CHAPTER 3 Beach chair and lateral decubitus setup—pros and cons
 Arthroscopic shoulder procedures are becoming increasingly popular as technology and arthroscopic instruments continue to evolve.
Arthroscopic shoulder procedures are becoming increasingly popular as technology and arthroscopic instruments continue to evolve. Shoulder surgeons routinely use either the lateral decubitus position or the beach chair position for their cases, or their choice depends on the planned procedure.
Shoulder surgeons routinely use either the lateral decubitus position or the beach chair position for their cases, or their choice depends on the planned procedure. No difference has been proven in outcomes between lateral decubitus and beach positioning for shoulder arthroscopy procedures.
No difference has been proven in outcomes between lateral decubitus and beach positioning for shoulder arthroscopy procedures. Proper setup, including positioning and draping, is essential regardless of the planned patient position.
Proper setup, including positioning and draping, is essential regardless of the planned patient position.Lateral decubitus
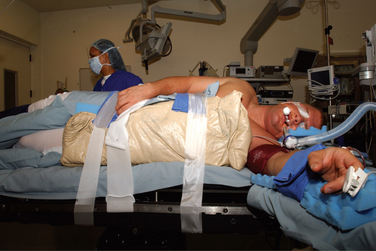
Although the shoulder arthroscopy was first performed in 1931, it was not as used as extensively as knee arthroscopy until the 1980s, when its use became more popular. The lateral decubitus position has been a traditional position for shoulder arthroscopy, and it is now used exclusively by many surgeons. Lateral decubitus positioning is facilitated through the use of several different types of commercially available traction apparatus. This equipment, allows weight to be used to pull traction both longitudinally on the arm and laterally at the axilla to permit lateral translation of the glenohumeral joint. Distraction of the glenohumeral joint provides optimum visualization during arthroscopic procedures.1–3 In the lateral decubitus position, the surgeon and assisting surgeon can function on both the anterior and the posterior aspects of the shoulder, while ideally visualizing separate monitors (Fig. 3-1).
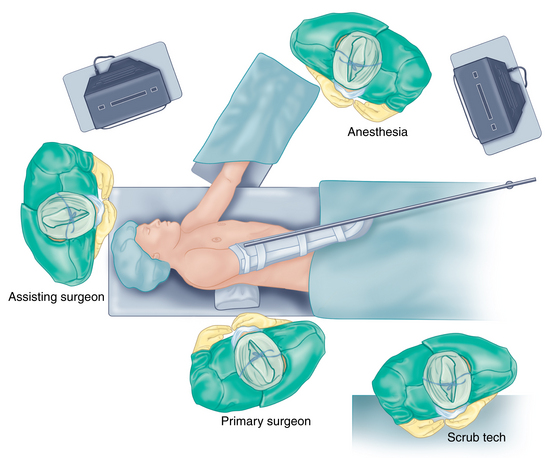
FIGURE 3-1 Overview of the lateral decubitus operating room setup.
(Modified from a sketch by David J. Wilson, MD.)
Description of setup (figs. 3-1 to 3-12)
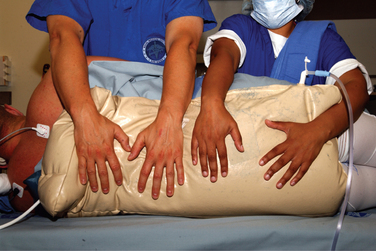
FIGURE 3-5 Patient positioned with two people holding while the vacuum suction to the bean bag is applied.
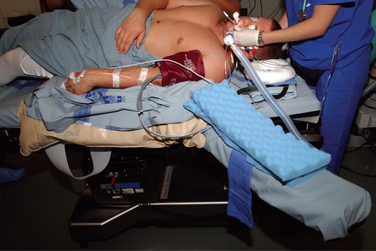
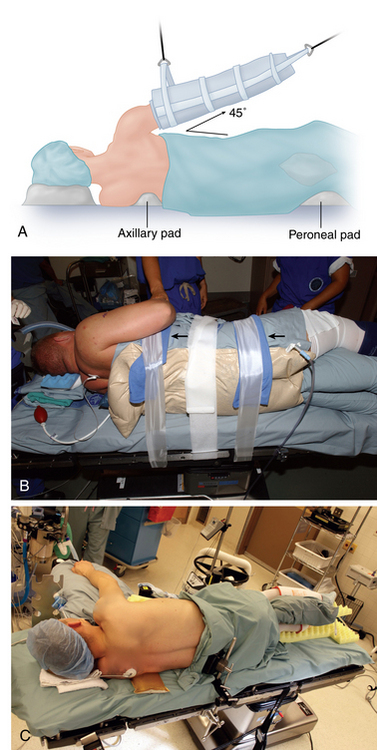
To support the body in the lateral decubitus position, a bean bag is utilized. Excessive trunk motion or loss of positioning can occur if the bean bag loses suction pressure. This may be minimized with the use of straps or tape around the trunk, securing the patient to the operating room table. Alternatively, commercially available lateral positioning systems, such as those commonly used for hip arthroplasty cases, also may be used to provide a more stable support without compromising the intraoperative position of the patient. In the lateral decubitus position, the patient is tilted approximately 20 to 30 degrees posterior to orient the glenoid parallel to the floor.4
The drapes are applied judiciously in an effort to maximize the surgical field about the shoulder, both anteriorly and posteriorly. For an arthroscopic case, two arthroscopy drape drains can be used to collect as much effluent as possible. The operative side axilla is commonly sealed off with a sterile sponge and a sterile adhesive after prepping. Planned incision sites are made away from acne and pustules if possible to avoid potential contamination with Proprionibacterium.5
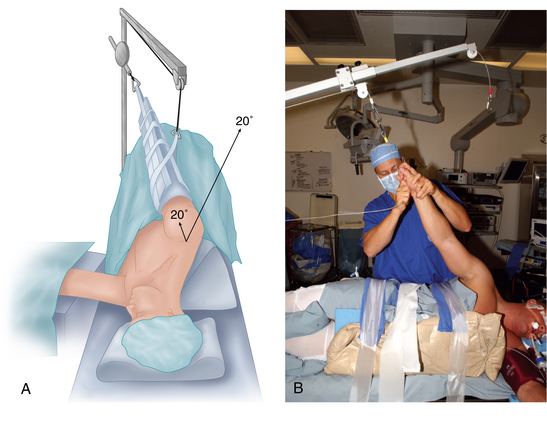
The arm is placed into a padded sleeve with the thumb pointing toward the ceiling and then is attached to one of the commercially available traction systems. These systems consist of a support that attaches to the end of the table and then uses a pulley system with weights to pull longitudinal balanced suspension on the arm and lateral traction in the axilla to obtain glenohumeral joint distraction.1–3 These pulleys and weights can be adjusted to provide abduction and forward flexion of the shoulder. The ideal forward flexion is 20 to 30 degrees and the ideal abduction is 25 to 45 degrees, although most surgeons adjust the abduction and forward flexion to personal preferences. Intraoperative changes in glenohumeral abduction, forward flexion, and lateral translation position are obtained easily by adjusting the pulley system. Intraoperative rotation of the humeral head can be adjusted by changing the position of the arm in the sleeve or by rotation of the entire sleeve.
Advantages of the lateral decubitus position
The lateral decubitus position has the following advantages:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree