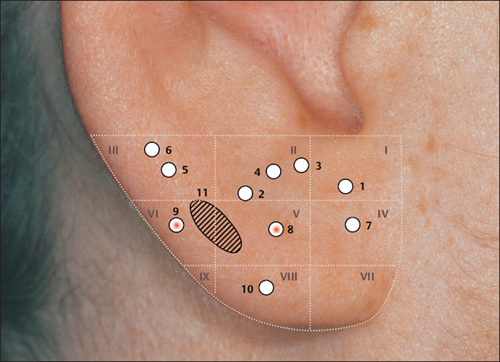
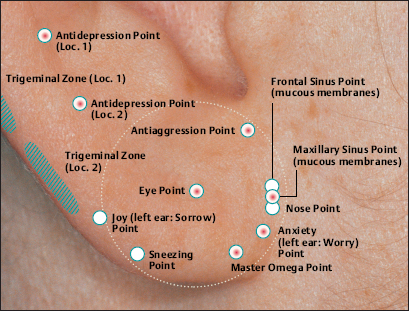
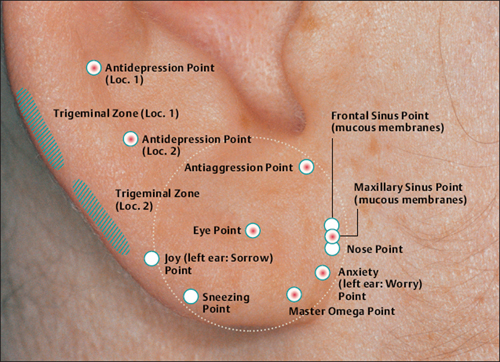
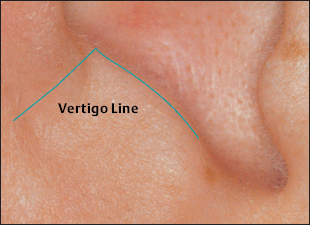
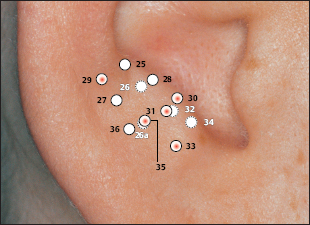
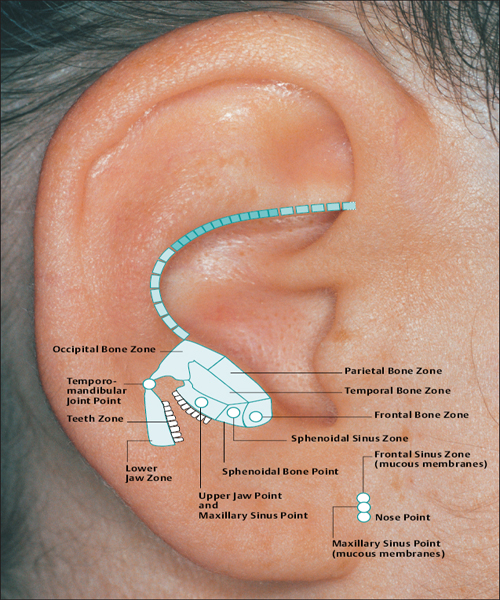
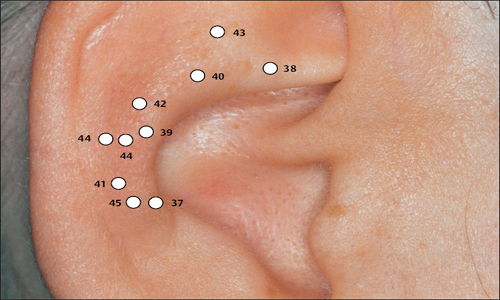
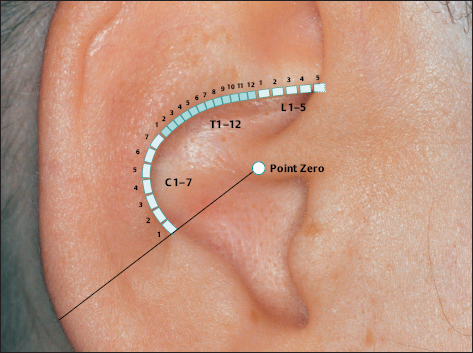
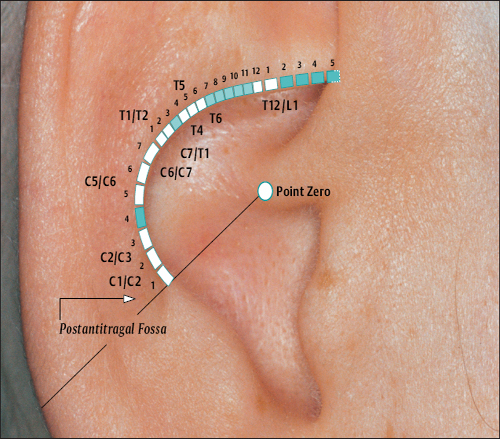
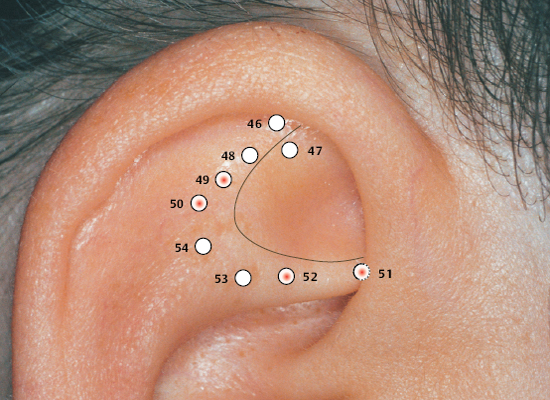
(H.-U. Hecker; B. Strittmatter, A. Steveling, E.T. Peuker) Points on the Lobule (1–11) According to Chinese Nomenclature We can divide the lobule into nine fields by drawing three horizontal and two vertical lines and using the natural border of the ear lobe. Inside these fields we find the 11 acupuncture points of the lobule. 1 Analgesic Point for Tooth Extraction Location: Quadrant I. Indication: Analgesia for tooth extraction. 2 Roof of Mouth Point Location: Quadrant II, dorsocaudal quadrant. Indication: Trigeminal neuralgia, toothache. 3. Floor of Mouth Point Location: Quadrant II, nasocaudal quadrant. Indication: Trigeminal neuralgia, toothache. 4 Tongue Point Location: Quadrant II, center. Indication: Stomatitis, toothache. 5 Upper Jaw Point Location: Quadrant III, roughly in the middle. Indication: Trigeminal neuralgia. 6 Lower Jaw Point Location: Quadrant III, upper demarcation of the field. Indication: Trigeminal neuralgia, toothache. 7 Analgesic Point for Tooth Extraction Location: Quadrant IV, center. Indication: Tooth extraction, migraine. 8 Eye Point Location: Quadrant V, center. Indication: Inflammatory eye disorders, hordeolum, glaucoma, cephalalgia that radiates into the eyes. 9 Inner Ear Point Location: Quadrant VI, in the middle. Indication: Vertigo, tinnitus, impaired hearing. 10 Tonsil Point Location: Quadrant VIII, center. Indication: The point has lymphatic activity. 11 Cheek Zone Location: Quadrants V and VI. Indication: Facial paresis, trigeminal neuralgia. For comparison: Points on the lobule according toNogier Points on the Lobule According to Nogier Trigeminal Zone (Different locations are indicated, depending on affiliation with one or the other school.) Location 1: On the lateral, upper edge of the lobule Location 2: In a more caudal location, dorsal demarcation of the fields (cf. Chinese points 6 [Lower Jaw Point] and 9 [Inner Ear Point]). Indication: Trigeminal neuralgia. ▶Pricking technique: Use the needle to prick the area of the trigeminal zone and possibly let it bleed. Prick electrically active or pressure-sensitive point with gold needle. Eye Point Location: In the middle of the lobule. Indication: Eye disorders, migraine, pollinosis. Sneezing Point Location: On the lower lateral part of the lobule. Indication: Pollinosis. Antiaggression Point Location: At the lower edge of the intertragic notch, toward the face. Indication: An important psychotropic point; addiction treatment (a silver point on the dominant ear). Master Omega Point Location: On the caudal part of the lobule toward the face. Indication: An important psychotropic point; intensely effective, harmonizes the vegetative system. Antidepression Point (Different locations are indicated, depending on affiliation with one or the other school.) Location 1: On the elongation of the Vegetative Groove, on a line which runs through Point Zero and C1. Location 2: On the nasocaudal side of the Jerome Point, on the cranial side of the intersection of the Vegetative Groove with a straight line through the Antiaggression Point. Indication: Depressive mood, psychosomatic disturbances. Anxiety/Worry Point Location: On the front edge of the lobule at the point where it emerges, at eye level. Indication: Anxiety, worry. In case of right-handedness: ▶Anxiety: Treatment via the right ear (silver needle); ▶Worry: Treatment via the left ear (silver needle). In case of left-handedness: vice versa. Nose Point Location: Just below the Maxillary Sinus Zone. Indication: Rhinitis, pollinosis. Point of Sorrow and Joy Location: On the occipital part of the lobule, at the same level as the Anxiety Zone. Indication: Sorrow, joy. Maxillary Sinus Point Location: In the middle of the point where the lobule emerges in the skin of the face. Indication: Afflictions of the nasal sinuses, field of disturbance. Frontal Sinus Point (Mucous Membranes) Location: On the cranial side of the Frontal Sinus Zone. Indication: Afflictions of the nasal sinuses, field of disturbance. Points on the Tragus (12–19) and Supratragic Notch (20 and 21) According to Chinese Nomenclature 12 Apex of Tragus Point Location: On the cranial side of a single-peaked tragus. On the cranial peak of a double-peaked tragus. Indication: Analgesia. The point has anti-inflammatory activity. 13 Adrenal Gland Point Location: On the lower third of a single-peaked tragus. On the caudal peak of a double-peaked tragus. Indication: Allergic diathesis, joint disorders, chronic inflammation, functional circulatory disorders, paresis, neuralgia. Generally indicated in all forms of adrenal gland dysfunction. 14 External Nose Point Location: In the middle of the base of the tragus. Indication: Local afflictions of the nose (eczema, rhinophyma, etc.). 15 Larynx, Pharynx Point Location: On the inside of the tragus at the level of Point 12. Indication: Pharyngitis, tonsillitis. 16 Inner Nose Point Location: On the inside of the tragus at the level of Point 13. Indication: Rhinitis, sinusitis. 16a Auriculotemporal Nerve Location: Between Point 15 and Point 16, inside. Indication: Neuralgia in the innervation zone of the nerve. 17 Thirst Point Location: Midway between Point 12 and Point 14. Indication: Thirst, bulimia. 18 Hunger Point Location: Midway between Point 13 and Point 14. Indication: For example, weight reduction. 19 Hypertension Point Location: At the transition to the intertragic notch. Indication: Hypertension. 20 External Ear Point Location: Roughly corresponds to TB-21 in body acupuncture. Indication: Inflammation of the external ear, tinnitus, hearing difficulties. 21 Heart Point Location: Roughly in the middle of the connecting line between Point 20 and Point 12. Indication: Functional heart complaints. For comparison: Points on the tragus and supratragic notch according to Nogier and Bahr Points on the Tragus and Supratragic Notch According to Nogier How to Find the Points A horizontal line through the middle of the tragus and another line through the bottom of the inter-tragic notch are connected by a vertical line roughly 3 mm in front of the tragus edge. The dis tance between the two lines is divided into thirds. In the middle of each subsection is located one of the following points: Valium Analogue Point, Nicotine Analogue Point, and Pineal Gland Point. Larynx/Pharynx Point Location: At the top end of the tragus, in the cavity of concha. Indication: Afflictions in the neck area, globus sensation, addiction treatment. Interferon Point Location: In the supratragic notch (gold point on the non-dominant ear). Indication: The point has an immuno-modulating effect and anti-inflammatory activity. Valium Analogue Point Location: On the tragus, roughly 2 mm before the edge of the tragus and just below the middle of the tragus (gold point on non-dominant ear). Indication: Addiction treatment; the point has general sedating activity. Nicotine Analogue Point Location: Just below the Valium Analogue Point (gold point on the non-dominant ear). Indication: Addiction treatment. Pineal Gland Point Location: On the lower edge of the intertragic notch (gold point on the non-dominant ear). Indication: Disturbed circadian rhythm; an adjuvant point in hormonal disorders. Subtragal Point Location: On the inside of the tragus, cranial side. Indication: Control point of reticular formation, overall vegetative harmonization, antioscillatory. (Normally an identical stimulus provoked in the body will involve the same reflex response every time. For example, the response to the point-searching device will always be identical or the number of pulse beats will always be the same while the pressure of the pressure button on the skin is the same. On the other hand, if the patient is oscillating, the body will respond to an identical stimulus in different ways every time, i.e. an auricular point will be found on one occasion and then not on another–the reflex response of the organism is unstable. Disturbed routing of stimuli in reticular formation is assumed to be the cause.) Laterality Control Point (Bahr) Location: On a horizontal line roughly 3 cm from the middle of the tragus. Indication: Laterality disturbances (gold point on the dominant ear). Statoacoustic Nerve Location: Tip of the tragus. Indication: Méniçre disease, vertigo. For comparison: Points 12–21 on the tragus and supratragic notch according to Chinese nomenclature Points on the Intertragic Notch (Points 22–24) According to Chinese Nomenclature 22 Endocrine Zone Location: At the bottom of the intertragic notch, toward the face. Indication: All endocrine disorders (gynecological and rheumatoid disorders, allergies, skin disor ders). 25 Ovary Point Location: On the ventral and outer ridge of the antitragus, “Eye of the Snake,” when viewing anthelix as a snake. Indication: Ovarian dysfunction, menstruation-related migraines, skin disorders. 24a Eye Point 1 Location: Below the intertragic notch, toward the face. Indication: Non-inflammatory eye disorders, possibly myopia, astigmatism, opticus atrophy. 24b Eye Point 2 Location: Below the intertragic notch, in the direction of the helix. Indication: Non-inflammatory eye disorders, possibly myopia, astigmatism, opticus atrophy. 34 Gray Substance Point Location: On the inside of the antitragus, above the Ovary Point (23, “Eye of the Snake”). Indication: The point has a general harmonizing effect, antiphlogistic activity, and analgesic activity. For comparison: Points on the intertragic notch according to Nogier Points on the Intertragic Notch According to Nogier Antiaggression Point Location: Below the edge of the intertragic notch, toward the face. Indication: An important psychotropic point; addiction treatment (gold point on the nondominant ear). TSH Point Location: In the middle of the intertragic notch, on the inside, just before the ACTH Point. Indication: Thyroid gland disorders, bulimia. Prolactin Point Location: On the cranial side just above the ACTH Point. Indication: Difficulties with breast-feeding, wish to have a child, hormonal dysfunction. Gonadotropin Point Location: On the ventral and outer edge of the antitragus, “Eye of the Snake,” when viewing anthelix as a snake. Indication: Sexual dysfunction, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea. ACTH Point (Different locations of the projection zones are indicated, depending on affiliation with one or the other school.) Location 1: In the front angle of the intertragic notch. Location 2: Further on the cranial side, roughly in the middle of the line between the apex of the tragus and the base of the intertragic notch. Indication: An important point in the treatment of rheumatoid disorders, bronchial asthma, and skin disorders. Vegetative Point Location: On the inside of the antitragus, on the caudal side. Indication: Analgesic, vegetative harmonization. For comparison: Points on the intertragic notch according to Chinese nomenclature Points on the Antitragus (Points 25–36) According to Chinese Nomenclature 25 Brain Stem Point Location: At the intersection of the antitragus and the anthelix, slightly nearer the antitragus. 26 Pituitary Gland Point Indication: Meningeal irritations, child development problems, consequences of concussion. 26 Toothache Point Location: On the inside of the antitragus, on the cranial side. Indication: Toothache. 26a Pituitary Gland Point (Thalamus Point According to Nogier) Location: Corresponds on the inside to the location of Point 35 (Sun Point), in the middle of the base of the antitragus. Indication: A general analgesic point. 27 Larynx and Teeth Point Location: On the upper, external third of the antitragus. Indication: An adjuvant point for afflictions in the oral region. 28 Brain Point (Pituitary Gland Point) Location: In the middle of the line from the peak of the antitragus to the anthelix–antitragus intersection. Indication: Hormone dysfunction. 29 Occiput Point Location: Roughly midway between the Vegetative Groove and Point 25, Brain Stem, in the postantitragal fossa. Indication: Broad spectrum of activity: conditions of pain, autonomic dysfunction, recovery phases. 30 Parotid Gland Point Location: On the tip of the antitragus. Indication: Pruritus (strong antipruritic effect), inflammation of the parotid gland, mumps. 31 Asthma Point Location: Below the tip of the antitragus in the direction of the base of the antitragus. Indication: Bronchitis, asthma. The point affects the respiratory center. 32 Testis Point Location: On the inside of the antitragus, corresponding to the external location of Point 31. Indication: Impotence, orchitis. 33 Forehead Point Location: End point of the Sensory Line (Nogiercalls the line connecting Points 29, 35, and 33 the Sensory Line), roughly at the level of a horizontal line through the middle of the caudal tragus side. Indication: Disturbances (-algia, -itis) in the forehead region, vertigo. 34 Gray Substance Point Location: On the inside of the antitragus, above the Ovary Point (23). Indication: The point has a general harmonizing effect, antiphlogistic activity and analgesic activity. 35 Sun Point Location: In the middle of the base of the antitragus. Indication: Very frequently used point. Cephalgia, migraine, eye disorders, vertigo, insomnia. 36 Roof of Mouth Point Location: Below Point 29. Indication: Frontal headache. For comparison: Points on the antitragus according to Nogier Points on the Antitragus According to Nogier Postantitragal Fossa Location: A straight line is drawn from Point Zero through the notch between the antitragus and anthelix to the edge of the ear. Important acupuncture points (29a, 29, 29b, 29c) are located on this line. We call the line connecting them the postantitragal fossa. Indication: For details, see the respective points. Sensory Line Nogiercalls the line between the Frontal Bone Point (33, Forehead Point), Temporal Bone Point (35, Sun Point), and Occipital Bone Point (29, Occiput Point) the Sensory Line. Energetic blood flow to the head is assigned to this line, as is the case with the body acupuncture points Ex-HN-3 and GV-16 (Bischko). The postantitragal fossa and the Sensory Line represent two basic pillars of ear acupuncture treatment. The respective conspicuous points may be used together with the related spinal column segment for basic therapy in pain treatment. Occipital Bone Point, Occiput Point Location: In the postantitragal fossa, roughly midway between Point 29a and Point 29b. According to Chinese nomenclature, the localization of the Occiput Point is slightly more toward the face. Indication: An important analgesic point with a broad spectrum of activity. Conditions of pain, vertigo, autonomic dysfunction, phase of recovery. 29a Kinetosis and Nausea Point Location: Between the anthelical edge and Point 29 (Occiput Point). Indication: Kinetosis, vomiting. 29b Jerome Point Relaxation Point Location: In the postantitragal fossa, at the intersection with the Vegetative Groove. Indication: For vegetative harmonization. Difficulty falling asleep. In case of difficulty staying asleep, the corresponding point on the back of the ear is needled. This relaxes the muscles. 29c Craving Point Location: At the end of the postantitragal fossa, at the intersection with the edge of the ear. Indication: Used within the scope of addiction therapy. Vertigo Point Location: On the inside in the area of the antitragus, shortly before the postantitragal fossa. Indication: Important vertigo point, cf. Vertigo Line according to von Steinburg. Temporomandibular Joint Point Location: The point is at the end of the scapha, at the transition to the ear lobe. In the area of the temporomandibular joint we also find the projection zones a) Palatine tonsil b) Molars of the upper and lower jaw c) Retromolar area d) Rear sections of the masticatory muscles e) Antidepression Point (cf. p. 41 and 55) f) Magnesium Point (Bahr) g) Parotid Gland Point h) Base of the lateral pterygoid muscle. Indication: Gnathological problems, pain syndrome, tinnitus. Frontal Bone Point (33 Forehead Point (Depending on the affiliation with one or the other school, different locations are indicated.) Location 1: On the ventral part of the antitragus, almost at the intersection with the intertragic notch. Location 2: End point of the Sensory Line (Nogiercalls the line connecting Points 29, 35 and 33 the Sensory Line), roughly at the level of a horizontal line through the middle of the caudal tragus side. Indication: Disturbances (-algia, -itis) in the forehead region, vertigo. Temporal Bone Point (35 Sun Point Location: In the middle of the base of the antitragus. Indication: Cephalgia, vertigo, conditions of pain. Upper Jaw Point (incl. Teeth) Location: Starting from the temporomandibular joint on the mediocaudal side. Indication: Pain and disturbances in the region of the upper jaw/teeth. Lower Jaw Point (incl. Teeth) Location: Starting from the temporomandibular joint on the caudal, lateral side. Indication: Pain and disturbances in the region of the lower jaw/teeth. Sensory Point Location: On the caudal side of the Temporal Bone Point (35, Sun Point according to Chinese nomenclature). Indication: Pain relief. Vegetative System II Location: On the inside of the antitragus, on the caudal leg. Indication: Analgesic, vegetative harmonization. Vertigo Line According to von Steinburg Location: Along the postantitragal fossa and upper edge of the antitragus, slightly on the inside. Indication: Vertigo. Gonadotropin Point Location: On the ventral and outer edge of the antitragus (“Eye of the Snake,” when viewing the anthelix as a snake). Indication: Sexual dysfunction, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea. Vertigo Line according tovon Steinburg Thalamus Point Location: On the inside of the antitragus, opposite the Temporal Bone Point (Point 35, Sun Point, according to Chinese nomenclature). Indication: Vegetative harmonization, a general analgesic point, premature ejaculation, frigidity; affects the homolateral side of the body. Antidepression Point (Different locations are indicated, depending on affiliation with one or the other school.) Location 1: On the elongation of the Vegetative Groove, on a line which runs through Point Zero and C1. Location 2: On the nasocaudal side of the Jerome Point, on the cranial side of the intersection of the Vegetative Groove with a straight line through the Antiaggression Point. Indication: Depressive mood, psychosomatic disturbances. For comparison: Points on the antitragus according to Chinese nomenclature Projection Zones of the Cranial Bones and Sinuses According to Nogier The cranial bones are projected on the area of the antitragus. The frontal bone is represented on the ascending part of the antitragus. The ethmoid bone and the upper jaw are projected more toward the helical rim. The parietal bone is represented in the ventral area on the apex of the antitragus. The projection of the occipital bone forms the border in a dorsal direction. The temporal bone is projected in the middle of the antitragus. The temporomandibular joint and the lower jaw with the teeth join the occipital bone. As a field of disturbance, the paranasal sinuses play a major role. They are also projected in the antitragus region (bony part of the maxillary sinuses, at the height of the upper jaw). However, the mucus membrane part of the maxillary sinuses is in the area in which the nose is located at the front edge of the ear lobe. The frontal sinus is slightly below the frontal bone. The sphenoidal and ethmoidal sinuses are projected on a line in the immediate vicinity of the maxillary sinus. Points of the Anthelix (Points 37–45) According to Chinese Nomenclature Unlike the differentiated representation of the spinal column in the area of the anthelix according to Nogier, Chinese auricular acupuncture in part only indicates individual points for the corresponding vertebral segments. These might correspond to maximum points. The responsiveness of the corresponding auricular acupuncture point is decisive. 37 Cervical Vertebrae Point Location: In the caudal area of the antitragus. Indication: Cervical vertebrae syndrome. 38 Sacrum and Coccyx Vertebrae Point Location: At the level of the intersection at the crura, on the anthelix. Indication: Lumbar vertebrae syndrome, coxalgia. 39 Thoracic Vertebrae Zone Location: In the elongation of the ascending root of helix to the helix, on the anthelix. Indication: Thoracodynia, pain in the thorax. 40 Lumbar Vertebrae Zone Location: On the cranial side of the Thoracic Vertebrae Zone. Indication: Lumbar vertebrae syndrome. 41 Throat Point Location: On the cranial side of the projection zone of the cervical vertebrae on the scapha. Indication: Cervical vertebrae syndrome, afflictions in the throat region. 42 Thorax Point Location: On the middle to cranial third of the thoracic vertebrae. Indication: Thoracodynia, mastitis. 43 Abdomen Point Location: On the cranial side of the projection zone for the lumbar vertebrae. Indication: Abdominal disorders, meteorism. 44 Mammary Gland Point (Dual Projection) Location: In the elongation of the ascending root of helix to the helical rim and on the scapha. Indication: Mastitis, mastodynia, pain in the chest region. 45 Thyroid Gland Point Location: On the upper third of the cervical vertebrae projection in the region of the anthelix. Indication: Thyroid gland dysfunction, globus sensation, pain in the region of the thyroid gland. For comparison: Points on the anthelix according to Nogier (projections of the spinal column) Projection Zones of the Spinal Column According to Nogier The projection area C0/C1 is at the intersection of the postantitragal fossa with the anthelix. The elongation of the upper edge of the ascending helix branch to the helical rim represents the transition C7/T1 at the intersection with the anthelix (the point is slightly above a horizontal line through Point Zero). The intersection area of both anthelical crura, projected vertically onto the anthelix, represents the transition T12/L1. The Ear Relief in Cross-Section (Zones I–VIII) I Zone of Organ Parenchyma II one of Nervous Organ Points of Paravertebral Chain of Sympathetic Ganglia III Zone of Nervous Control Points of Endocrine Glands IV Zone of Intervertebral Disks V Zone of Vertebrae VI Zone of Paravertebral Muscles and Ligaments VII Vegetative Groove (Zone of Origin of Sympathetic Nuclei) VIII Zone of Spinal Cord with projections of Nervous Organ Points of the Paravertebral Chain of Sympathetic Ganglia C2/C1 Location: Zone II, Superior Cervical Ganglion Point. Indication: Tinnitus, vertigo. C3/C2 Location: Zone II, Middle Cervical Ganglion Point. Indication: Functional heart problems. C7/T1 Location: Zone II, Inferior Cervical Ganglion Point, Stellate Ganglion Point. Indication: Tinnitus, pain in the chest, used for detecting fields of disturbance, migraine, obstruction of the first rib. Nervous Control Points of Endocrine Glands (According to Bahr,all the endocrine glands are gold points on the non-dominant ear.) T12/L1 (Adrenal Gland Point, Loc. 1) T6 (Adrenal Gland Point, Loc. 2) (Different locations are indicated, depending on affiliation with one or the other school.) Location: Zone III, Adrenal Cortex Point, Cortisone Point. Indication: PcP, allergies. This point has general anti-inflammatory and analgetic activities. T12 (Pancreas, Loc. 1) T6 (Pancreas, Loc. 2) (Different locations are indicated, depending on affiliation with one or the other school.) Location: Zone III, Pancreas Point, Insulin Point. Indication: Indigestion. T4 (Thymus Gland Point, Loc. 1) T1/T2 (Thymus Gland Point, Loc. 2) (Different locations are indicated, depending on affiliation with one or the other school.) Location: Zone III, Thymus Gland Point. Indication: Allergic disorders, counteracts fields of disturbance. T5 (Mammary Gland Point) (Also partly indicated as a nonendocrine gland in this area [variation according to school]). Location: Zone III, Mammary Gland Point. Indication: Difficulties with breast-feeding, premenstrual mastodynia. C6/C7 Thyroid Gland Point) Location: Zone III, Thyroid Gland Point. Indication: Thyroid disorders, globus sensation. C5/C6 (Parathyroid Gland Point) Location: Zone III, Parathyroid Gland Point. Indication: Bone diseases, osteoporosis, fracture healing, cramps. Points on the Superior and Inferior Antihelical Crura (Points 46–54) According to Chinese Nomenclature 46 Toe Point Location: Located at the cranial end of the superior anthelical crus, on the fold of the helical rim. Indication: Pain in the toe region. 47 Heel Point Location: Located at the cranial end of the superior anthelical crus to the triangular fossa. Indication: Pain in the heel region. 48 Ankle Point Location: Below Toe Point 46, forms an approximately isosceles triangle with Point 46 and Point 47. Indication: Pain in the ankle region. 49 Knee Joint Point Location: In the middle of the superior anthelical crus. Indication: Pain in the knee area related to the function of the knee joint. 50 Hip Point Location: On the caudal side of the projection zone for the knee joint, above the point at which both anthelical crura meet on the superior anthelical crus. Indication: Pain in the hip region. 51 Vegetative Point Location: At the intersection of the inferior anthe lical crus and the helix. Indication: An important point; vegetative stabilization of all visceral organs. 52 Sciatic Nerve Point Location: Roughly in the center of the inferior anthelical crus. Indication: Pain in the innervation area of the sciatic nerve. 53 Posterior Point Location: Lateral to Point 52. Indication: Pain in the posterior region. 54 Loin Pain Point Location: At the intersection of the superior and inferior anthelical crura. Indication: Pain in the loin region. For comparison: Points on the superior and inferior anthelical crura and the triangular fossa according to Nogier Points in the Triangular Fossa (Points 55–61) According to Chinese Nomenclature 55 Shen men (Spirit Gate) Location: In the angle formed by the superior and inferior anthelical crura, more toward the superior anthelical crus. Indication: An important point. Very effective for emotional stabilization; a point of overriding importance in conditions of pain, anti-inflammatory activity; frequently used as part of the treatment of yang diseases. 56 Pelvis Point Location: In the angle formed by the superior and inferior anthelical crura. Indication: Pain in the pelvic area. 57 Hip Point Location: On the inside the inferior anthelical crus, on the caudal side of the intersection area of both anthelical crura. Indication: Pain in the hip region. 58 Uterus Point Location: In the triangular fossa, cranial portion, partially below the helix. Indication: Condition after uterus extirpation, for example, postoperative pain. 59 Blood Pressure–Reduction Point Location: At the intersection of the superior anthelical crus and helix in the direction of the triangular fossa. Indication: Hypertension, possibly microphlebotomy. 60 Dyspnea Point Location: Caudal and lateral to Point 59 on a level with the Uterus Point (58). Indication: Bronchial asthma. 61 Hepatitis Point Location: Lateral to Point 58 on the edge of the superior anthelical crus. Indication: Adjuvant point in liver diseases. For comparison: Points on the triangular fossa according to Nogier Projection Zones of the Lower Extremity According to Nogier Points in the Region of the Superior and Inferior Anthelical Crura and in the Triangular Fossa According to Nogier The entire lower extremity is projected in the triangular fossa. The hip, knee, and ankle joint form an axis. The foot is projected diagonally to this axis and is located on the uppermost edge of the scapha. Hip Joint Point Location: At the tip of the triangular fossa at the intersection of both crura. Indication: Hip complaints. NOTE In this area we also find the projection zones of the groin, greater trochanter, and gluteal musculature. Corresponding disturbances can also be treated via this area. Femur Point Location: In the region between the hip joint and knee joint. Indication: Pain in the thigh region. Knee Joint Point Location: In the middle of the triangular fossa. Indication: Knee joint complaints. Ankle Point Location: In the continuation of a line connecting the hip joint and knee joint in front of (in) the helix. The point is partially covered by the helical rim. Indication: Pain in the ankle region. Iliosacral Joint Point Location: On the inferior anthelical crus at the level of L2. Indication: Obstructions in the iliosacral joint, lumbar vertebrae complaints, pain syndrome. Gluteal Muscle Point Location: On the inferior anthelical crus lateral to the projection zone of the iliosacral joint. Indication: Pain and complaints in the hip and gluteal area. Lower Leg Point (Femur and Fibula Point) Location: Between the projection zones for knee and ankle joint. Indication: Pain and complaints in the lower leg region. Here we also find the projection zones for the peroneal musculature. Heel Point Location: On the inferior anthelical crus covered by the helix. (The projection zone of the coccyx is also in the immediate vicinity.) Indication: Pain and complaints in the foot region. Toe Point Location: The projection zone of the toes extends over the part of the triangular fossa and the superior anthelical crus near the helix. The zones are partially covered by the helix. Indication: Pain and complaints in the toe region. Achilles Tendon Point Location: On the inferior anthelical crus, slightly caudal to the heel point covered by the helix. Indication: Achillodynia.
2 Topography and Indications
of Auricular Acupuncture
Points According to Regions






 Impaired zest for life: Treatment via the right ear,
Impaired zest for life: Treatment via the right ear,
 Sorrow: Treatment via the left ear.
Sorrow: Treatment via the left ear.
 (Mucous Membranes)
(Mucous Membranes)




 Caution: Caution: Danger of collapse (vagus irritation).
Caution: Caution: Danger of collapse (vagus irritation).

 Caution: Danger of collapse (vagus irritation).
Caution: Danger of collapse (vagus irritation).
 According to Nogier,the ACTH Point is at this location.
According to Nogier,the ACTH Point is at this location.





 Possible needling in combination with the Stellate Ganglion Zone.
Possible needling in combination with the Stellate Ganglion Zone.

 According to Nogier, this zone corresponds to the points of the adrenal gland, thyroid gland, and parathyroid gland.
According to Nogier, this zone corresponds to the points of the adrenal gland, thyroid gland, and parathyroid gland.
 (Gonadotropin Point According to Nogier
(Gonadotropin Point According to Nogier
 (Vegetative Point II According to Nogier)
(Vegetative Point II According to Nogier)
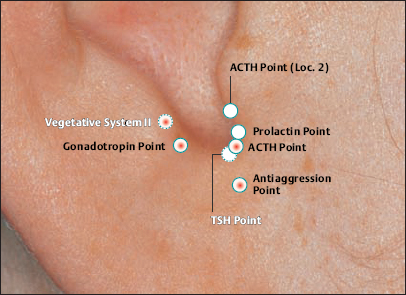
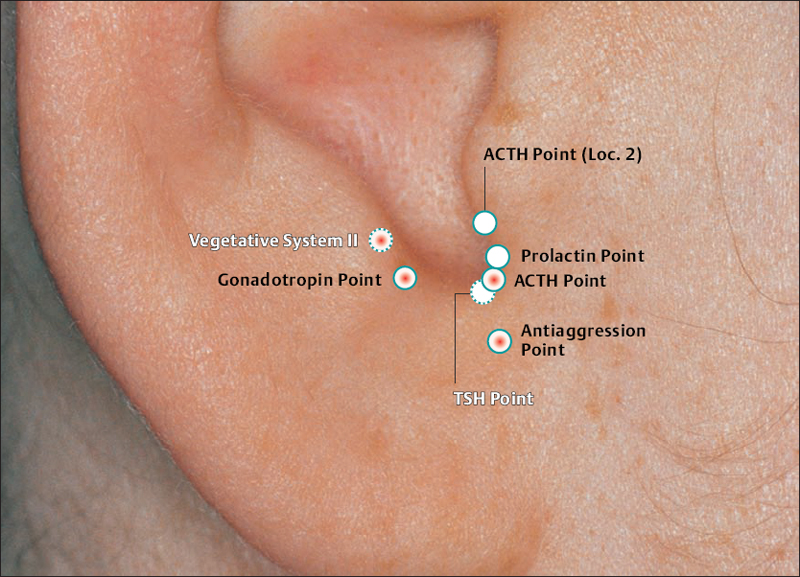

 (23 Ovary Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)
(23 Ovary Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)

 II (34 Gray Substance Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)
II (34 Gray Substance Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)
 (Thalamus Point According to Nogier)
(Thalamus Point According to Nogier)
 According to Nogier,the point affects the homolateral side of the body.
According to Nogier,the point affects the homolateral side of the body.
 Caution: Contraindicated during pregnancy.
Caution: Contraindicated during pregnancy.
 (Occipital Bone Point According to Nogier)
(Occipital Bone Point According to Nogier)


 (Frontal Bone Point According to Nogier)
(Frontal Bone Point According to Nogier)
 (Vegetative Point II According to Nogier)
(Vegetative Point II According to Nogier)
 (Temporal Bone Point According to Nogier)
(Temporal Bone Point According to Nogier)
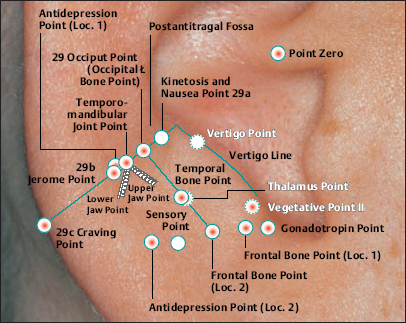
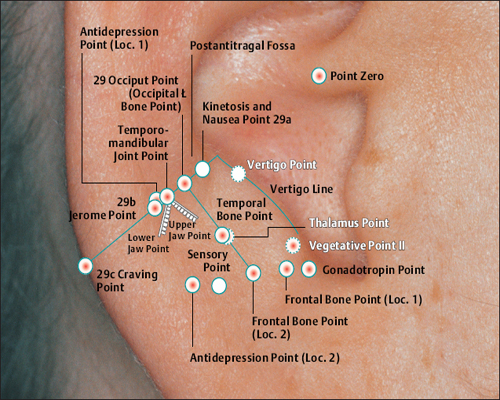
 (29 Occiput Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)
(29 Occiput Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)



 According to Chinese Nomenclature)
According to Chinese Nomenclature)
 According to Chinese Nomenclature)
According to Chinese Nomenclature)
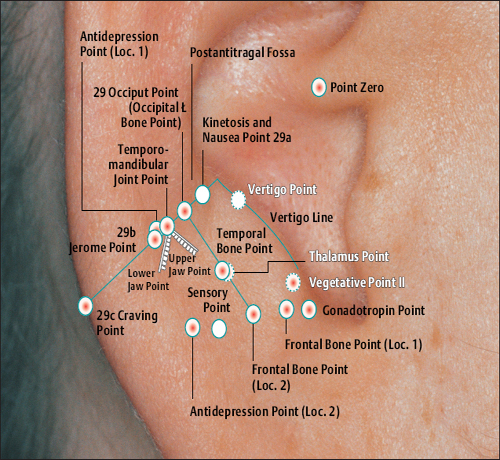
 (34 Gray Substance Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)
(34 Gray Substance Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)


(26a Pituitary Gland Point According to Chinese Nomenclature)
 In case of articular rheumatism: use gold needles.
In case of articular rheumatism: use gold needles.
 Caution: Contraindicated during pregnancy.
Caution: Contraindicated during pregnancy.

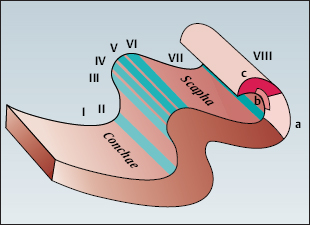
a: Motor tracts
b: Autonomic tracts
c: Sensory tracts.
 The French Knee Point is located in the middle of the triangular fossa.
The French Knee Point is located in the middle of the triangular fossa.
 The French Knee Point represents the anatomical projection of the knee joint and as a result its indications comprise local, degenerative changes.
The French Knee Point represents the anatomical projection of the knee joint and as a result its indications comprise local, degenerative changes.





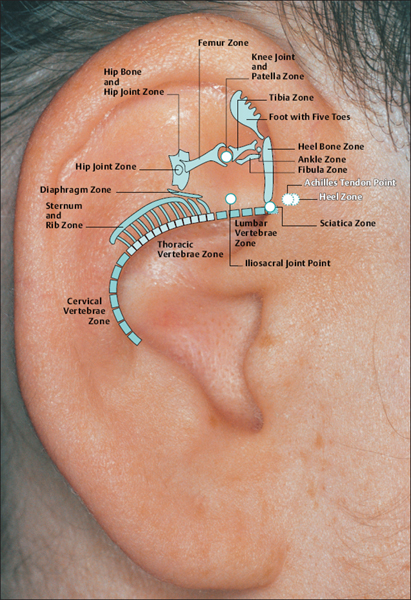
 Hip Point and Pelvis Point according to Nogier are identical with Point 56.
Hip Point and Pelvis Point according to Nogier are identical with Point 56.









Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


 8 Eye Point (Eye Point)
8 Eye Point (Eye Point) 9 Inner Ear Point
9 Inner Ear Point Eye Point (8 Eye Point)
Eye Point (8 Eye Point) Antiaggression Point
Antiaggression Point Worry Point (only left ear)
Worry Point (only left ear) Master Omega Point
Master Omega Point Antidepression Point
Antidepression Point Maxillary Sinus Point (mucous membranes)
Maxillary Sinus Point (mucous membranes)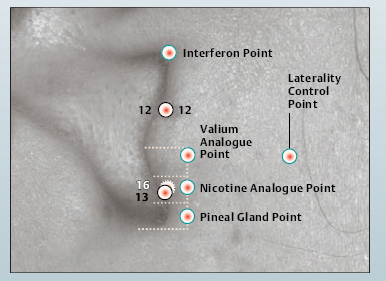
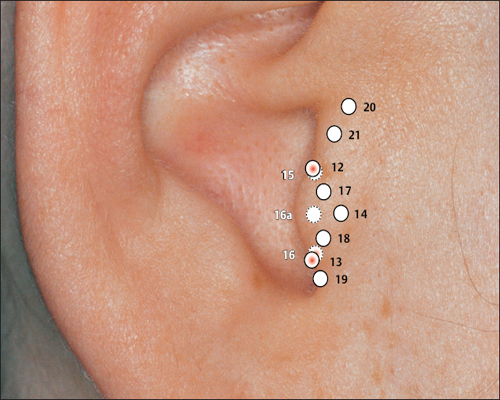
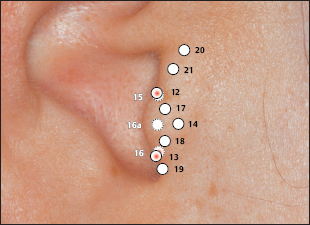
 12 Apex of Tragus Point
12 Apex of Tragus Point 13 Adrenal Gland Point
13 Adrenal Gland Point 16 Inner Nose Point
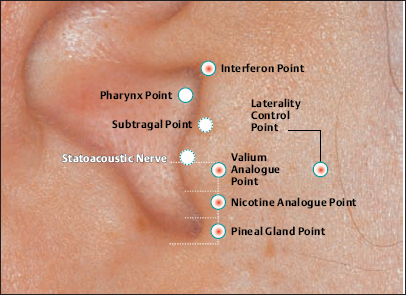
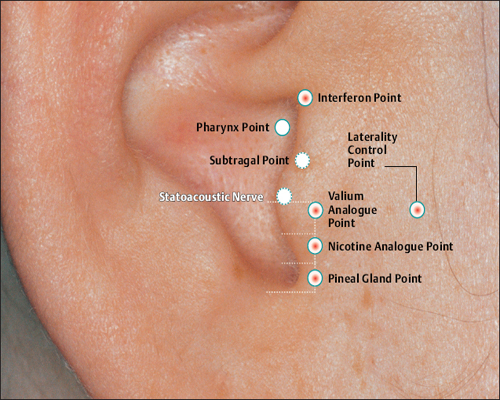
16 Inner Nose Point Valium Analogue Point
Valium Analogue Point Nicotine Analogue Point
Nicotine Analogue Point Pineal Gland Point
Pineal Gland Point Laterality Control Point
Laterality Control Point Interferon Point
Interferon Point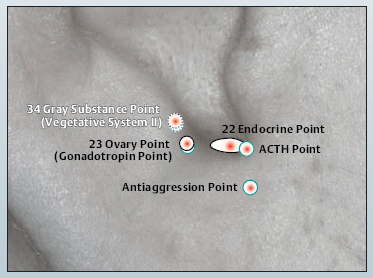
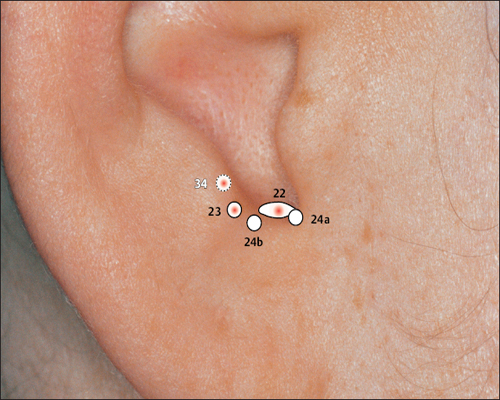
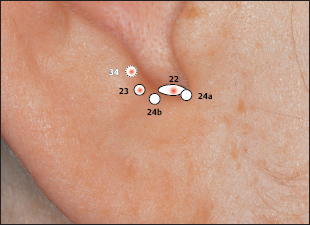
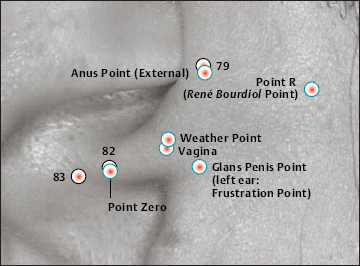
 22 Endocrine Point
22 Endocrine Point 23 Ovary Point (Gonadotropin Point)
23 Ovary Point (Gonadotropin Point) 34 Gray Substance Point (Vegetative Point II)
34 Gray Substance Point (Vegetative Point II) Antiaggression Point
Antiaggression Point Gonadotropin Point (23 Ovary Point)
Gonadotropin Point (23 Ovary Point) ACTH Point
ACTH Point Vegetative Point II (34 Gray Substance Point)
Vegetative Point II (34 Gray Substance Point)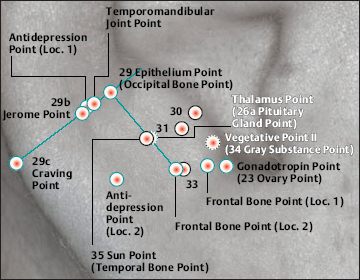
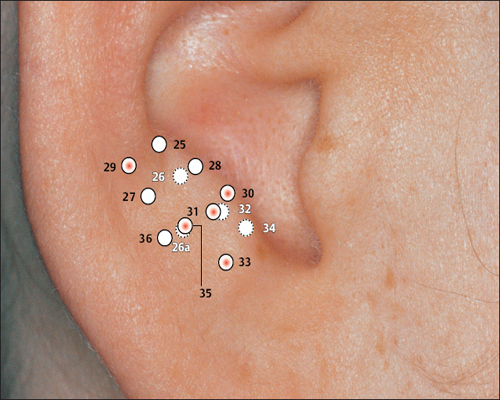
 23 Ovary Point (Gonadotropin Point)
23 Ovary Point (Gonadotropin Point) 26a Pituitary Gland Point (Thalamus)
26a Pituitary Gland Point (Thalamus) 29 Epithelium Point (Occipital Bone Point)
29 Epithelium Point (Occipital Bone Point) 30 Parotis
30 Parotis 31 Asthma
31 Asthma 33 Forehead (Os frontale)
33 Forehead (Os frontale) 34 Gray Substance Point (Vegetative Point II)
34 Gray Substance Point (Vegetative Point II) 35 Sun Point (Os temporale)
35 Sun Point (Os temporale)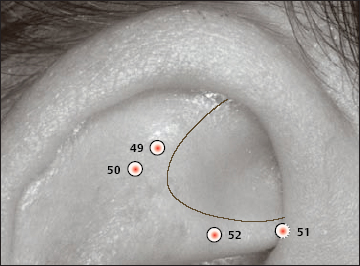
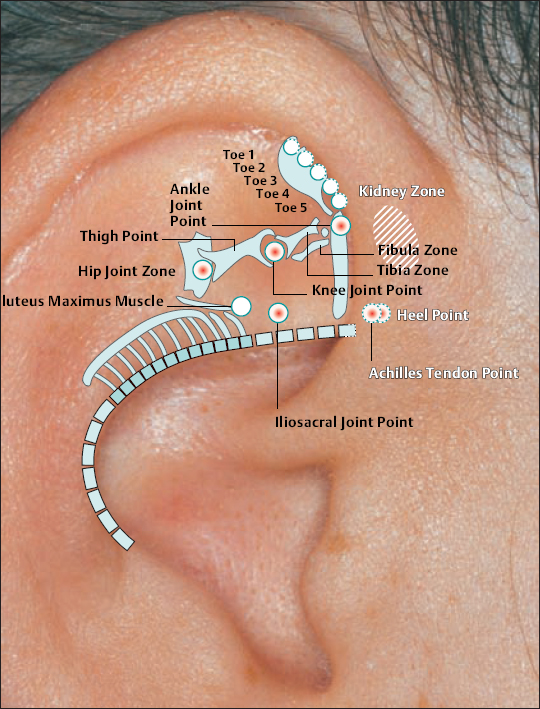
 49 Knee Joint Point
49 Knee Joint Point 50 Hip Point
50 Hip Point 51 Vegetative Point
51 Vegetative Point 52 Sciatic Nerve Zone
52 Sciatic Nerve Zone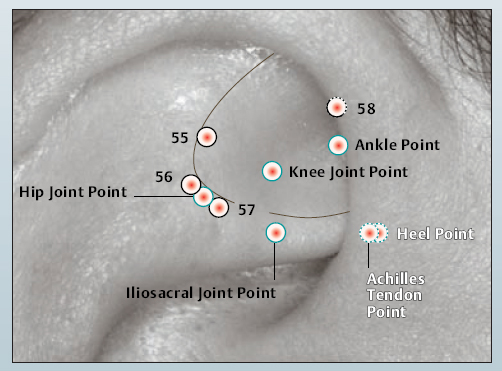
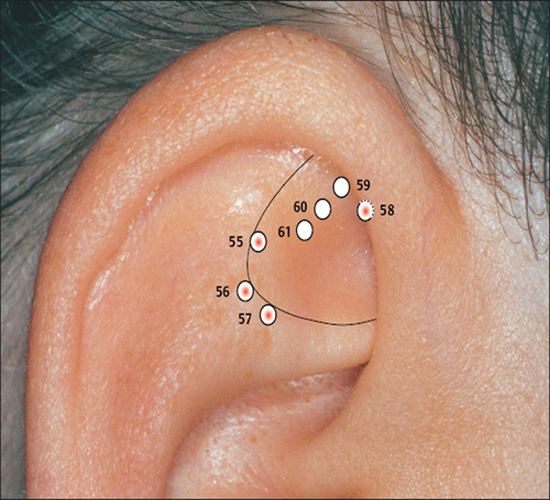
 55 shen men
55 shen men 56 Pelvis Point
56 Pelvis Point 57 Hip Point
57 Hip Point 58 Uterus Point
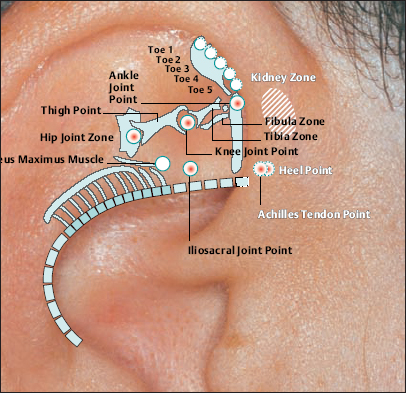
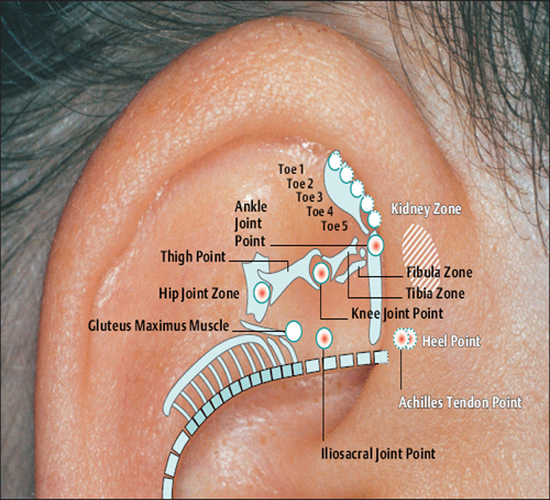
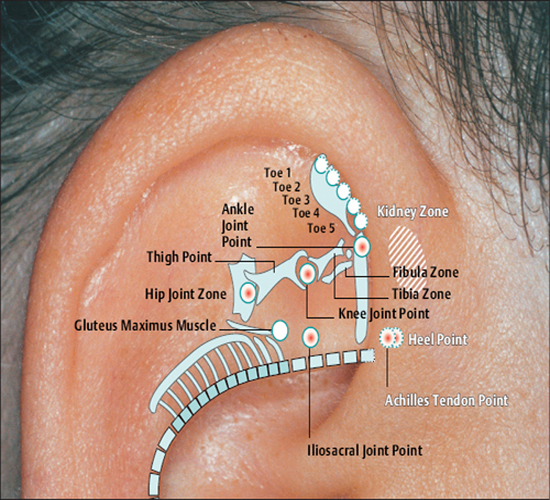
58 Uterus Point Hip Joint Point
Hip Joint Point Ankle Point
Ankle Point Knee Joint Point
Knee Joint Point Achilles Tendon Point
Achilles Tendon Point Heel Point
Heel Point Iliosacral Joint Point
Iliosacral Joint Point



