17. Encephalitis and other nervous system infections
Encephalitis
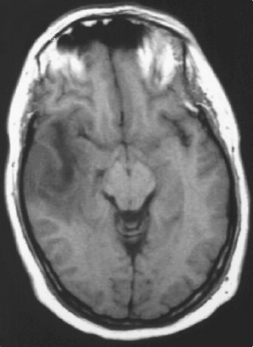
Encephalitis is predominantly a viral disease (Table 3.17.1), with herpes simplex infection being the most common in the UK (Fig. 3.17.1). Cerebral dysfunction presents as behavioural disturbance, fits and diminished consciousness. If progressive, then localized neurological signs, coma and death may occur. Diagnosis of the condition is clinical with confirmation from imaging and electroencephalography. Virus may also be detectable in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) but may not be cultivable. Brain biopsy offers the definitive means of diagnosis but is only used in specialist centres. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) encephalitis has a 70% mortality unless treated with aciclovir. Rabies is fatal but can be treated with postexposure prophylaxis, as the long incubation period allows time for an adequate immune response.
Table 3.17.1 CAUSES OF ENCEPHALITIS
| Cause | Features |
|---|---|
| Viruses | |
| Herpes simplex virus (herpesvirus) | Bitemporal localization detectable by imaging; HSV2 common in neonates, HSV2 in adults |
| Mumps virus (herpesvirus) | Meningoencephalitis may precede parotitis |
| Eastern and Western equine encephalitis virus (toga/bunyavirus) | Mosquito-borne in parts of North America |
| Rabies virus (rhabdovirus) | Incubation period of weeks to months after mammal bite; fatal if not treated |
| Tick-borne flaviviruses | Forested areas of Scandinavia; vaccine available |
| Japanese B virus (flavivirus) | Southeast Asia; vaccine available |
| Poliovirus and enteroviruses | Most commonly causes meningitis but may cause meningoencephalitis |
| Rubella and measles viruses | Subacute panencephalitis with high mortality |
| JC virus (papovavirus) | Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in the immunocompromised |
| Post-viral infection/post-vaccination | Immune mediated; occurs with measles, influenza and others; good prognosis |
| Protozoa/fungi | |
| Toxoplasma gondii | Immunocompromised and newborn |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | Common in HIV infection |
| Plasmodium falciparum | Cerebral malaria |
| Trypanosomas spp. | Sleeping sickness; central Africa |
| Prions | Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease |
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree