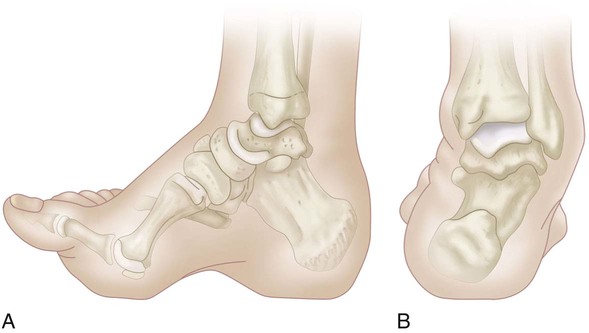
• This technique is easier and more reliable than the Coleman block test. It allows the surgeon to tell if a sliding calcaneal osteotomy will be necessary to correct heel varus. • The patient’s forefoot is hinded to check the calcaneus position relative to the tibia; if valgus, the forefoot only is corrected.
Osteotomies of the Foot for Cavus Deformities
Examination/Imaging
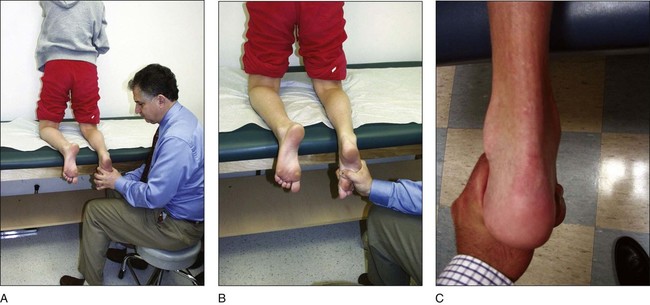
 All patients are assessed to evaluate the flexibility of the hindfoot varus using the kneeling test (Fig. 3A–C).
All patients are assessed to evaluate the flexibility of the hindfoot varus using the kneeling test (Fig. 3A–C).
 Standing anteroposterior (AP) radiographs of both ankles are obtained.
Standing anteroposterior (AP) radiographs of both ankles are obtained.
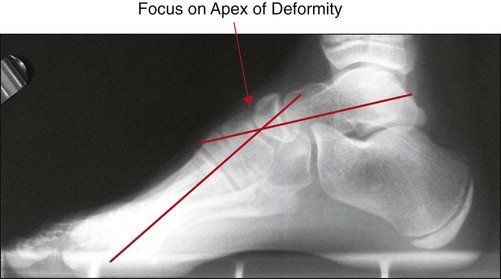
 Standing AP and lateral (Fig. 4) radiographs of both feet are examined, focusing of the apex of the deformity.
Standing AP and lateral (Fig. 4) radiographs of both feet are examined, focusing of the apex of the deformity.
 Preoperative computed tomography scans with three-dimensional reconstruction may be considered to visualize the deformity.
Preoperative computed tomography scans with three-dimensional reconstruction may be considered to visualize the deformity.
Procedure
Step 1: First Ray Osteotomies
 A dorsal closing wedge osteotomy of the first metatarsal and opening wedge osteotomy of the medial cuneiform are performed.
A dorsal closing wedge osteotomy of the first metatarsal and opening wedge osteotomy of the medial cuneiform are performed.
 The first metatarsal and cuneiform are identified through a medial incision on the foot (Fig. 5).
The first metatarsal and cuneiform are identified through a medial incision on the foot (Fig. 5).
 The anterior tibial tendon is partially dissected free of its attachment to the cuneiform in order to perform an osteotomy in the middle of this bone.
The anterior tibial tendon is partially dissected free of its attachment to the cuneiform in order to perform an osteotomy in the middle of this bone.
49: Osteotomies of the Foot for Cavus Deformities