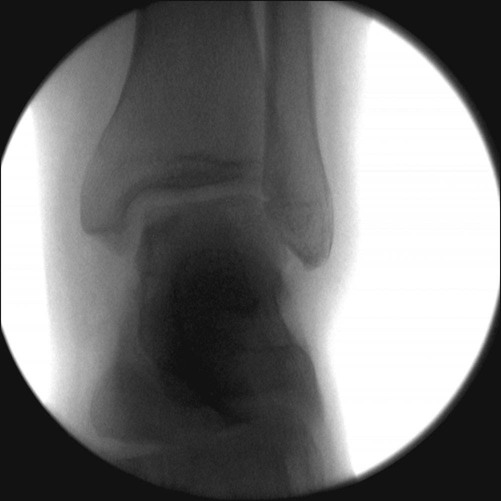
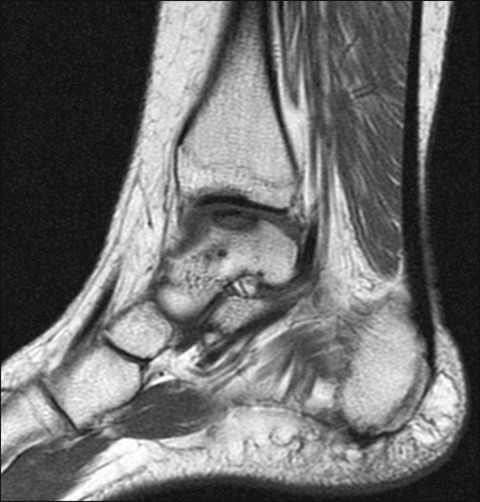
• Anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and mortise views are obtained. • OCD lesions are usually diagnosed by radiographs (Fig. 1). • MRI provides valuable information regarding the stability of the lesion. • The size, location (posteromedial, anterolateral, or central), and stability can be evaluated. • The arthroscopic surgical approach (anterior vs. posterior portals) is chosen from the location of the OCD on MRI (Fig. 2).
Arthroscopic Management for Juvenile Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Talus
Examination/Imaging
 Ankle pain and swelling are the most common complaints with OCDs.
Ankle pain and swelling are the most common complaints with OCDs.
 A standard ankle examination should be performed, including a thorough neurovascular and motor examination, and a range-of-motion examination with comparison to the opposite side.
A standard ankle examination should be performed, including a thorough neurovascular and motor examination, and a range-of-motion examination with comparison to the opposite side.
 Lateral ankle instability should be assessed with the anterior drawer test and the talar tilt test. These tests examine the anterior talofibular ligament and calcaneofibular ligaments, respectively.
Lateral ankle instability should be assessed with the anterior drawer test and the talar tilt test. These tests examine the anterior talofibular ligament and calcaneofibular ligaments, respectively.
 Medially, the deltoid ligament should also be examined for tenderness and laxity.
Medially, the deltoid ligament should also be examined for tenderness and laxity.
 Other sources of ankle pain should be excluded: peroneal tendon pathology, flexor hallucis longus pathology, and os trigonum pain.
Other sources of ankle pain should be excluded: peroneal tendon pathology, flexor hallucis longus pathology, and os trigonum pain.
 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
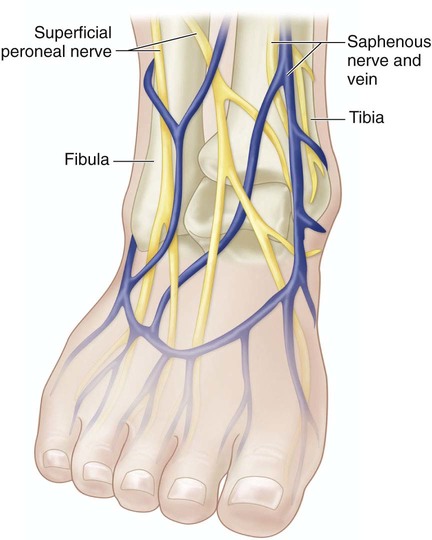
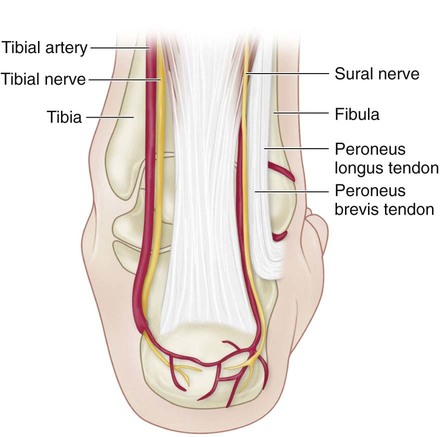
Surgical Anatomy
Musculoskeletal Key
Fastest Musculoskeletal Insight Engine