Fig. 66.1
Paget’s disease of the skull. Radiographic features presenting large ill-defined lytic area with cotton-wool-like opacities
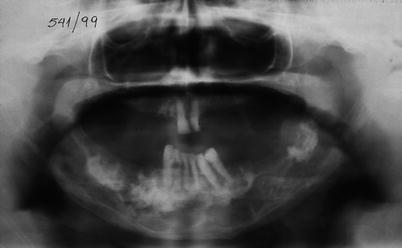
Fig. 66.2
Paget’s disease of the mandible with typical periapical dentinal hyperplasia
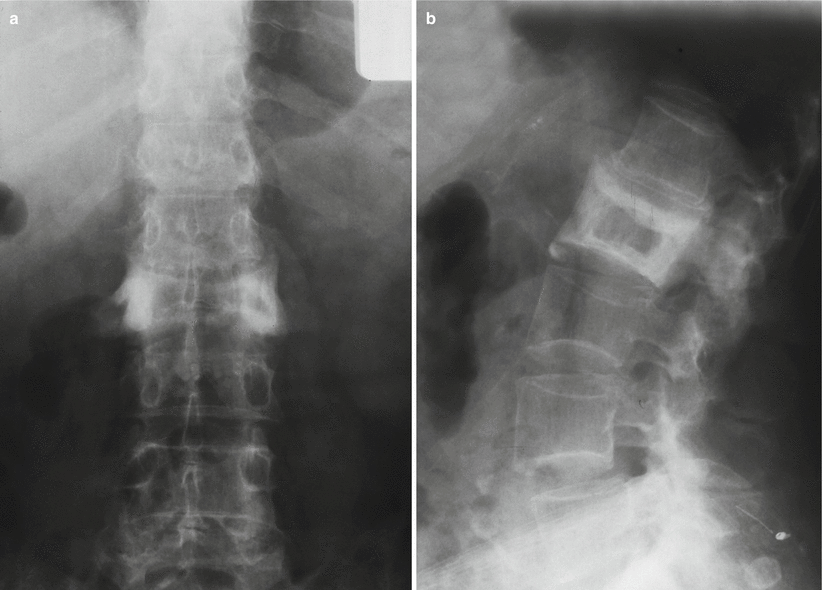
Fig. 66.3
(a, b) Paget’s disease of the vertebra. Anteroposterior and lateral X-rays show enlargement of the vertebral body with coarsening of the trabecular pattern and sclerotic margins, with the typical “picture frame” pattern
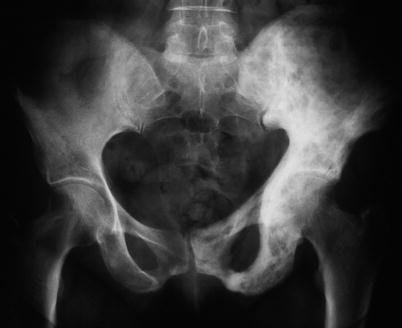
Fig. 66.4
Paget’s disease involving the left pelvis with expansion of the bone
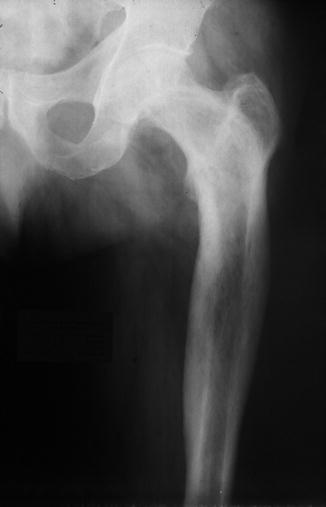
Fig. 66.5
Radiograph showing Paget’s disease of the diaphyso-metaphyseal femur, with increased thickening of the cortex and medullary bone
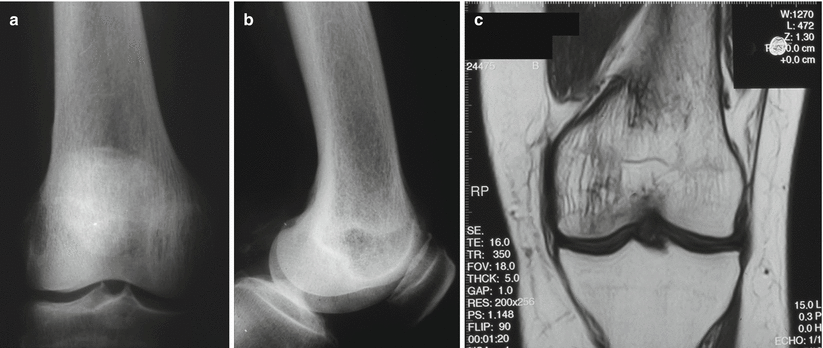
Fig. 66.6
(a, b) Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs: Paget’s disease of the distal femur. (c) MRI: Different trabeculation as compared to the non-affected bone of the tibia
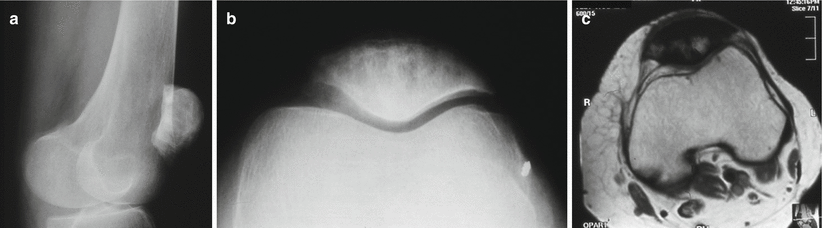
Fig. 66.7
Paget’s disease. (a, b) X-ray and (c) MRI of the patella
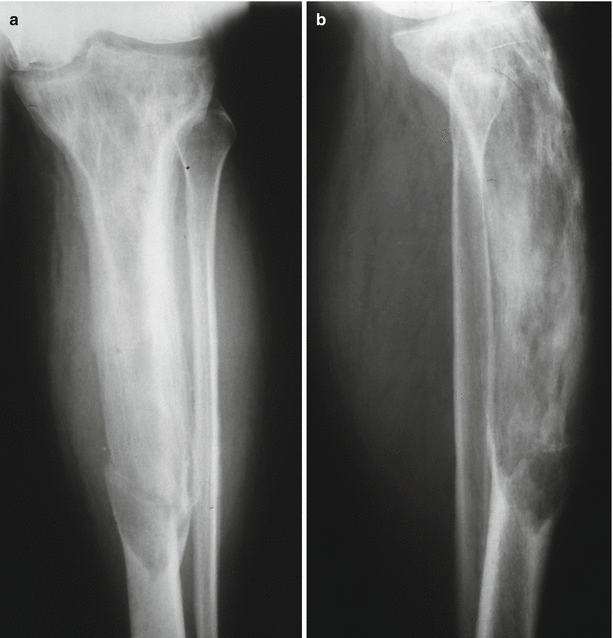
Fig. 66.8
(a, b) Extensive Paget’s disease involving the tibia, with anterior bowing deformity and coarse trabecular pattern; there is lack of the corticomedullary demarcation, complicated with transverse fracture
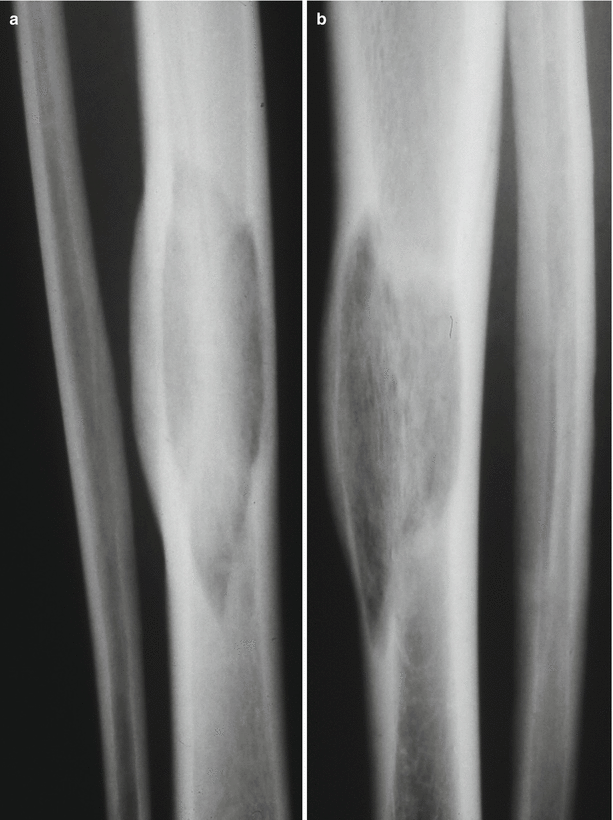
Fig. 66.9
(a, b) Paget’s disease. Well-defined radiolucent defect in the tibia and proximal and distal margins showing a flame-shaped pattern
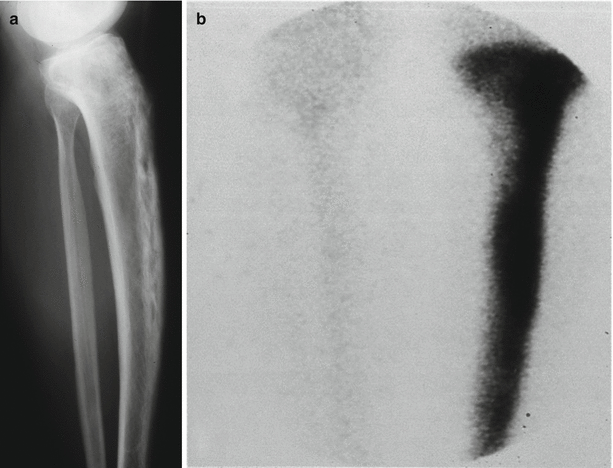
Fig. 66.10




(a) Lateral X-ray with Paget’s disease of the tibia. It is possible to appreciate some bowing; (b) High uptake of Tc99 in old stage lesion
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








