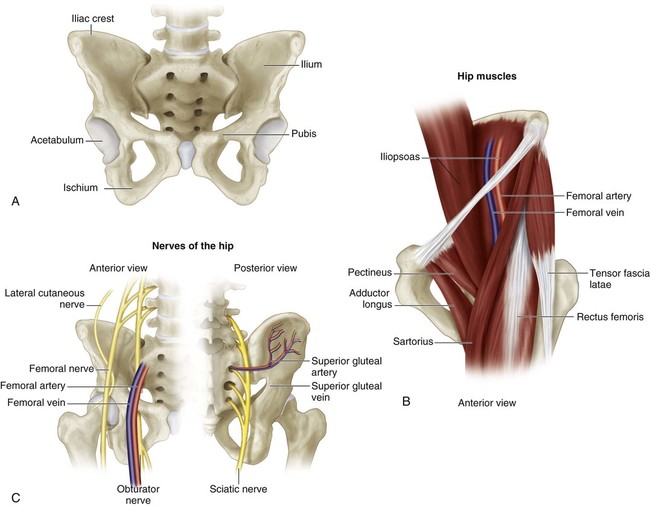
• Bones (Fig. 2A): iliac apophysis, iliac crest, greater sciatic notch, acetabular labrum and lateral acetabular epiphysis • Muscles and ligamentous complexes (Fig. 2B): sartorius and tensor fascia femoris, straight head of the rectus femoris, transverse acetabular ligament, ligamentum teres, iliopsoas muscle/tendon • Nerves (Fig. 2C): lateral femoral cutaneous nerve of the thigh, superior gluteal nerve • Vessels in the greater sciatic notch and the surrounding soft tissues of the ilium (see Fig. 2C) • Just distal to this point, the tendon is tagged with a suture for later repair and then transected. The reflected head is separated from the capsule and detached from the ilium posteriorly to just beyond the most proximal point of the dislocated femoral head. • If the hip is not dislocated, the rectus femoris may be left intact as the innominate osteotomy is done just proximal to the insertion of the straight head into the anterior inferior iliac spine.
Innominate Osteotomy
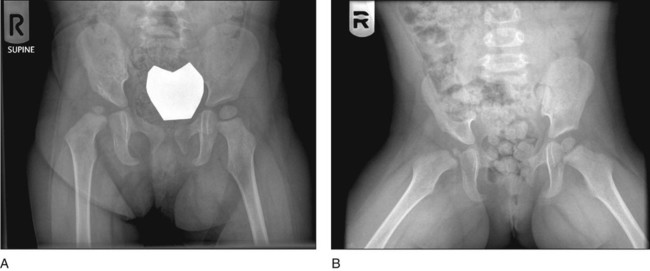
Surgical Anatomy
 The surgeon should be familiar with the following anatomic structures:
The surgeon should be familiar with the following anatomic structures:
Portals/Exposures
 A transverse “bikini line” incision is made centered on and just distal to the anterior superior iliac spine.
A transverse “bikini line” incision is made centered on and just distal to the anterior superior iliac spine.
 The interval between the sartorius and tensor fascia femoris is separated, taking care to protect the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve of the thigh.
The interval between the sartorius and tensor fascia femoris is separated, taking care to protect the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve of the thigh.
 If capsulorrhaphy is to be done for dislocation, the straight head of the rectus femoris is separated from the hip joint capsule, tagged with a suture, and divided just distal to the anterior inferior iliac spine.
If capsulorrhaphy is to be done for dislocation, the straight head of the rectus femoris is separated from the hip joint capsule, tagged with a suture, and divided just distal to the anterior inferior iliac spine.
 The iliac apophysis is split equally with a scalpel from the anterior inferior iliac spine to the junction of the anterior and middle thirds of the iliac crest.
The iliac apophysis is split equally with a scalpel from the anterior inferior iliac spine to the junction of the anterior and middle thirds of the iliac crest.
 The iliac crest is stripped subperiosteally both medially and laterally to the greater sciatic notch (Fig. 4A and 4B). Rang sciatic notch retractors (Fig. 5) facilitate protection of the superior gluteal nerve and vessels in the notch and the surrounding soft tissues when cutting the ilium with the Gigli saw.
The iliac crest is stripped subperiosteally both medially and laterally to the greater sciatic notch (Fig. 4A and 4B). Rang sciatic notch retractors (Fig. 5) facilitate protection of the superior gluteal nerve and vessels in the notch and the surrounding soft tissues when cutting the ilium with the Gigli saw.

Procedure
Step 1
 Prior to making the skin incision, a percutaneous tenotomy of the adductor longus is done.
Prior to making the skin incision, a percutaneous tenotomy of the adductor longus is done.
 An anterolateral approach via a transverse (bikini line) incision is used (see Portals/Exposures).
An anterolateral approach via a transverse (bikini line) incision is used (see Portals/Exposures).
 The tendon of the rectus femoris is retracted from the hip joint capsule and the straight and reflected heads are identified.
The tendon of the rectus femoris is retracted from the hip joint capsule and the straight and reflected heads are identified.
 If the innominate osteotomy is being done for dysplasia or mild subluxation, proceed to Step 7.
If the innominate osteotomy is being done for dysplasia or mild subluxation, proceed to Step 7.
Step 2 (When Hip Is Dislocated)
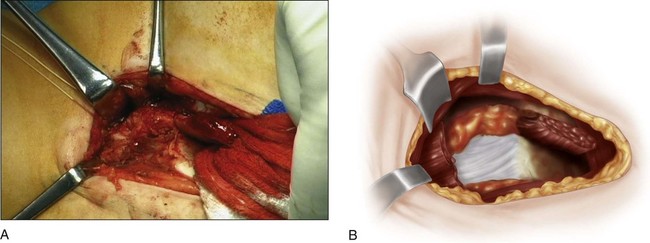
 The capsule is cleared anteromedially of soft tissue, including the overlying iliopsoas, with a periosteal elevator.
The capsule is cleared anteromedially of soft tissue, including the overlying iliopsoas, with a periosteal elevator.
 The periosteum previously stripped from the medial wall of the ilium overlying the iliopsoas muscle is incised longitudinally and its tendon separated from the surrounding muscle at the level of the pelvic brim. The tendon lies on the posterior surface of the muscle, so the muscle needs to be inverted with a retractor in order to expose the tendon prior to cutting it while leaving the muscle intact to bridge the recessed tendon.
The periosteum previously stripped from the medial wall of the ilium overlying the iliopsoas muscle is incised longitudinally and its tendon separated from the surrounding muscle at the level of the pelvic brim. The tendon lies on the posterior surface of the muscle, so the muscle needs to be inverted with a retractor in order to expose the tendon prior to cutting it while leaving the muscle intact to bridge the recessed tendon.
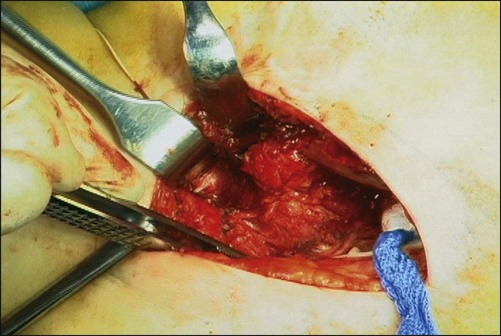
 The capsule is now exposed from the level of the transverse acetabular ligament to the top of the femoral head (Fig. 6).
The capsule is now exposed from the level of the transverse acetabular ligament to the top of the femoral head (Fig. 6).
11: Innominate Osteotomy