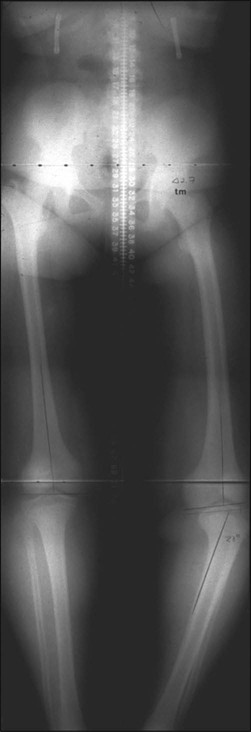
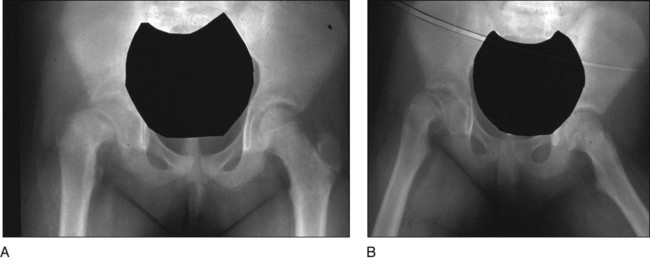
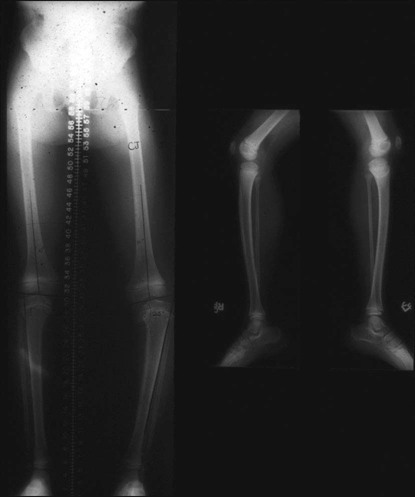
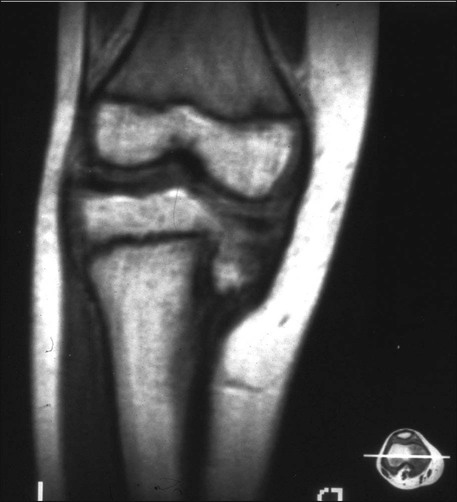
• Presence/absence of rotational abnormality • Hip examination for possible slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) • An orthoroentgenogram is obtained to assess alignment, ± femoral deformity, and limb length discrepancy. Figure 1 shows a typical preoperative orthoroentgenogram, obtained with the patient facing anterior, delineating coronal tibial and/or femoral deformity and limb length discrepancy. • Anteroposterior (AP) and frog-leg lateral radiographs are obtained to assess the hips. In Figure 2, the AP (Fig. 2A) and frog-leg lateral (Fig. 2B) radiographs demonstrate a right SCFE. • An AP/lateral radiograph is obtained of the entire tibia, including the ankle joint. Figure 3 shows an orthoroentgenogram and lateral radiograph of the tibia in a 6-year-old. • Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be done if the patient is young or in a patient with long-standing problems to assess the joint surface. Figure 4 shows an MRI of the right proximal tibia delineating both the joint contour and the proximal physis. • CT or MRI is also used for possible growth plate assessment.
Proximal Tibial Osteotomy for Blount’s Disease
Examination/Imaging
 Complete physical examination with emphasis on:
Complete physical examination with emphasis on:
Positioning
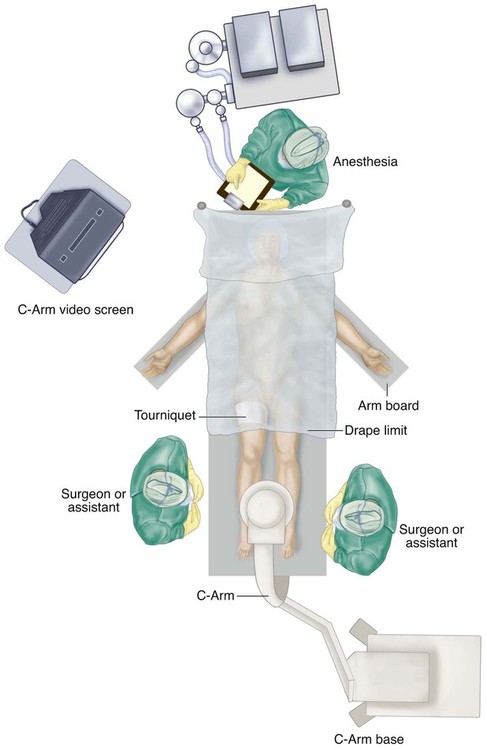
 The patient is placed supine with the patellae anterior and a tourniquet on the thigh. Draping is just distal to the tourniquet, leaving both legs visible for comparison, especially in acute correction (Fig. 5).
The patient is placed supine with the patellae anterior and a tourniquet on the thigh. Draping is just distal to the tourniquet, leaving both legs visible for comparison, especially in acute correction (Fig. 5).
 The involved leg is prepped distal to the tourniquet.
The involved leg is prepped distal to the tourniquet.
 The C-arm is placed perpendicular to the end of the bed, allowing both the surgeon and the assistant access from either side, as shown in Figure 5.
The C-arm is placed perpendicular to the end of the bed, allowing both the surgeon and the assistant access from either side, as shown in Figure 5.
Portals/Exposures
 The tourniquet is elevated to 350 mm Hg.
The tourniquet is elevated to 350 mm Hg.
 A distal fibular osteotomy (> 5 cm proximal to mortise) is performed. Bone is subcutaneous in this location, and osteotomy ≥ 5 cm from the joint will not interfere with the ankle.
A distal fibular osteotomy (> 5 cm proximal to mortise) is performed. Bone is subcutaneous in this location, and osteotomy ≥ 5 cm from the joint will not interfere with the ankle.
 Two small Hohmann retractors facilitate the exposure.
Two small Hohmann retractors facilitate the exposure.
 Bone is transected with a narrow oscillating saw with irrigation.
Bone is transected with a narrow oscillating saw with irrigation.
40: Proximal Tibial Osteotomy for Blount’s Disease















