Fig. 7.1
X-ray of the humerus. In the metaphyseal area, the sclerotic round intramedullary lesion corresponds to an enostoma
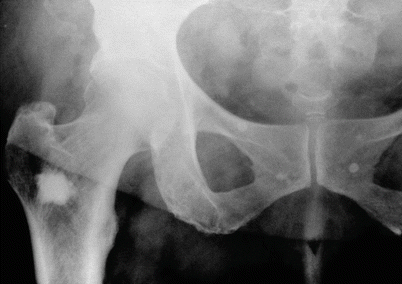
Fig. 7.2
Enostoma located in the upper end of the femur. The periphery of the lesion is irregular and spiculated due to the continuity with medullary bone trabeculae
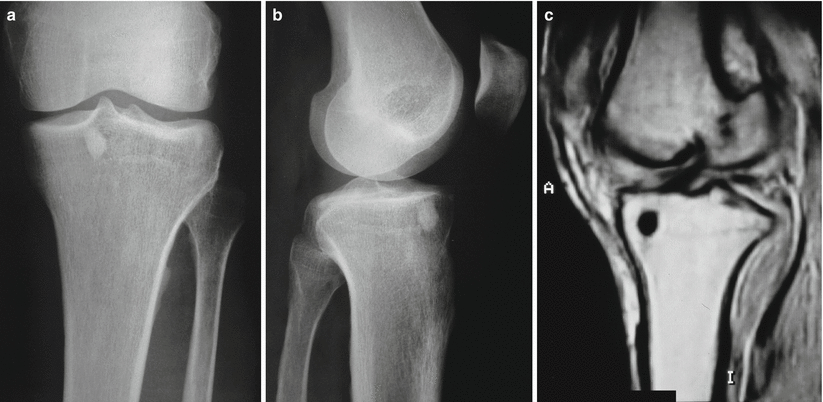
Fig. 7.3
(a–c) Roentgenograms and MRI of an enostoma located in the tibial epiphysis. By MRI, the lesion presents low signal in T1- and T2-weighted images similar to cortical bone
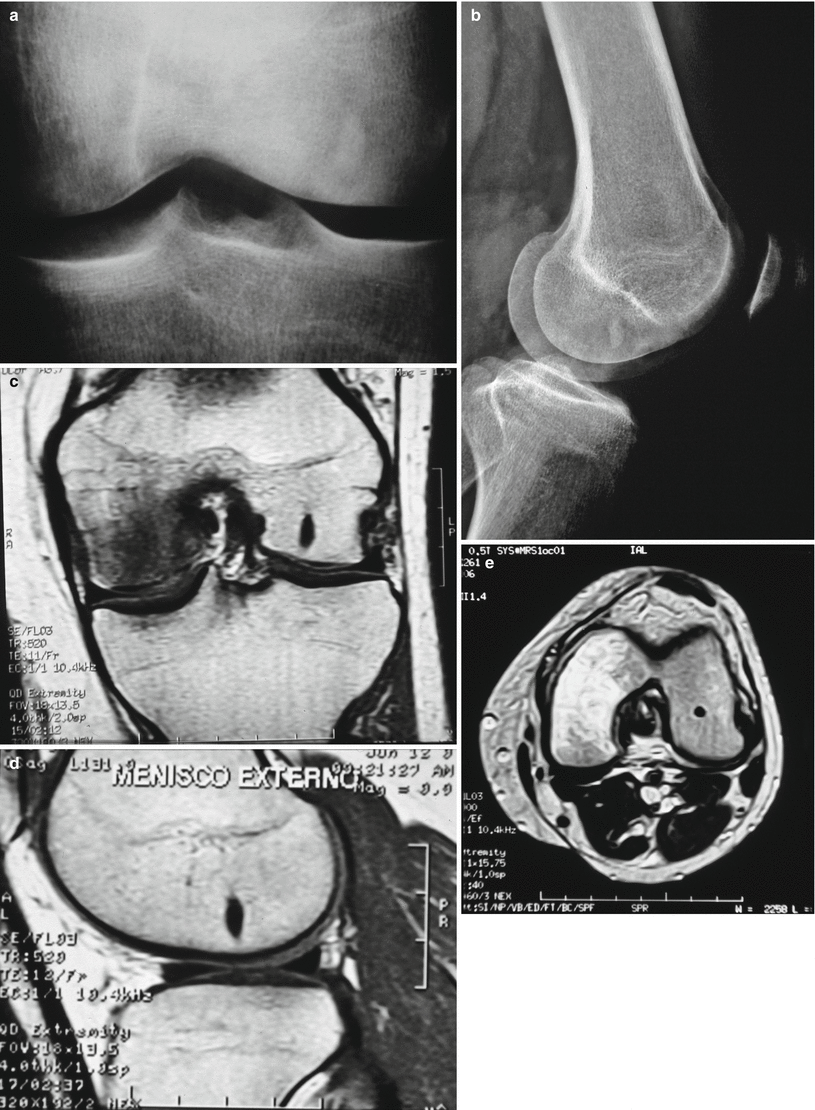
Fig. 7.4
(a, b) An enostoma in lower femoral epiphysis. In ovoid enostomas, long axis is parallel to the host bone’s long axis. (c–e) MRI of the lesion
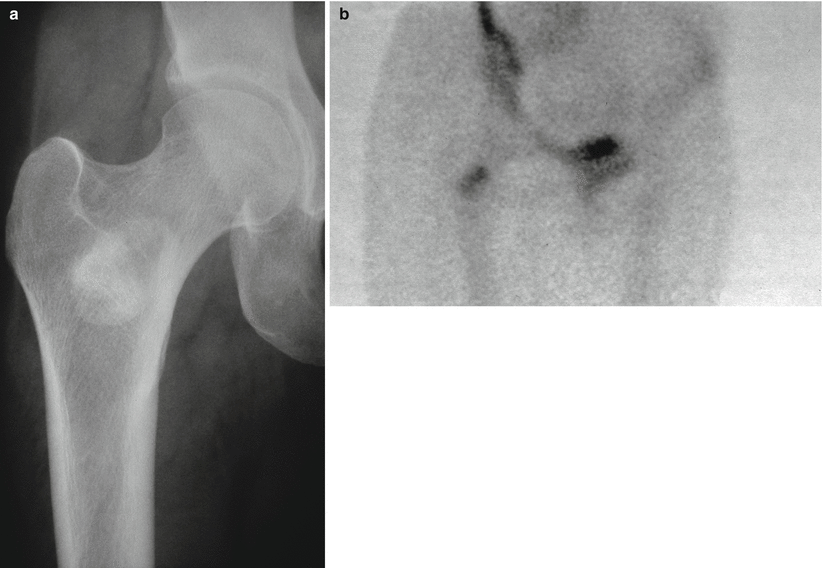
Fig. 7.5
(a) Radiograph of an enostoma in the upper metaphysis of a femur. (b) The bone scan showing very slow uptake
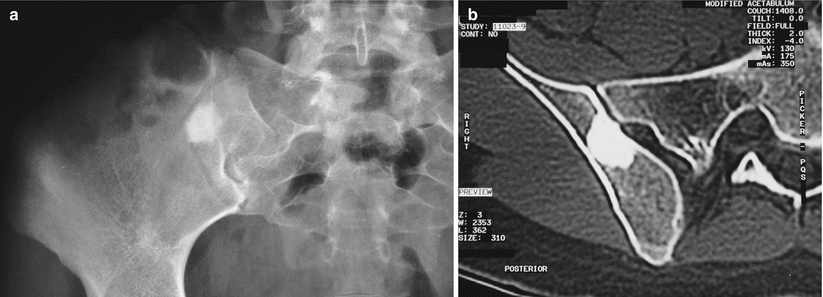
Fig. 7.6




(a) Enostoma involving the iliac bone. The lesion is round and radiodense. (b) CT scan of the lesion. Note the homogeneous radiodensity and the irregular periphery
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








