(1)
Department of Pathology and Orthopaedic Surgery, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, MD, USA
Abstract
Adamantinoma is a primary low-grade malignant bone tumor that has nests of epithelial cells in a fibro-osseous background. Epithelial nests pattern are commonly basaloid type but can be spindle shaped, tubular, or squamoid. Ninety-five percent of cases involve the tibia or the fibula. On rare occasions, other long bones may be involved. Patients are mostly in their 30s and often have symptoms of long duration. Radiologically, adamantinomas are diaphyseal multifocal cortical-based lesions that can invade the adjacent soft tissue or the medullary canal. It is best treated by wide resection and late metastases can occur. Osteofibrous dysplasia-like adamantinomas are not malignant.
Keywords
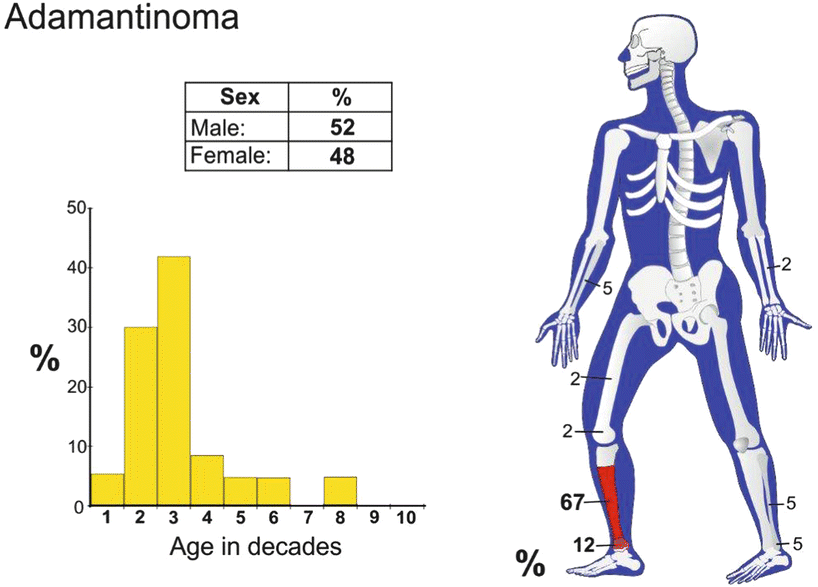
AdamantinomaBoneImmunohistochemistryTibiaDefinition
A primary bone tumor that has nests of epithelial cells in a fibro-osseous background
Etiology
Unknown
Clinical Features
Sites of Involvement
Ninety percent of cases involve the tibia or (10 %) the fibula.
On rare occasions, other long bones, such as the femur, humerus, and ulna, may be involved. This neoplasm has also been reported in the pretibial soft tissues.
Epidemiology
Adamantinoma is a very rare neoplasm.
Patients range from age 3 to age 72, but most are in their 30s.
Clinical Signs and Symptoms
Patients usually complain of pain and swelling, often of long duration.
Approximately one-third of patients have had symptoms for longer than 5 years. One reported patient had symptoms for 50 years.
Image Diagnosis
Radiologic Features
Adamantinomas are cortical-based lesions, and 90 % of cases involve the diaphysis (Fig. 37.1).
Many lesions show invasion of the adjacent soft tissue or the medullary canal (Fig. 37.2).
Some lesions show multiloculated lytic areas surrounded by dense reactive bone.
Often the lesion appears multifocal and involves long segments of the tibial shaft.
MRI Features
MRI usually shows a uniform high signal on T2-weighed images.
Image Differential Diagnosis
Osteofibrous dysplasia
This disease is cortical based and does not involve the medullary canal or adjacent soft tissue.
Any non-matrix producing primary bone tumor.
Metastatic carcinoma
Pathology
Histologically, adamantinomas consist of various patterns of epithelial cells in a fibrous and fibro-osseous stroma. Keratin stains are positive (Fig. 37.3).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








