Chapter 60 Arthritis
Osteoarthritis
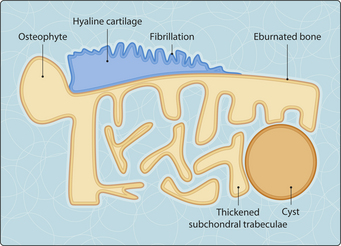
Figure 3.60.1 shows some of the morphological changes in osteoarthritis. In the early stages, the surface of the hyaline cartilage becomes ragged and split, an appearance known as fibrillation. The subchondral bone becomes sclerotic through thickening of the bony trabeculae. Later, proliferation of bone at the edge of the joint produces irregular nodules called osteophytes. There is a chronic inflammatory infiltrate of the synovium and surrounding tissues, but it is not as marked as in rheumatoid arthritis. If the cartilage wears away completely, the underlying bone becomes polished smooth and comes to resemble ivory, a process known as eburnation. Cyst-like spaces form in the bone underlying the joint as synovial fluid is forced into it through microfractures.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree