9. Pathogenesis of infectious disease
1. The organism occurs in every case of the disease and under circumstances which account for the pathological changes and clinical course of the disease
3. After being isolated from the body and grown in pure culture, the organism can repeatedly produce exactly the same disease when inoculated into new, susceptible hosts
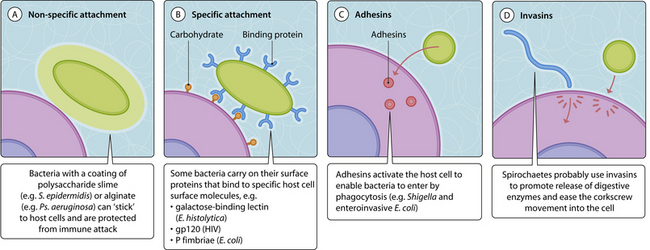
In order to cause an infection, a microorganism has to make contact with the host (Fig. 3.9.1), multiply within it and then be transmitted to another host/area.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue