements as well as the anatomy of the hemivertebra posterior elements.
The relevant surgical anatomy for hemivertebra excision relies on a thorough understanding of the posterior spinal elements as well as the anatomy of the hemivertebra posterior elements.
 The preoperative CT scan is of utmost importance in order to assess for bifid midline structures and the relationship of the hemilamina compared to the levels above and below.
The preoperative CT scan is of utmost importance in order to assess for bifid midline structures and the relationship of the hemilamina compared to the levels above and below.
 Key points to resection are as follows: visualization down the corresponding pedicle and its relationship to the nerve roots above and below, the dura near the medial wall, and the epidural venous plexus.
Key points to resection are as follows: visualization down the corresponding pedicle and its relationship to the nerve roots above and below, the dura near the medial wall, and the epidural venous plexus.
 Understanding the anterior anatomy and whether or not the hemivertebra is segmented or partially segmented helps with complete resection anteriorly.
Understanding the anterior anatomy and whether or not the hemivertebra is segmented or partially segmented helps with complete resection anteriorly.
Positioning
 The patient is placed in the prone position on a radiolucent spinal frame.
The patient is placed in the prone position on a radiolucent spinal frame.
 Padding is placed on the chest and iliac crests, taking care to keep the abdomen free to facilitate venous return (Fig. 3).
Padding is placed on the chest and iliac crests, taking care to keep the abdomen free to facilitate venous return (Fig. 3).
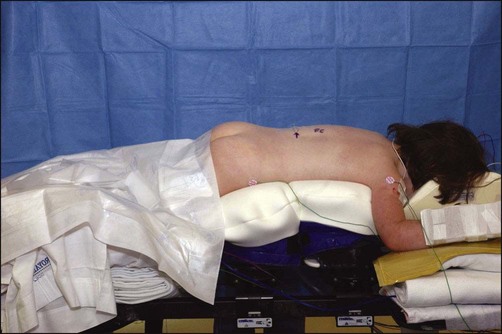
 The convex side needs to be elevated by 10–20° in order to allow bleeding and the dura to fall away from the operated resection site.
The convex side needs to be elevated by 10–20° in order to allow bleeding and the dura to fall away from the operated resection site.
 The patient must have appropriate somatosensory and motor evoked potential monitoring in place.
The patient must have appropriate somatosensory and motor evoked potential monitoring in place.
Portals/Exposures
 Standard posterior element exposure is done.
Standard posterior element exposure is done.
 A hypotensive anesthetic may be used, keeping the mean arterial pressure between 65 and 70 mm Hg, in order to help avoid excessive bleeding. Judicious use of electrocautery is done to keep the surgical field dry.
A hypotensive anesthetic may be used, keeping the mean arterial pressure between 65 and 70 mm Hg, in order to help avoid excessive bleeding. Judicious use of electrocautery is done to keep the surgical field dry.
 Wide dissection is performed bilaterally to the tips of the transverse processes. The posterior element anatomy on the preoperative CT scans must be studied and understood for two main reasons.
Wide dissection is performed bilaterally to the tips of the transverse processes. The posterior element anatomy on the preoperative CT scans must be studied and understood for two main reasons.
55: Hemivertebra Resection







