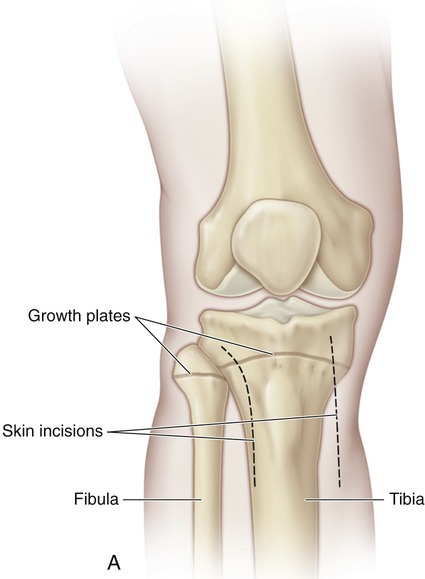
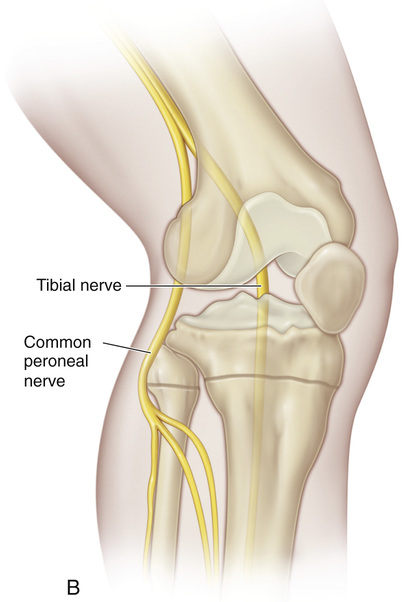
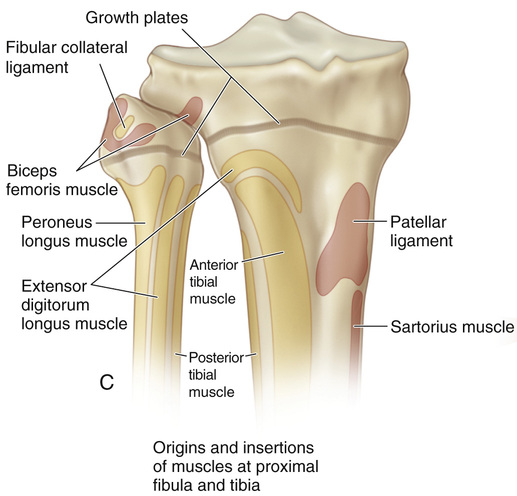
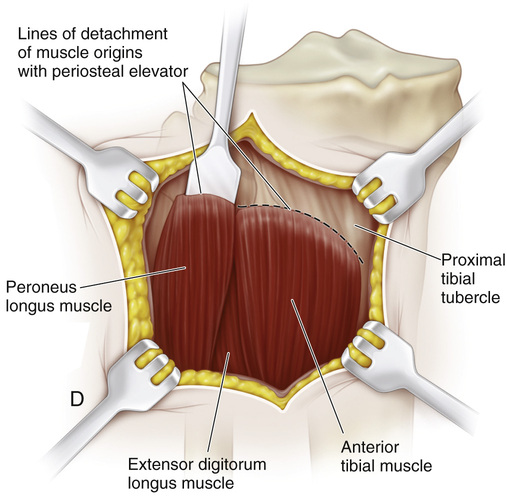
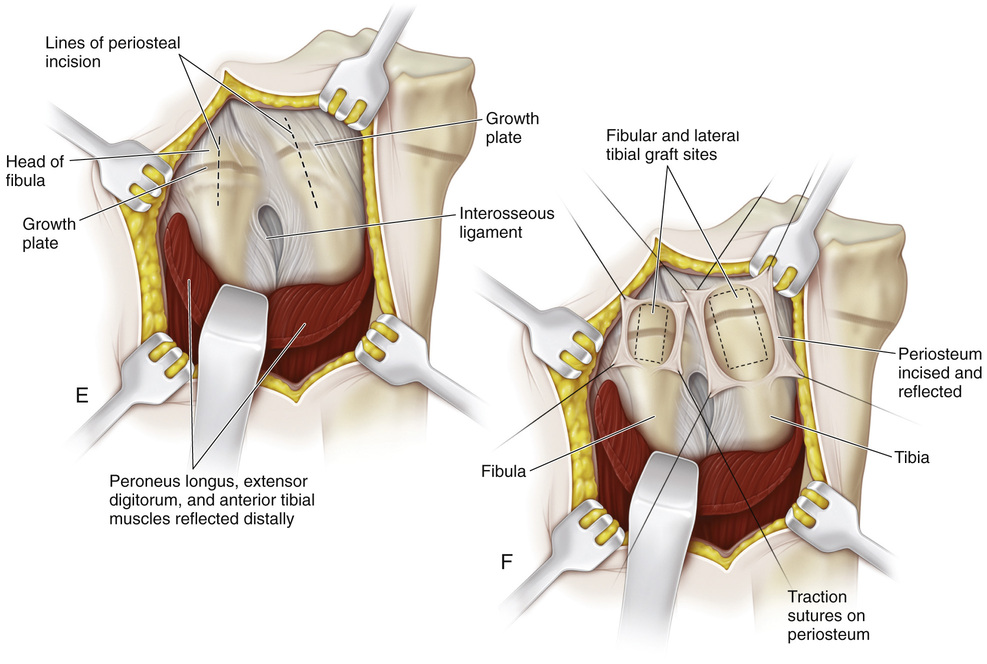
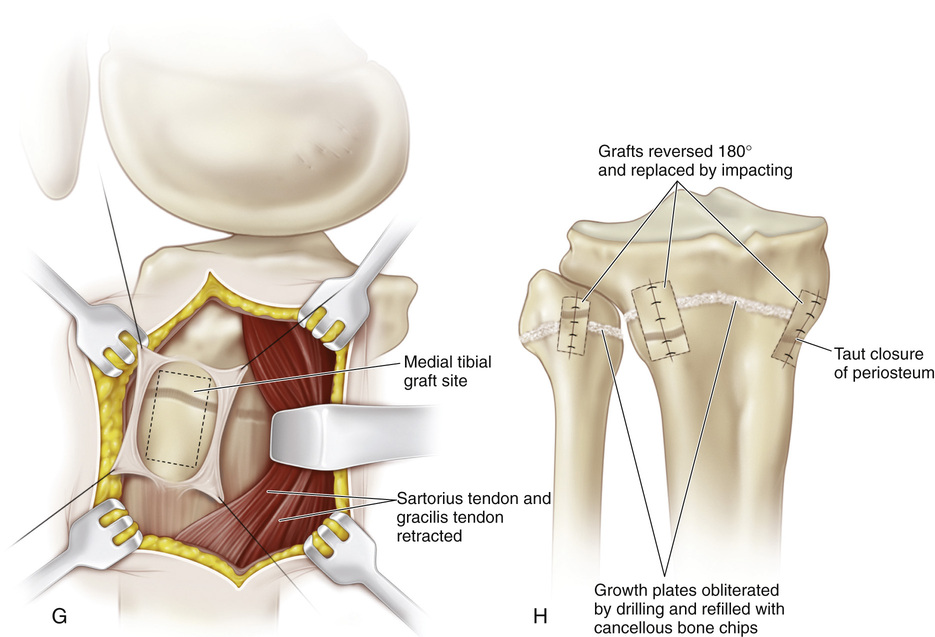
A, The patient is placed supine or in a semilateral position. A sterile folded sheet is placed under the knee for support. The knee joint line, the head of the fibula, and the proximal tibial tubercle are identified. A 30-degree slanted oblique incision is made midway between the proximal tibial tubercle and the fibular head; it begins proximally 1 cm inferior to the joint line and 1 cm anterior to the fibular head and extends distally and forward for a distance of 5 cm. The subcutaneous tissue is divided, and the wound flaps are widely undermined and retracted. B and C, The head of the fibula is in line with the proximal growth plate of the tibia. The capsule of the knee joint, the insertion of the biceps tendon, and the fibular collateral ligament of the knee are identified. The common peroneal nerve lies close to the medial border of the biceps femoris muscle in the popliteal fossa; then it passes distally and laterally between the lateral head of the gastrocnemius and the biceps tendon. Behind the fibular head, the nerve is subcutaneous. At the site of origin of the peroneus longus muscle at the head and neck of the fibula, the common peroneal nerve winds anteriorly around the fibular neck and then passes deep to the peroneus longus muscle and branches into the superficial and deep peroneal nerves. D, The origins of the toe extensors, extensor hallucis longus, and anterior tibial muscles, along with a cuff of periosteal flap, are elevated from the arcuate line. With a periosteal elevator, the origin of the peroneus longus muscle is detached from the head of the fibula. Keeping the dissection anterior to the fibular head prevents injury to the nerve. E and F, The site of the growth plate of the proximal fibula is identified. Next a longitudinal incision is made on the anterior aspect of the fibular head and is extended distally to include the growth plate. Alternatively, a rectangular piece of bone (¼ inch wide and ½ inch long) is removed from the proximal fibula, thus straddling the physis. Three fourths of the length of the bone graft includes the fibular head, so that only one fourth of the graft length includes the metaphysis. The growth plate is thoroughly curetted, the ends of the bone graft are reversed (180 degrees), and the piece of bone is placed securely back in the graft bed. I simply curet the growth plate anteriorly to posteriorly. The lateral aspect of the proximal tibial physis is already exposed for the fibular epiphysiodesis. A longitudinal incision is made midway between the anterior and posterior borders of the lateral tibia. The periosteum is elevated, and a rectangular piece of bone is resected in a manner similar to that described for the bone graft technique in the distal femur. The steps of the epiphysiodesis are the same as those outlined in Procedure 51G to KG to K for epiphysiodesis of the distal femur. G and H, The medial side of the proximal tibial physis is exposed by a longitudinal incision approximately 3 cm long, beginning 1 cm distal to the joint line and continuing distally midway between the proximal tibial tubercle and posteromedial margin of the tibia. The subcutaneous tissue and deep fascia are divided in line with the skin incision. The anterior margins of the sartorius tendon and tibial collateral ligament are partially elevated and retracted posteriorly. The steps for growth arrest of the proximal tibial physis follow the steps described for a distal femoral epiphysiodesis. The rectangular piece of bone graft removed from the tibia, usually ½ inch wide and ¾ inch long, is smaller than that removed from the femur. Before closure of the wound, the tourniquet is released, and hemostasis is secured.
Epiphysiodesis of the Proximal Tibia and Fibula (the Green Modification of the Phemister Technique)
Operative Technique
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








