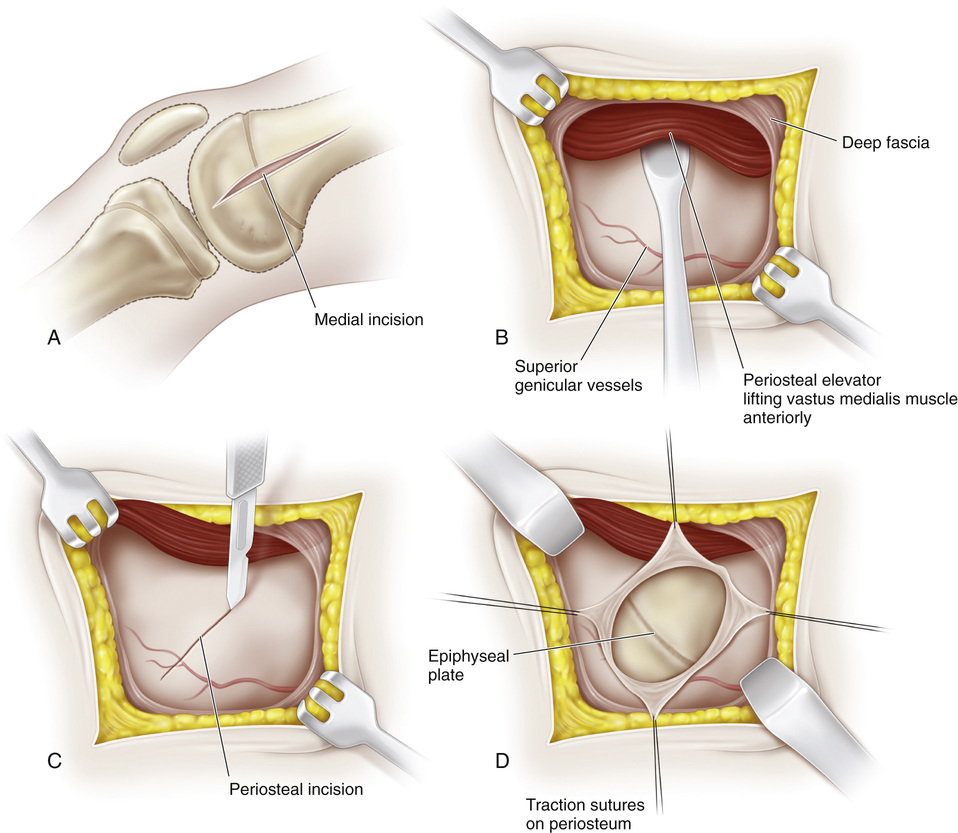
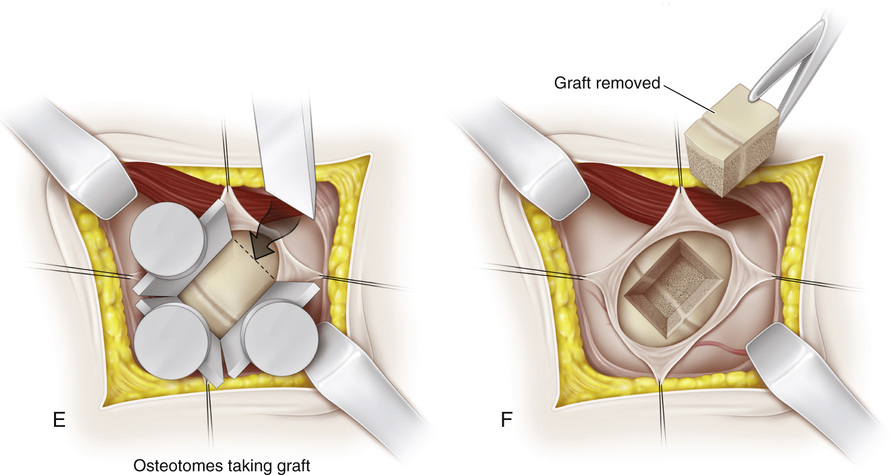
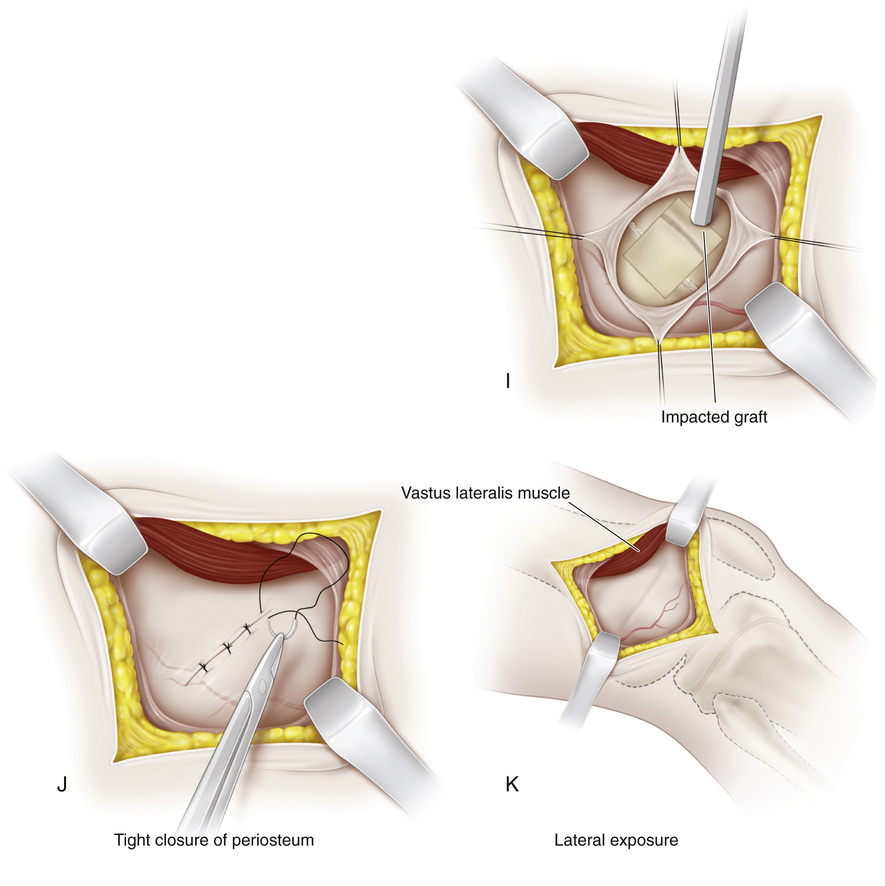
A, The knee is supported in 20 to 30 degrees of flexion, and the joint line is identified. First, the medial aspect of the distal femur is exposed. Beginning 1 cm superior to the joint line, a longitudinal incision approximately 3 cm long is made midway between the anterior and posterior margins of the femoral condyles. The subcutaneous tissue and deep fascia are divided in line with the skin incision. B, Following the anterior surface of the medial intermuscular septum, the vastus medialis muscle is lifted anteriorly with a blunt periosteal elevator. The suprapatellar pouch should not be entered. In the inferior margin of the wound, the capsule and reflected synovial membrane of the knee joint are gently elevated and retracted with blunt instruments distally. The superior medial genicular vessels traverse the wound; it is best to coagulate them to prevent troublesome bleeding later. C, A midline longitudinal incision is made in the periosteum, starting proximally and extending throughout the extent of the wound. D, The medial distal femoral physis is exposed by raising anterior and posterior flaps of periosteum by subperiosteal dissection; it appears as a white, glistening transverse line that is softer than adjacent cancellous bone. Some surgeons prefer to make a longitudinal I-shaped incision in the periosteum to expose the growth plate. The periosteum is gently retracted. Rough traction and shredding of the periosteum should be avoided. If necessary, elevators are placed subperiosteally on the anterior and posterior aspects of the distal femur for adequate exposure. Dull right-angled retractors are used for proximal and distal retraction. E and F, With matched pairs of osteotomes, a rectangular piece of bone G, The growth plate is curetted in anterior, posterior, and distal directions. It should be remembered that the distal femoral physis is pointed inferiorly. The softness of the cartilaginous plate serves as a guide to its direction. Cancellous bone graft is taken from the proximal bed and packed into the defect created by removal of the growth plate. H, The bone graft is then reinserted into its original bed, with its ends reversed by 180-degree rotation. I, With an impactor and mallet, the bone graft is securely seated in the bony defect. It should be tapped in a distal direction because the growth plate is inferior in location. J, The periosteum is tightly closed with interrupted sutures. It is important not to include the patellar retinaculum with the periosteum because doing so will bind it down and thus restrict knee motion. The periosteum is sutured with the knee in complete extension. K, The same procedure is repeated on the lateral side.
Epiphysiodesis of the Distal Femur (the Green Modification of the Phemister Technique)
Operative Technique
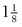 to
to 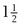 inches long and ½- to ⅝-inch wide is excised. The epiphyseal plate should be at the junction of the distal one third and proximal two thirds of the length of bone graft resected, at a point equidistant between the anterior and posterior surfaces of the femur. The posterior cortex of the femur should not be broken. The depth of the bone graft is ½ to ¾ inch. Because of the flare of the femoral condyles, the anterior and posterior osteotomes should be tilted somewhat distally so that they are perpendicular to the medial surface of the femur. Following removal of the osteotomes, the completeness of the osteotomy is checked with a thin (⅜- or ¼-inch) osteotome. Then the graft is removed with curved osteotomes. Breakage of the graft at the physis is prevented by straddling the growth plate with the osteotomes.
inches long and ½- to ⅝-inch wide is excised. The epiphyseal plate should be at the junction of the distal one third and proximal two thirds of the length of bone graft resected, at a point equidistant between the anterior and posterior surfaces of the femur. The posterior cortex of the femur should not be broken. The depth of the bone graft is ½ to ¾ inch. Because of the flare of the femoral condyles, the anterior and posterior osteotomes should be tilted somewhat distally so that they are perpendicular to the medial surface of the femur. Following removal of the osteotomes, the completeness of the osteotomy is checked with a thin (⅜- or ¼-inch) osteotome. Then the graft is removed with curved osteotomes. Breakage of the graft at the physis is prevented by straddling the growth plate with the osteotomes.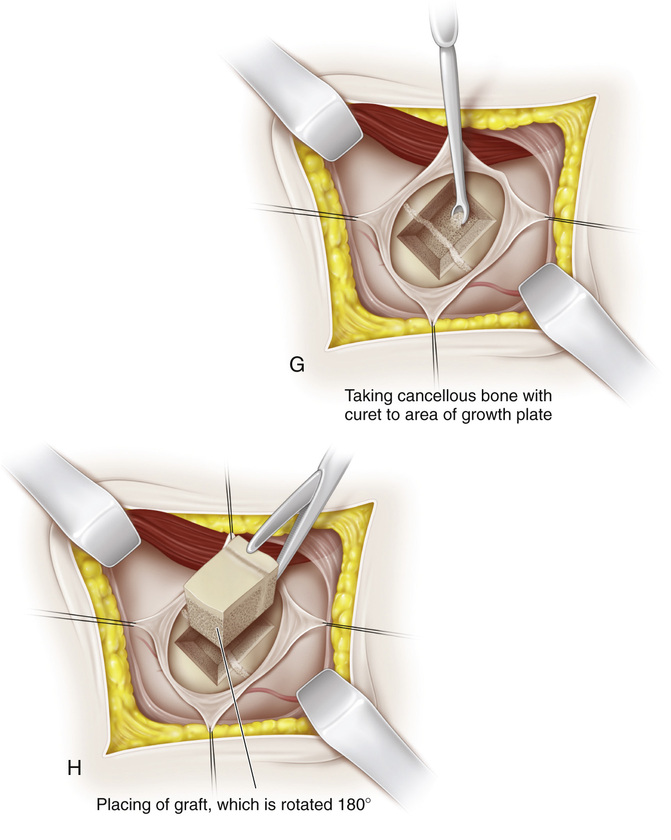
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








