8. Epidemiology of infectious diseases
Route of transmission
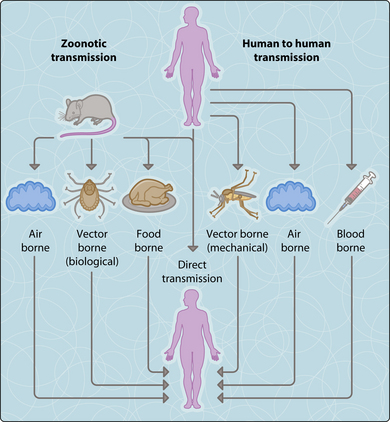
For an infectious agent to persist within a population there must be a cycle of transmission from a contaminated source, through a portal of entry, into a susceptible host and on again (Fig. 3.8.1).
Vector-borne transmission. Infection is mediated by arthropods or insects; it is mechanical if the vector is simply a source of contamination, but biological if the vector is necessary for the multiplication or maturation of the infectious agent.
Vehicle-borne transmission. This describes spread from all contaminated inanimate objects. Vehicles include clothing, food, water, surgical instruments and also biological substances such as blood and tissues.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree