Reflexes
Pathological Upper Extremity Reflexes
This chapter discusses various pathological reflexes that usually are present in corticospinal disease and higher cortical dysfunction, such as stroke, tumor, demyelinating diseases, and vasculitis. If no corticospinal pathology or other higher cortical dysfunction is present, these reflexes should be absent. These reflexes are not graded on the Wexler scale but are referred to as being either present or absent. Babinski’s and Rossolimo’s foot signs are considered normal in infants.
Procedure
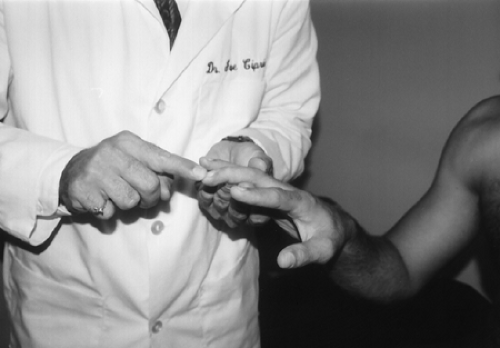
With the patient’s forearm pronated, grasp the patient’s hand and middle finger. With your opposite hand, flick the distal end of the patient’s middle finger, stretching the flexor and eliciting a stretch reflex (Fig. 18-1).
Rationale
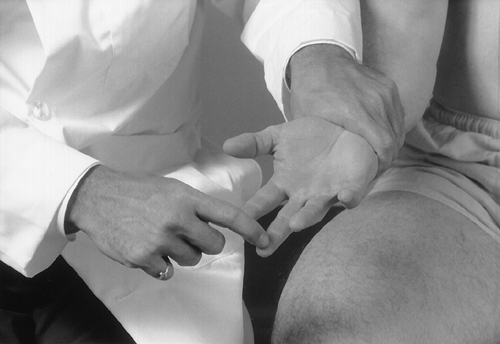
A positive sign is elicited if the patient flexes the thumb and forefinger (Fig. 18-2). A positive sign indicates a hyperactive reflex only. If this sign is present, it may be one indicator of pyramidal tract disease.
Procedure
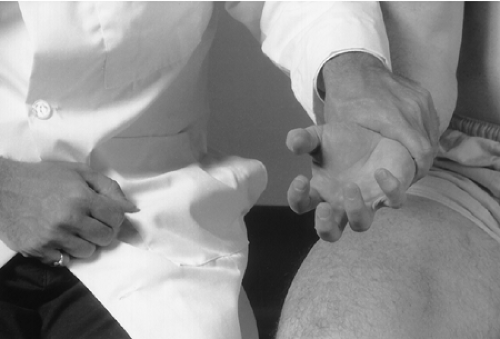
Grasp the patient’s wrist and tap the plantar surface of the tip of the index and middle digits (Fig. 18-3).
Rationale
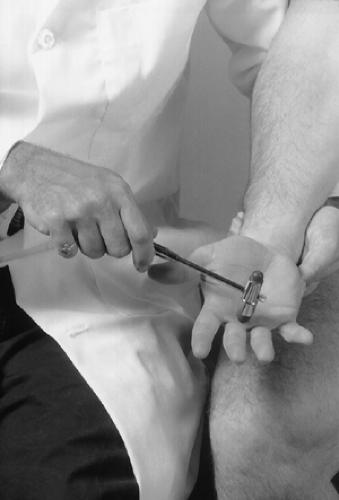
A positive sign is elicited if the patient flexes all of the fingers (Fig. 18-4). A positive sign indicates a hyperactive reflex only. If this sign is present, it may be one indicator of corticospinal tract disease.
Rossolimo’s Hand Sign
Procedure
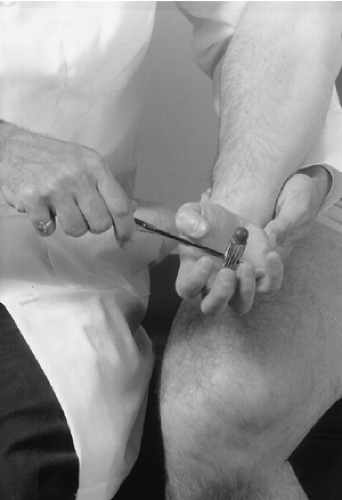
With a neurological reflex hammer, tap the palmar surface of the metacarpophalangeal joint (Fig. 18-5).
Rationale
A positive sign is elicited if the patient flexes all of the fingers (Fig. 18-6). This sign is present in pyramidal tract disease.
Pathological Lower Extremity Reflexes
Procedure
With the patient supine, stroke the sole of the foot with a blunt object like the handle of a neurological reflex hammer. Begin with the lateral aspect of the heel and move superiorly and medially to the big toe (Fig. 18-9).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree