• The tibial spine fracture site is identified. • The surgeon should look for an entrapped anterior horn of the medial meniscus or intermeniscal ligament. • An arthroscopic probe is used to pull out the meniscus or intermeniscal ligament from the fracture site.
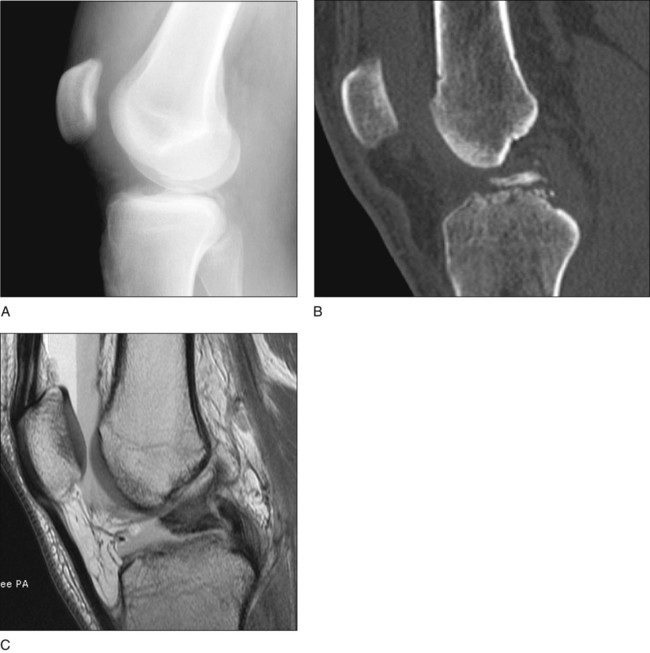
Tibial Spine Fracture
Arthroscopic and Open Reduction and Internal Fixation
Surgical Anatomy
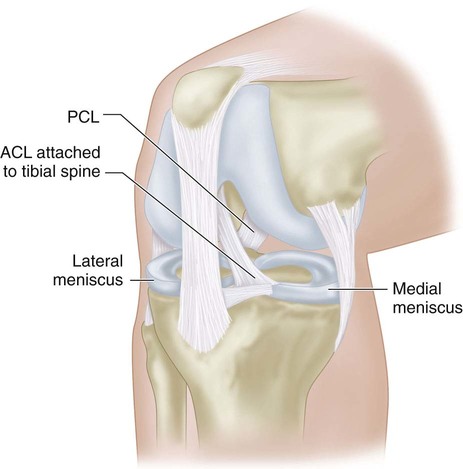
 The tibial spine represents the broad insertion point of the ACL.
The tibial spine represents the broad insertion point of the ACL.
 The anterior horn of the medial meniscus and intermeniscal ligament lie directly next to the tibial spine and can become entrapped in the fracture site (Fig. 2).
The anterior horn of the medial meniscus and intermeniscal ligament lie directly next to the tibial spine and can become entrapped in the fracture site (Fig. 2).
 The proximal tibial physis is open in most patients, as fracture most commonly occurs in skeletally immature adolescents.
The proximal tibial physis is open in most patients, as fracture most commonly occurs in skeletally immature adolescents.
Positioning
 The patient is placed supine with the leg hanging over the side of the bed.
The patient is placed supine with the leg hanging over the side of the bed.
 A tourniquet is positioned proximally on the thigh.
A tourniquet is positioned proximally on the thigh.
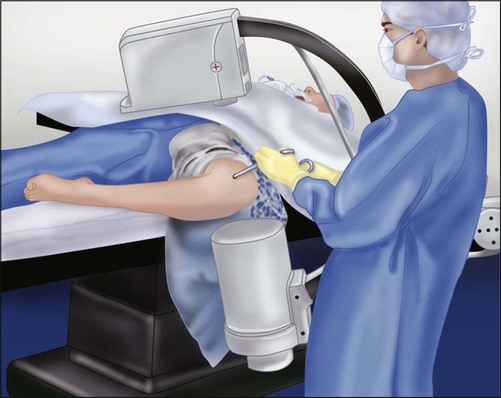
 A standard fluoroscopy unit or mini C-arm is positioned so that it can easily be brought in to obtain a lateral fluoroscopic image of the reduction and fixation (Fig. 3). This can be accomplished with the leg in the figure-of-4 position.
A standard fluoroscopy unit or mini C-arm is positioned so that it can easily be brought in to obtain a lateral fluoroscopic image of the reduction and fixation (Fig. 3). This can be accomplished with the leg in the figure-of-4 position.
Procedure
Step 1: Exposure of the Fragment
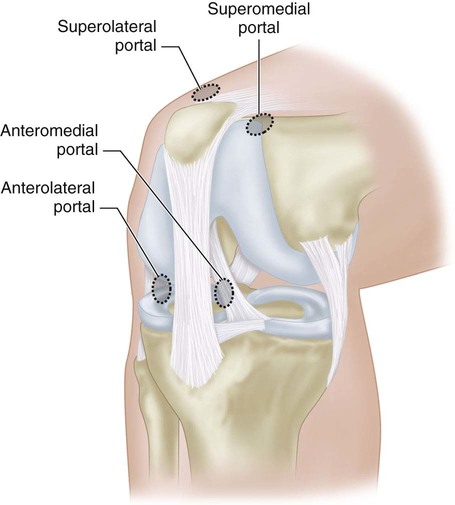
 The arthroscope is placed in the anterolateral portal.
The arthroscope is placed in the anterolateral portal.
 The knee is lavaged immediately to clear hemarthrosis.
The knee is lavaged immediately to clear hemarthrosis.
 An oscillating shaver is used to perform extensive fat pad débridement.
An oscillating shaver is used to perform extensive fat pad débridement.
 Diagnostic arthroscopy is performed to identify and treat concurrent meniscal pathology.
Diagnostic arthroscopy is performed to identify and treat concurrent meniscal pathology.
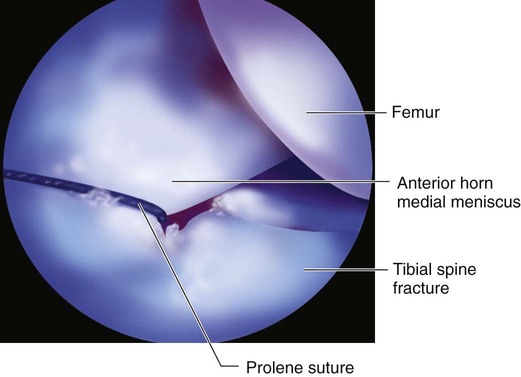
 A spinal needle is used through the anteromedial portal to place a temporary outside-in suture (0 Prolene works well) around the anterior horn of the medial meniscus or intermeniscal ligament (Fig. 5). This suture is used to retract the anterior horn and keep it out of the fracture site during reduction and fixation.
A spinal needle is used through the anteromedial portal to place a temporary outside-in suture (0 Prolene works well) around the anterior horn of the medial meniscus or intermeniscal ligament (Fig. 5). This suture is used to retract the anterior horn and keep it out of the fracture site during reduction and fixation.
Step 2: Preparation of the Fragment and Fracture Site
 Fibrinous clot material is removed from the fracture site using tiny mastoid curettes and a shaver.
Fibrinous clot material is removed from the fracture site using tiny mastoid curettes and a shaver.
 If the fragment is hinged, the surgeon should try to leave the hinge intact.
If the fragment is hinged, the surgeon should try to leave the hinge intact.
 A smaller (2.9-mm) shaver can be useful for débriding the tissue in the fracture bed (Fig. 6A).
A smaller (2.9-mm) shaver can be useful for débriding the tissue in the fracture bed (Fig. 6A).![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


34: Tibial Spine Fracture: Arthroscopic and Open Reduction and Internal Fixation