• Standard radiographs used in the evaluation of patients with acetabular dysplasia include anteroposterior (AP) pelvic (Fig. 1), frog-leg lateral (Fig. 2), false profile, and abduction and internal rotation views. • The diagnosis of dysplasia is established based upon plain radiographs. The acetabular version may not be determined due to skeletal immaturity. Upper femoral dysplasia and epiphyseal morphology are assessed on both AP and frog-leg views. Hip joint congruity and concentricity are established based upon the AP and abduction and internal rotation radiographs. • Though not required for all patients, CT scanning can be useful to define acetabular anatomy in patients with neurologic or syndromic types of acetabular dysplasia, as nonstandard corrective maneuvering may be necessary during corrective surgery. • CT scanning with three-dimensional modeling is most helpful in defining the region of acetabular insufficiency. • Care is taken to ensure that the frontal plane of the pelvis is horizontal, and a postpositioning AP pelvis radiograph is obtained to establish a baseline with which intraoperative acetabular alignment can be compared. • Positioning the contralateral arm over the chest on an armholder facilitates maneuvering of the fluoroscope.
Single-Incision Supraperiosteal Triple Innominate Osteotomy
Examination/Imaging
 A complete physical examination is necessary in the evaluation of children with developmental dysplasia of the hip. The patient’s stature, spinal alignment, relative limb length, and neurologic examination must be assessed. In addition, a careful examination of the hip includes assessment of gait, and precise documentation of range of motion. A patient must have at least 20–30° of hip abduction in order to undergo acetabular reorientation.
A complete physical examination is necessary in the evaluation of children with developmental dysplasia of the hip. The patient’s stature, spinal alignment, relative limb length, and neurologic examination must be assessed. In addition, a careful examination of the hip includes assessment of gait, and precise documentation of range of motion. A patient must have at least 20–30° of hip abduction in order to undergo acetabular reorientation.
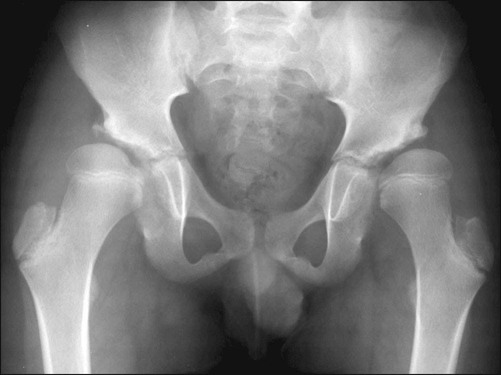
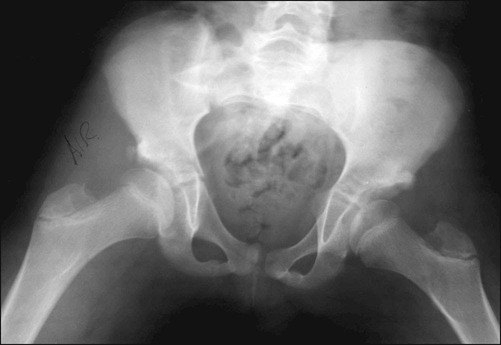
 Arthrographic evaluation is still the most accurate diagnostic method to establish hip joint congruency, and may be necessary to determine the position of congruity, particularly when the femoral epiphysis is significantly deformed.
Arthrographic evaluation is still the most accurate diagnostic method to establish hip joint congruency, and may be necessary to determine the position of congruity, particularly when the femoral epiphysis is significantly deformed.
 Improvements in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology have enabled visualization of the acetabular labrum and articular cartilage. Although its role in the assessment of skeletally immature patients is evolving, MRI is useful if significant intra-articular abnormality is suspected based upon the clinical scenario.
Improvements in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology have enabled visualization of the acetabular labrum and articular cartilage. Although its role in the assessment of skeletally immature patients is evolving, MRI is useful if significant intra-articular abnormality is suspected based upon the clinical scenario.
 Arthroscopic hip joint assessment can be useful either as a staging study to evaluate articular surfaces or for concomitant treatment of either labral or chondral pathology. The role of simultaneous arthroscopic treatment of labral pathology with correction of acetabular dysplasia remains to be studied.
Arthroscopic hip joint assessment can be useful either as a staging study to evaluate articular surfaces or for concomitant treatment of either labral or chondral pathology. The role of simultaneous arthroscopic treatment of labral pathology with correction of acetabular dysplasia remains to be studied.
Positioning
 The patient is positioned supine on a radiolucent operating table without a roll behind the ipsilateral pelvis in order to facilitate intraoperative evaluation of acetabular position (Fig. 3).
The patient is positioned supine on a radiolucent operating table without a roll behind the ipsilateral pelvis in order to facilitate intraoperative evaluation of acetabular position (Fig. 3).
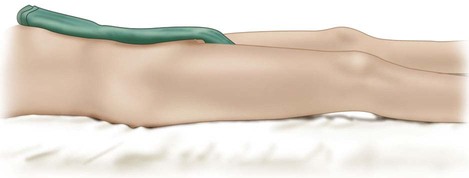
 The surgeon stands on the side of the operative hip and the assistant stands opposite. A fluoroscope is positioned opposite the surgeon with the monitor at the patient’s foot.
The surgeon stands on the side of the operative hip and the assistant stands opposite. A fluoroscope is positioned opposite the surgeon with the monitor at the patient’s foot.
 The entire leg, hip, abdomen, and lower chest are included in the surgical field so that exposure is not compromised following draping.
The entire leg, hip, abdomen, and lower chest are included in the surgical field so that exposure is not compromised following draping.
 Following anesthetic induction, Foley catheterization is performed in order to protect the bladder during intrapelvic surgery.
Following anesthetic induction, Foley catheterization is performed in order to protect the bladder during intrapelvic surgery.
Portals/Exposures
 An oblique “bikini line” skin incision is made just distal to the anterior superior iliac spine.
An oblique “bikini line” skin incision is made just distal to the anterior superior iliac spine.
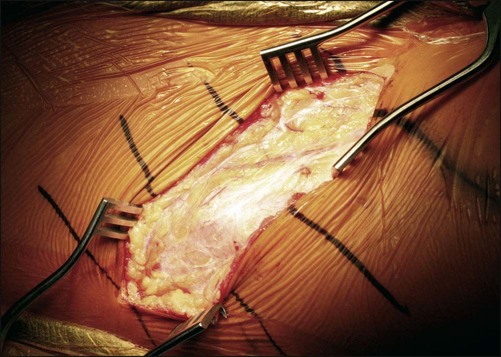
 The subcutaneous tissue is divided in line with the incision. The external oblique muscle fascia is exposed proximal to the incision, and a subcutaneous flap is elevated distally in order to expose the distal tensor fascia lata–sartorius interval (Fig. 4).
The subcutaneous tissue is divided in line with the incision. The external oblique muscle fascia is exposed proximal to the incision, and a subcutaneous flap is elevated distally in order to expose the distal tensor fascia lata–sartorius interval (Fig. 4).
Procedure
Step 1: Superficial Dissection
 The external oblique muscle fascia is incised laterally and the muscle is elevated from the iliac apophysis. The tensor-sartorius interval is opened longitudinally while protecting the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.
The external oblique muscle fascia is incised laterally and the muscle is elevated from the iliac apophysis. The tensor-sartorius interval is opened longitudinally while protecting the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


14: Single-Incision Supraperiosteal Triple Innominate Osteotomy






