7 Tibial Tubercle Osteotomy
Indications
- Difficulty in everting the patella during exposure for total knee arthroplasty
- Revision total knee arthroplasty
- Total knee replacement after proximal tibial osteotomy
- Severe preoperative varus deformity
- Restricted preoperative flexion
Surgical Procedure
- Anterior midline skin incision beginning approximately 6 to 8 cm proximal to the superior pole of the patella and extending distally 6 to 8 cm distal to the tibial tubercle
- The distal incision should be medial to the tibial tubercle, not directly over it.
- Medial arthrotomy, beginning at the apex of the quadriceps tendon and continuing distally leaving a one-half centimeter cuff of tendon on the medial border. The arthrotomy is continued over the medial border of the patella and extends distally, medial to the border of the patellar tendon.
Surgical Technique
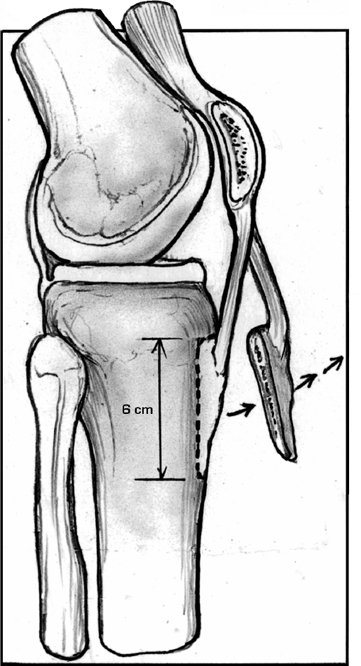
- Use an oscillating saw to create a transverse osteotomy of the tibial crest approximately 6 to 8 cm distal to the proximal edge of the tibial tubercle (Fig. 7–1).
- Use a 0.5-inch curved osteotome to divide the medial cortex of the tibia along the tibial tubercle and anterior tibial crest.
- Transect the lateral cortex through the osteotomy.
- Leave the muscular and periosteal attachments intact laterally.
- Elevate and evert the tubercle and extensor mechanism.
- Proceed with the arthroplasty.
- At the conclusion of the procedure, the osteotomy is repaired.
- Pass two or three wires through the lateral edge of the tibial tubercle and through the medial tibial cortex to reattach the bone fragment and patellar tendon (Fig. 7–2).
- Angle the wires downward 45 degrees and twist until tight.
Dressings, Braces, Splints, and Casts
1. Standard postoperative dressing can be used.
Tips and Pearls
- In insensate knees or cases in which manipulation is expected, tibial components with stems that bypass the osteotomized area should be considered.
- Care should be taken to leave soft tissues intact at the osteotomy site. Intact lateral capsular structures and muscular attachments maintain the blood supply to the tubercle and patellar tendon, contributing to rapid healing.
- Tibial tubercle osteotomies less than 3 cm in length, and those fixed with screws have a high risk of fracture.
Pitfalls and Complications
- Tibial tubercle avulsion fracture
- Tibia fracture
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
- Early mobilization
- Leg raising as tolerated
- Rehabilitation protocol not modified. Full weight bearing in primary cases and in revision cases with good bone support.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








