4. Fungi
the basic facts
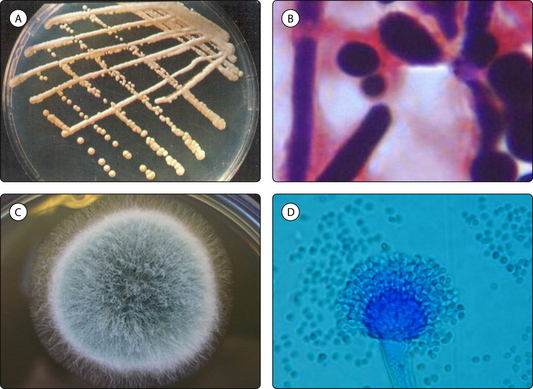
Yeasts (e.g. Candida albicans) are the simplest of the fungi. They are unicellular, spherical in shape and reproduce by budding (Fig. 3.4.1A). In some yeasts, including the medically important genus Candida, the buds elongate to form filaments (pseudohyphae) (Fig. 3.4.1B).
Moulds are composed of numerous microscopic branching, filamentous hyphae (e.g. Aspergillus fumigatus; Fig. 3.4.1C,D), known collectively as mycelia; these are involved in gaining nutrients and reproduction. The reproductive mycelia produce spores, termed conidia, either asexually or by sexual reproduction from opposite mating strains. Spores are disseminated in the atmosphere, enabling fungi to colonize new environments.