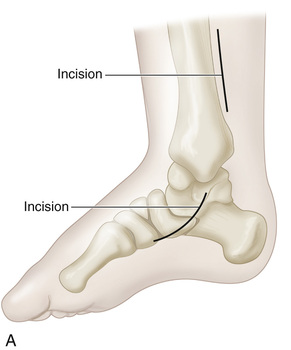
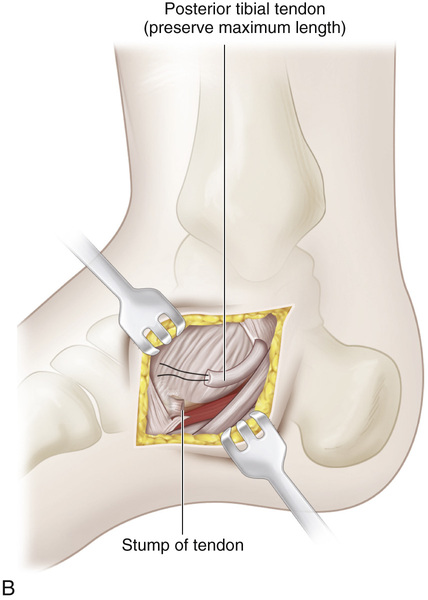
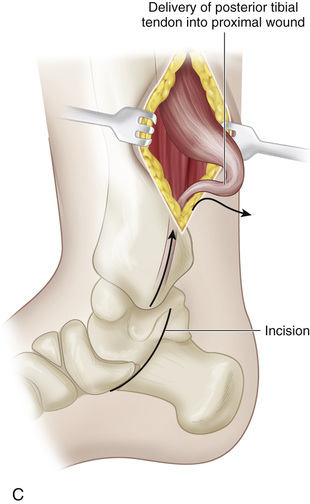
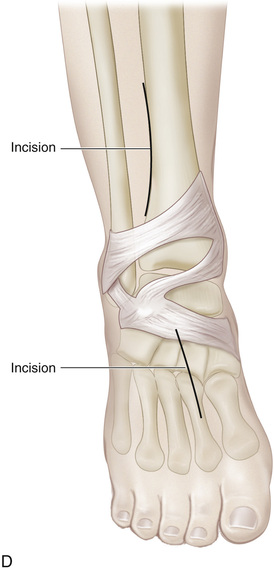
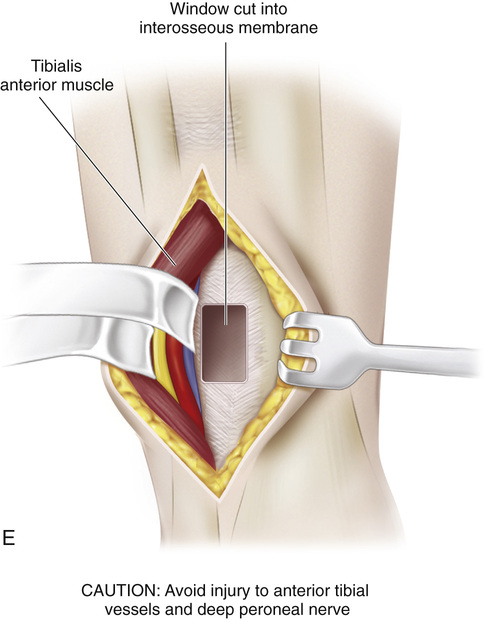
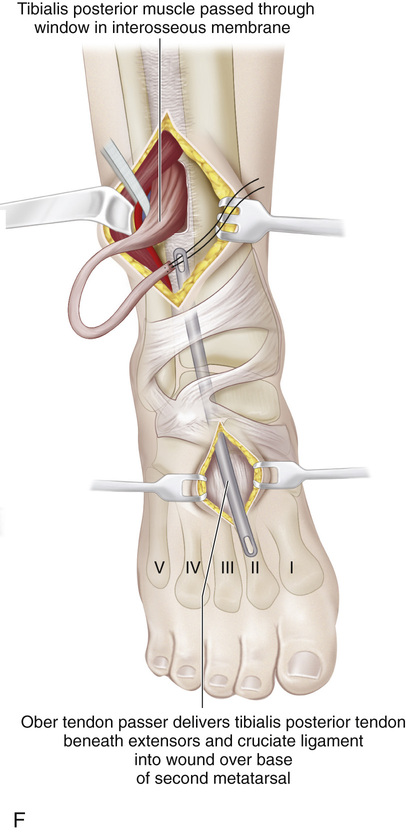
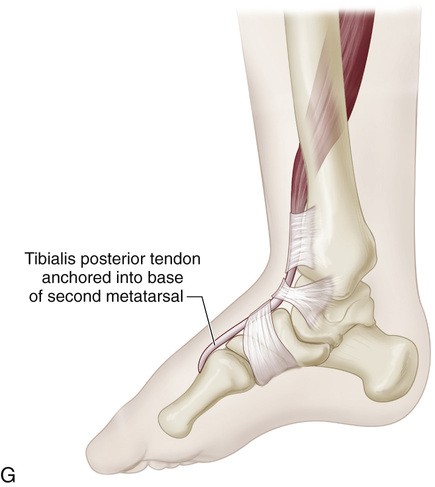
A, A 4-cm-long incision is made over the medial aspect of the foot, beginning posterior and immediately distal to the tip of the medial malleolus and extending to the base of the first cuneiform bone. A second longitudinal incision is made 1.5 cm posterior to the subcutaneous medial border of the tibia and ends 3 cm from the tip of the medial malleolus. B, The posterior tibial tendon is identified at its insertion, and its sheath is divided. The tendon is freed and sectioned at its attachment to the bone, with maximal length preserved. A 0-0 silk whip suture is inserted in its distal end. C, The posterior tibial muscle is identified through the leg incision, and its sheath is opened and freed. Traction on the stump in the foot incision can help in its identification. Moist sponges and a two-hand technique are used to deliver the posterior tibial tendon into the proximal wound. The surgeon must be careful to preserve the nerve and blood supply to the posterior tibial muscle. D, A longitudinal skin incision is made anteriorly one fingerbreadth lateral to the crest of the tibia, starting at the proximal margin of the cruciate ligament of the ankle and extending 7 cm proximally. A 4-cm-long longitudinal incision is then made over the dorsum of the foot, centered over the base of the second metatarsal. E, The anterior tibial muscle is exposed together with the anterior tibial artery and extensor hallucis longus muscle. It is retracted laterally to expose the interosseous membrane. Next, a large rectangular window is cut in the interosseous membrane. F and G, With an Ober tendon passer, the posterior tibial tendon is passed posteriorly through the window in the interosseous membrane into the anterior tibial compartment. Care is needed to not twist the tendon or damage its nerve or blood supply. Next, with the aid of an Ober tendon passer, the posterior tibial tendon is passed beneath the cruciate ligament and the extensors and is delivered into the wound on the dorsum of the foot. It is anchored to the base of the second metatarsal bone through a bone tunnel. The wounds are closed in layers in the usual manner. A short-leg cast that will hold the foot in neutral position at the ankle joint is applied.
Anterior Transfer of the Posterior Tibial Tendon Through the Interosseous Membrane
Operative Technique
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








