Fig. 34.1
Macular, morbilliform rash on the trunk in an 11-month-old boy
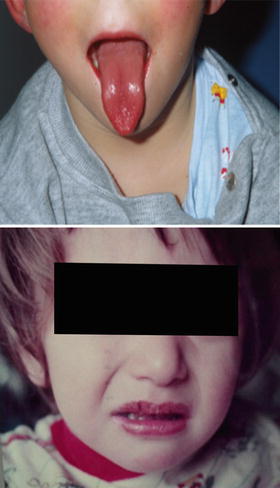
Fig. 34.2
Strawberry tongue, mucosal redness, and cracked lips in a 3-year-old boy
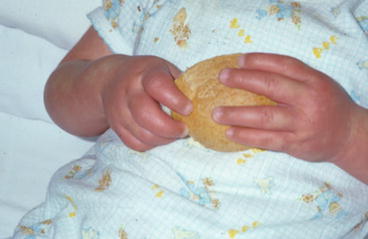
Fig. 34.3
Edema of dorsum of both hands in a 2-year-old girl
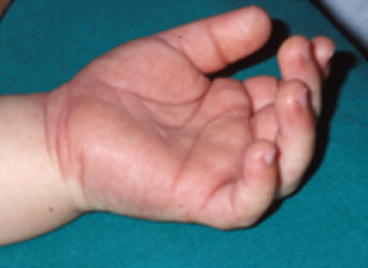
Fig. 34.4
Palmar erythema in a 9-month-old infant with Kawasaki disease
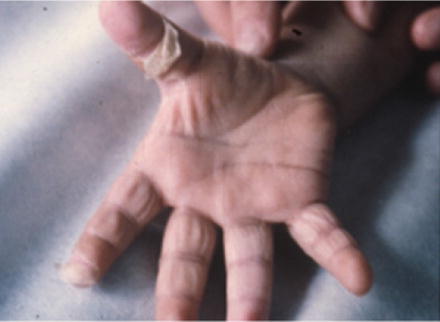
Fig. 34.5
Typical peeling, exfoliation of hands in a 7-month-old baby
Symptoms evolve over the first 10 days and then gradually resolve even in untreated patients. Less common symptoms are urethritis, aseptic meningitis, pneumonia, otitis, and gastroenteritis. Arthritis develops both in the acute and in convalescent phase and usually involves one or more large joints. Fever of 5 days duration plus 4 of the 5 remaining criteria or typical fever and CAA detected on 2D echocardiogram are required to diagnose KD. Patients with fever and two to three of clinical features are defined as “incomplete” KD. In the most recent classification criteria, fever is mandatory, in addition to 4 of the typical clinical findings. Desquamation in the perineal area has been added to changes in peripheral extremities. Digital peeling, a useful diagnostic hint, usually occurs 10–15 days from onset. The therapy includes IVIG (2 g/Kg) within the first 10 days from fever onset and aspirin (50–80 mg/kg). In severe cases, a second IVIG pulse, i.v. methylprednisolone (30 mg/Kg), and anti-TNF drug are required [1–3].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








