Fig. 24.1
Traction tower setup
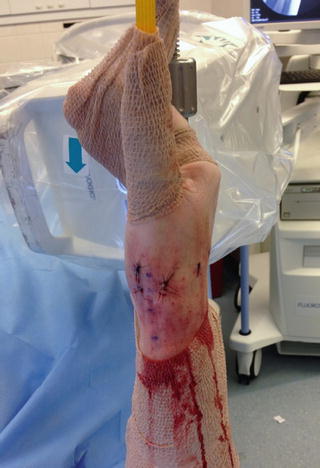
Fig. 24.2
Traction tower setup
Often it is helpful to have a mini C-arm fluoroscope available during these procedures. This should be draped and brought into the surgical field at a 90° angle so that the “C” is oriented in a dorsal to volar direction with the image intensifier at the dorsum of the wrist.
Landmarks and Portals
Standard 1R and 1U portals have been described for CMC joint arthroscopy; however it is necessary to be familiar with the surrounding anatomy. The thumb metacarpal should be palpated and marked along with the joint line. The abductor pollicis longus (APL), extensor pollicis brevis (EPB), and extensor pollicis longus (EPL) tendons should be marked. The radial artery has been described as lying ulnar to the EPB at an average distance of 11 mm (range 4–17 mm) in a cadaveric study. However, the average distance from the EPL is within 1 mm in greater than 70 % of specimens studied [8].
The 1R portal is located at the joint line directly radial to the APL (volar), and the 1U portal is located directly ulnar to the EPB (dorsal). Approximately 1 cm will separate the two portals from one another.
An 18 gauge needle should be used to confirm the location and determine the appropriate entry angle to the joint. The needle should be directed into the joint slightly proximal to the mark for the portal. The joint should be insufflated with 1–2 mL of normal saline and the distension of the capsule should be visible. A number 11 blade should be used to cut skin only. A small mosquito type hemostat should be used to bluntly dissect the soft tissues until the capsule can be palpated with the tip of the instrument. The surgeon should be mindful of the branches of the superficial radial nerve; thus careful blunt dissection is necessary to avoid injury. Cadaveric studies have shown that of 11 specimens at least one branch of the superficial radial nerve was lying over the EPB tendon in 7 specimens, the APL tendon in 6 specimens, and over the EPL in all 11 specimens.
After careful dissection, a blunt trocar with its surrounding sheath is then gently introduced into the joint. The inclination is slightly distal at a 10–20° angle. The 1U portal is typically the first portal established. The 1U portal is in the area of the DRL (volar) and the POL (dorsal). Sweeping the trocar to find the natural division between these two ligaments can help to preserve their integrity and make entry into the joint less traumatic. Trocar placement can be confirmed with fluoroscopy, since it is easy to fall erroneously into the STT joint. For the 1R portal, the capsule is immediately deep to the APL tendon since there is no ligamentous reinforcement in this area. This portal is usually made under direct visualization and will serve as the primary working portal. Switching portals is commonly done and should be used to obtain complete visualization of the entire joint.
Diagnostic Arthroscopy Technique
Often the initial view of the joint is obscured with hypertrophic synovium. This may be resected under visualization using a small joint arthroscopic shaver or thermal device according to the surgeon’s preference. It is quite common with these small shavers to have to clear debris from them several times during the case. Continuous inflow is encouraged to clear as much debris as possible to maximize visualization and inspection of the surrounding ligaments. Irrigation fluid will also help to dissipate the heat generated by these devices.
General inspection of the joint should be done systematically, looking for osteophytes, loose bodies, and damage to the articular surface. With the camera in the 1U portal, the superficial and deep portions of the anterior oblique ligament can be identified and inspected (Fig. 24.3). Moving the camera in a more dorsal direction, the ulnar collateral ligament can be visualized (Fig. 24.4).
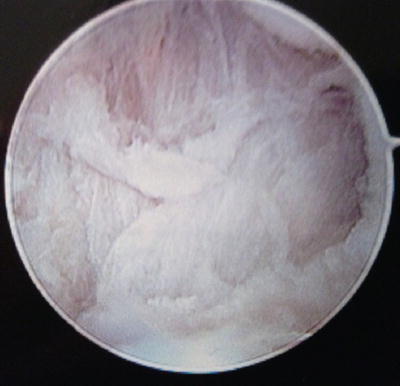

Fig. 24.3




Anterior oblique ligament
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








