Other Neuromuscular Disorders
George H. Thompson
Frank R. Berenson
Neuromuscular disorders other than cerebral palsy and myelodysplasia are less common; however, patients with these disorders do present in pediatric orthopaedic and neuromuscular clinics. These disorders include the muscular dystrophies and congenital myopathies, spinal muscular atrophy, Friedreich ataxia, hereditary motor sensory neuropathies (HMSN), and poliomyelitis. It is important that an accurate diagnosis be established so that an effective treatment program can be planned and initiated. Delaying the diagnosis of these disorders may lead to inappropriate treatment; furthermore, the mother of an affected child might have further pregnancies and give birth to another child with the genetic disorder (1). Accurate diagnosis requires a careful evaluation of history, physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic studies (2).
HISTORY
The history should include the details of pregnancy, delivery, and growth and development of the child involved. Questions should be asked regarding in utero activity, complications of delivery, birth weight, Apgar score, problems during the neonatal period, age at achievement of developmental motor milestones, age at onset of the current symptoms, and information that will clarify whether the condition is static or progressive. Systemic symptoms, such as cardiac disease, cataracts, seizures, or other abnormalities, should also be ascertained.
The family history is important in diagnosis because these disorders, with the exception of poliomyelitis, are genetic in origin. In order to arrive at an accurate diagnosis, family members of the child or adolescent involved may need to be examined for subtle expressions of the same disorder and may also be required to undergo hematologic or other studies.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Most children who present for evaluation of a suspected neuromuscular disorder usually have one or more of the following: a delay in developmental milestones, abnormal gait, foot deformity, or spinal deformity. There is usually a history of progression. Physical examination consists of a thorough musculoskeletal and neurologic evaluation. Observing the child walking and performing simple tasks, such as rising from a sitting position on the floor, can be useful. Observation of the gait may reveal decreased arm swing, circumduction of the legs, scissoring, or short cadence. Standing posture may reveal increased lumbar lordosis or a wide base position for balance. Also, in the standing position, the appearance of the feet should be observed. Pes cavus or cavovarus deformities are common physical findings in many of these disorders. Having the child walk on the heels and toes gives a gross assessment of motor strength, and having the child run may reveal an increase in muscle tone or ataxia. There is an increased incidence of scoliosis in patients with neuromuscular disorders (3, 4).
Inspection of the skin should be performed for evidence of skin rashes or other abnormalities. Typical facies of the patient with spinal muscular atrophy and congenital myotonic dystrophy should become familiar to orthopaedic surgeons. The tongue should be examined to detect evidence of fasciculation suggestive of anterior horn cell diseases. Excessive drooling is common in both cerebral palsy and congenital myotonic dystrophy. In the latter, nasal speech may also be present. A thorough ophthalmologic examination is necessary in order to elicit external ophthalmoplegia or retinitis pigmentosa. In myotonic dystrophy, cataracts may develop during adolescence.
Muscle testing should be carefully performed. Generally, myopathic disorders selectively affect proximal limb muscles before affecting distal muscles. Early in the disease process, the muscles demonstrate proportionally greater weakness than
would be expected from the degree of atrophy. The converse is true in neuropathies.
would be expected from the degree of atrophy. The converse is true in neuropathies.
A careful neurologic evaluation usually completes the musculoskeletal examination. Sensory responses must be checked individually and recorded. Decreased vibratory sensation may be present in HMSNs such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. In spinal muscular atrophy, the deep-tendon reflexes may be absent, but in cerebral palsy, they are increased. A positive Babinski sign confirms upper motor neuron disease. Abnormalities in the Romberg test and rapid alternating movements may indicate cerebellar involvement. Mental function evaluation may be necessary, because organic mental deterioration may be part of some neurologic syndromes. In many cases, the assistance of a pediatric neurologist can be invaluable in performing a careful neurologic and mental evaluation, because minor subtleties may offer clues to diagnosis.
DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES
Appropriate diagnostic studies are imperative for the accurate diagnosis of myopathic and neuropathic disorders (5, 6). These can be divided into hematologic studies, electromyography (EMG) with nerve conduction studies and needle electrode exam, muscle biopsy, and nerve biopsy. Molecular diagnostic studies have become available for many of these disorders, including Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies, myotonic dystrophy, the hereditary sensory motor neuropathies, and spinal muscular atrophy.
Hematologic Studies.
The measurement of serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) is the most sensitive test for demonstrating abnormalities of striated muscle function. The level of elevation parallels the rate and amount of muscle necrosis and decreases with time as the muscle is replaced by fat and fibrous tissue. The highest CPK levels are typically seen in the earliest stages of Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy, in which increases of 20 to 200 times the normal values may be found (6). The level of elevation of CPK does not correlate with the severity or rate of progression of the disorder. The highest levels are usually found in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Umbilical cord blood CPK levels should be obtained in all male infants who are suspected of having this disorder (7). Birth trauma may elevate the CPK in umbilical cord blood, but in the healthy child, this elevation disappears promptly, whereas the enzyme level remains elevated in muscular dystrophy. Serum CPK may be mildly or moderately elevated in other dystrophic disorders, such as facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy and Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. It is also mildly elevated in female carriers of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, although they are asymptomatic. In congenital myopathies and peripheral neuropathies, the CPK levels are usually normal or only mildly elevated. In other neuromuscular disorders that do not directly affect striated muscle, the CPK levels are normal. Serum enzymes, such as aldolase and serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), are also important in the study of striated muscle function. Aldolase levels correlate well with the CPK levels.
Electromyography.
EMG can differentiate between a myopathic and a neuropathic process but is rarely helpful in establishing a definitive diagnosis. Characteristics of neuropathic disorders include the presence of fibrillation potentials, increased insertional activity, and high-amplitude, increased-duration motor unit potentials (6). The fibrillation potential represents denervated individual muscle fibers firing spontaneously.
The EMG in myopathy is characterized by low-voltage, short-duration polyphasic motor unit potentials (6). Myopathies rarely demonstrate EMG changes characteristic of a neuropathy, although in an inflammatory muscle disease with significant muscle breakdown, there may be prominent fibrillations. The use of an experienced electromyographer is imperative in the accurate performance of the test and interpretation of EMG data.
Nerve Conduction Studies.
Nerve conduction studies are important in the establishment of the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy in children. Nerve conduction velocities are normal in children with anterior horn cell diseases, nerve root diseases, and myopathies. The normal value in the child older than 5 years is 45 to 65 m per second. In infants and younger children, the velocity is lower because myelination is incomplete.
Motor conduction velocity may be slowed in HMSN (e.g., Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease) before clinical deficits are present. The nerve conduction studies can help determine whether the neuropathy involves an isolated nerve or is a disseminated process.
Muscle Biopsy.
Historically, muscle biopsy has been the most important test in determining the diagnosis of a neuromuscular disorder. More recently, molecular genetic testing has become equally, if not more, important. Muscle biopsy material is usually examined by routine histology, special histochemical stains, and electron microscopy. The criterion for selecting the muscle for biopsy is clinical evidence of muscle weakness. Muscles that are involved but are still functioning are selected in chronic diseases, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, because they demonstrate the greatest diagnostic changes. A more severely involved muscle may be chosen in an acute illness because the process has not had sufficient time to progress to extensive destruction. In patients who have proximal lower extremity muscle weakness, biopsy of the vastus lateralis is performed, whereas in those with distal weakness, a biopsy of the gastrocnemius is performed. Biopsy of the deltoid, biceps, or triceps is performed for shoulder girdle or proximal upper extremity weakness.
Muscle biopsies can be performed as an open procedure (8) or by percutaneous needle (9). The biopsies are obtained under general anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, regional nerve block, or a field block surrounding the area of incision. It is important that local anesthetic not be infiltrated into the biopsied muscle, because this may alter the morphology of the muscle. The vastus
lateralis is the most common muscle chosen. A 4-cm incision is made and the underlying fascia is incised longitudinally. The muscle is directly visualized in order to avoid including normal fibrous septae in the specimens. Muscle clamps are used for obtaining three specimens. The clamps are oriented in the direction of the muscle fibers. A 2- to 3-mm piece of muscle is grasped in each end of the clamp. The muscle is cut at the outside edge of each clamp and a cylinder of muscle is excised. The use of a muscle clamp helps keep the muscle at its resting length and minimizes artifact. One specimen is quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen (-160°C) to prevent loss of soluble enzymes. This specimen is used for light microscopy with a variety of special preparations. The other specimens are used for routine histology and electron microscopy. The wound is subsequently closed in layers. Electrocautery may be used during the closure. If it is used before the biopsy, it may inadvertently damage the specimens and alter the morphology.
lateralis is the most common muscle chosen. A 4-cm incision is made and the underlying fascia is incised longitudinally. The muscle is directly visualized in order to avoid including normal fibrous septae in the specimens. Muscle clamps are used for obtaining three specimens. The clamps are oriented in the direction of the muscle fibers. A 2- to 3-mm piece of muscle is grasped in each end of the clamp. The muscle is cut at the outside edge of each clamp and a cylinder of muscle is excised. The use of a muscle clamp helps keep the muscle at its resting length and minimizes artifact. One specimen is quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen (-160°C) to prevent loss of soluble enzymes. This specimen is used for light microscopy with a variety of special preparations. The other specimens are used for routine histology and electron microscopy. The wound is subsequently closed in layers. Electrocautery may be used during the closure. If it is used before the biopsy, it may inadvertently damage the specimens and alter the morphology.
Nerve Biopsy.
Occasionally, biopsy of a peripheral nerve is helpful in demyelinating disorders. Usually, the sural nerve is selected for biopsy because of its distal location and lack of autogenous zone of innervation. The patient notices no sensory change or only a mild sensory diminution after excision of the 3-to 4-cm segment of the nerve. Hurley et al. (8) reported a single incision for combined muscle and sural nerve biopsy. An incision over the posterolateral aspect of the calf allows access to the nerve and either the soleus or the peroneal muscle. This avoids the necessity for making two incisions. This technique was demonstrated to be useful in disorders in which both a muscle and a nerve biopsy may be necessary for arriving at a diagnosis.
Other Studies.
Other studies that may be helpful in establishing the diagnosis of a neuromuscular disorder include electrocardiogram (ECG), pulmonary function studies, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ophthalmologic evaluation, amniocentesis, and pediatric neurology evaluation.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Friedreich ataxia, and myotonic dystrophy demonstrate ECG abnormalities. Duchenne muscular dystrophy is frequently associated with mitral valve prolapse secondary to papillary muscle involvement (10, 11). Arrhythmias under anesthesia have been reported with both Duchenne and Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophies (12, 13).
Pulmonary function studies demonstrate involvement of respiratory muscles, but they do not establish the diagnosis. If respiratory muscle involvement is present, the rate of deterioration can be followed up with periodic studies. This is important if surgery is contemplated in children or adolescents with muscular dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, or Friedreich ataxia. The forced vital capacity (FVC) is the most important study after arterial blood gas measurements (14).
MRI has been demonstrated to distinguish muscles affected by neuropathic disorders from those affected by myopathic disorders (15). Imaging estimates of the disease severity by degree of muscle involvement correlate well with clinical staging. MRI may also be important in selecting appropriate muscles for biopsy.
Ophthalmologic evaluation may demonstrate subtle or more obvious ocular changes associated with specific disorders.
GENETIC AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY STUDIES
Genetic research through molecular biologic techniques has tremendously enhanced our understanding of the genetic aspects of many of these disorders (16, 17). The determination of the exact location of chromosomal and gene defects has led to the possibility of genetic engineering being used to correct these disorders. Unfortunately, genetic testing is quite costly, and for many disorders, such testing is not commercially available. Also, a negative test does not necessarily exclude certain disorders. For this reason, the decision to carry out genetic testing should be made only by a neuromuscular specialist or geneticist. In each of the various disorders, the current status of genetic and molecular biology research is discussed in this chapter.
MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
The muscular dystrophies are a group of noninflammatory inherited disorders with a progressive degeneration and weakness of skeletal muscle that has no apparent cause in the peripheral or the central nervous system (CNS). These have been categorized according to clinical distribution, severity of muscle weakness, and pattern of genetic inheritance (Table 16-1). An accurate diagnosis is important, both for prognosis and management of the individual patient and for identification of genetic factors that may be crucial in planning for subsequent children by the family involved.
SEX-LINKED MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is the most common form of muscular dystrophy (18).
TABLE 16-1 Classification of Muscular — Dystrophies | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transmission is by an X-linked recessive trait. A single gene defect is found in the short arm of the × chromosome. The disease is characterized by its occurrence exclusively in the male sex, except for rare cases associated with Turner syndrome. In this rare event, the XO karyotype who carries the defective gene may demonstrate the phenotype found in male patients with the disorder (6). This disorder is associated with a high mutation rate, and a positive family history is present in approximately 65% of the cases. Duchenne muscular dystrophy occurs in approximately 1 in 3500 live male births, with about one-third of the children involved having acquired the disease because of a new mutation.
Becker muscular dystrophy is a similar, but less common and less severe form of muscular dystrophy. It occurs in approximately 1 in 30,000 live male births, becomes apparent later in childhood, and has a more protracted and variable course than Duchenne muscular dystrophy. This disorder is discussed later but is mentioned here because of the similar inheritance pattern and molecular biology abnormality.
Clinical Features.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is generally clinically evident when the child is at an age of between 3 and 6 years. Earlier onset may also occur. The family may have observed that the child’s ability to achieve independent ambulation was delayed or that he has become a toe walker. Children at the age of 3 years or older may demonstrate frequent episodes of tripping and falling, in addition to difficulty in activities requiring reciprocal motion, such as running or climbing stairs. Inability to hop and jump normally is commonly present.
In Duchenne muscular dystrophy, there is progressive weakness in the proximal muscle groups that descend symmetrically in both lower extremities, particularly the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, quadriceps, and tibialis anterior muscles. The abdominal muscles are involved. Involvement of the shoulder girdle muscles (i.e., trapezius, deltoid, and pectoralis major muscles) and lower facial muscles occurs later. Pseudohypertrophy of the calf muscles caused by the accumulation of fat is common but not invariably present. Most patients have cardiac involvement, most commonly a sinus tachycardia and right ventricular hypertrophy. Life-threatening dysrhythmia or heart failure ultimately develops in approximately 10% of patients. Many also have a static encephalopathy, with mild or moderate mental retardation (19). Death from pulmonary failure and occasionally from cardiac failure occurs during the second or third decades of life.
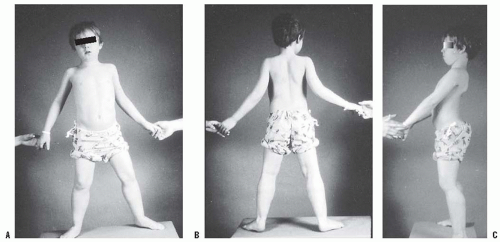
During gait the child’s cadence is slow, and he or she develops compensatory changes in gait and stance as weakness progresses. Sutherland et al. (20, 21) documented disease progression by measuring the gait variables of cadence, swing phase, ankle dorsiflexion, and anterior pelvic tilt. The hip extensors, primarily the gluteus maximus, are the first muscle group to be involved. Initially, the patient compensates by carrying the head and shoulders behind the pelvis, maintaining the weight line posterior to the hip joint and center of gravity (Fig. 16-1). This produces an anterior pelvic tilt and increases
lumbar lordosis. Cadence and swing-phase ankle dorsiflexion decrease, and the patient develops a waddling, wide-based gait with shoulder sway to compensate for gluteus medius weakness. Muscle weakness requires that the force line remains behind the hip joint and in front of the knee joint throughout single limb support (20, 21 and 22), and hip abductors and quadriceps muscles force the patient to circumduct during the swing phase of gait while at the same time shifting the weight directly over the hip joint. The generalized pelvic weakness requires considerable forward motion to be generated by the spine for the patient to advance. Ankle plantar flexion becomes fixed, and the stance phase is reduced to the forefoot, resulting in even more difficulty with balance and cadence. Foot inversion develops as peroneal strength diminishes. The tibialis posterior muscle, which is one of the last muscles to be involved, is responsible for the inversion or varus deformity of the foot.
lumbar lordosis. Cadence and swing-phase ankle dorsiflexion decrease, and the patient develops a waddling, wide-based gait with shoulder sway to compensate for gluteus medius weakness. Muscle weakness requires that the force line remains behind the hip joint and in front of the knee joint throughout single limb support (20, 21 and 22), and hip abductors and quadriceps muscles force the patient to circumduct during the swing phase of gait while at the same time shifting the weight directly over the hip joint. The generalized pelvic weakness requires considerable forward motion to be generated by the spine for the patient to advance. Ankle plantar flexion becomes fixed, and the stance phase is reduced to the forefoot, resulting in even more difficulty with balance and cadence. Foot inversion develops as peroneal strength diminishes. The tibialis posterior muscle, which is one of the last muscles to be involved, is responsible for the inversion or varus deformity of the foot.
Weakness in the shoulder girdle, which occurs 3 to 5 years later, precludes the use of crutches to aid in ambulation. It also makes it difficult to lift the patient from under the arms. This tendency for the child to slip a truncal grasp has been termed Meyeron sign. As the weakness in the upper extremities increases, the child becomes unable to move his or her arms. Although the hands retain strength longer than the arms, use of the hands is limited because of weakness of the arms.
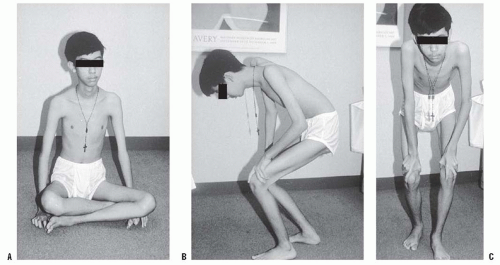
Clinical diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy is established by physical examination, including gait and specific muscle weakness, and by the absence of sensory deficits. The upper extremity and knee deep-tendon reflexes are lost early in the disease, whereas the ankle reflexes remain positive until the terminal phase. A valuable clinical sign is the Gower sign. The patient is placed prone or in the sitting position on the floor and asked to rise. This is usually difficult, and the patient may require the use of a chair for assistance. The patient is then asked to use his or her hands to grasp the lower legs and force the knees into extension. The patient then walks his or her hands up the lower extremities to compensate for the weakness in the quadriceps and gluteus maximus. This sign may also be found in congenital myopathies and spinal muscular atrophy. The contracture of the iliotibial band can be measured by the Ober test. To perform this test, the child is placed on his or her side with both hips flexed. The superior leg is then abducted and extended and allowed to fall into adduction. The degree of abduction contracture can be measured by the number of degrees the leg lacks in coming to the neutral position. Tendo-Achilles contractures also occur. Contracture of the tendo-Achilles and the iliotibial band are the most consistent deformities noted during the physical examination.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy progresses slowly but continuously. A rapid deterioration may be noted after immobilization in bed, even for short periods after respiratory infections or, perhaps, extremity fractures. Every effort should be made to maintain a daily ambulatory program. In the absence of treatment, children are usually unable to ambulate effectively by the age of 10 years (5, 23, 24 and 25). The chief cause is loss of strength in the hip extensors and ankle dorsiflexors (26). These two factors can be used as a guide to predict when ambulation will cease. With loss of standing ability, the child becomes wheelchair dependent. This results in a loss of the accentuated lumbar lordosis that protected the child from kyphoscoliosis (27). As a consequence, most patients subsequently develop a progressive spinal deformity.
Myocardial deterioration is also a constant finding. ECG changes are present in more than 90% of children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The average intelligence quotient of these patients has been shown to be approximately 80 (19).
Hematologic Studies.
The serum CPK is markedly elevated in the early stages of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. This may be 200 to 300 times the normal value, but decreases as the disease progresses and muscle mass is reduced. CPK levels are also elevated in female carriers of the disease (two to three times the normal value for women and girls), although not to the same extent as in affected boys. There is an 80% consistency in the results when the CPK test is repeated at three consecutive monthly intervals (28). Aldolase and SGOT levels may also be elevated, but the elevations are not unique to striated muscle disease.
Electromyography.
Although EMG will support the diagnosis of a myopathy, if the clinical findings and CPK are both suggestive of a muscular dystrophy, this test is typically not necessary. EMG shows characteristic myopathic changes with reduced amplitude, short duration, and polyphasic motor action potentials (6).
Muscle Biopsy.
The muscle biopsy specimen reveals degeneration with subsequent loss of fiber, variation in fiber size, proliferation of connective tissue and, subsequently, of adipose tissue as well (6). Increased cellularity is present, with occasional internal migration of the sarcolemmal nuclei. Histochemical testing reveals loss of clear-cut subdivisions of fiber types, especially with adenosine triphosphatase reaction, and a tendency toward type I fiber predominance. In the past, this was the diagnostic procedure of choice. However, the standard today is to first obtain blood samples for DNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for dystrophinopathies. If this is positive, there is no need for a muscle biopsy. If PCR testing is negative, then muscle biopsy is indicated for arriving at a definitive diagnosis.
Genetic and Molecular Biology Studies.
A single gene defect in the short arm of the × chromosome has been identified as being responsible for both Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies (16, 17, 29, 30). The status of genetic and molecular biology in Duchenne muscular dystrophy has been summarized by Shapiro and Specht (6). The gene is located at the Xp21.2 region and spans 2 million base pairs (31, 32). It includes 65 exons (i.e., coding regions) and encodes the 400-kDa protein dystrophin. The large size of the gene correlates with the high rate of spontaneous mutation. Dystrophin is a component of cell membrane cytoskeleton and represents 0.01% of skeletal muscle protein. Its distribution within
skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle and within the brain correlates well with the clinical features in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. A structural role for the dystrophin protein is suggested by studies that demonstrate concentration of the protein in a lattice organization in the cytoplasmic membrane of skeletal muscle fibers (33, 34). Demonstrable mutations, deletions, or duplications of dystrophin are found in 70% to 80% of the affected male patients (31, 32, 35, 36). The reading frame hypothesis distinguishes the mutations that correlate with the more severe Duchenne muscular dystrophy from those that correlate with the less severe Becker muscular dystrophy. Mutations that disrupt the translational reading frame or the promoter (i.e., the specific DNA sequence that signals where RNA synthesis should begin) result in a presumably unstable protein, and this correlates with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In contrast, mutations that do not disrupt the translational reading frame or the promoter have a lower molecular weight and semifunctional dystrophin. This correlates with the less severe Becker muscular dystrophy (31, 37).
skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle and within the brain correlates well with the clinical features in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. A structural role for the dystrophin protein is suggested by studies that demonstrate concentration of the protein in a lattice organization in the cytoplasmic membrane of skeletal muscle fibers (33, 34). Demonstrable mutations, deletions, or duplications of dystrophin are found in 70% to 80% of the affected male patients (31, 32, 35, 36). The reading frame hypothesis distinguishes the mutations that correlate with the more severe Duchenne muscular dystrophy from those that correlate with the less severe Becker muscular dystrophy. Mutations that disrupt the translational reading frame or the promoter (i.e., the specific DNA sequence that signals where RNA synthesis should begin) result in a presumably unstable protein, and this correlates with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In contrast, mutations that do not disrupt the translational reading frame or the promoter have a lower molecular weight and semifunctional dystrophin. This correlates with the less severe Becker muscular dystrophy (31, 37).
Dystrophin testing (by dystrophin immunoblotting), DNA mutation analysis (by PCR or DNA Southern blot analysis), or both, provide methods of differentiating between Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies on the one hand, and other initially similar disorders [such as dermatomyositis, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD), Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, and congenital muscular dystrophy] on the other (36, 38, 39). In the latter disorders, the dystrophin is normal. In patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, there is a complete absence of dystrophin, whereas in Becker muscular dystrophy, dystrophin is present, but is altered in size, decreased in amount, or both. Nicholson et al. (40) reported a positive relation between the amount of dystrophin and the age at loss of independent ambulation in 30 patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and in 6 patients with Becker muscular dystrophy. The researchers found that even low concentrations of dystrophin in Duchenne muscular dystrophy may have functional significance and may explain the variability of age at which ambulation ceases. The presence of partially functional dystrophin protein is sufficient to minimize the phenotypic expression, leading to the milder disorder of Becker muscular dystrophy (31, 35, 38). The same tests can be used to improve detection of female carriers (36, 39). On the basis of smaller-than-normal dystrophin protein, two atypical forms of Becker muscular dystrophy have been recognized. These are myalgia without weakness in male patients (similar to metabolic myopathy), and cardiomyopathy with little or no weakness in male patients (41).
Research studies are investigating the possibility of dystrophin replacement in diseased muscles. This involves the implantation of myoblasts, or muscle precursor cells, into the muscles of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (42). This has been successful in producing dystrophin in the murine mdx model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (43). Unfortunately, the results in human male patients have been disappointing (44, 45, 46, 47 and 48). Perhaps the most promising evolving treatment for Duchenne’s is the genetic technique of “exon skipping” or splice modulation, where there is modulation of dystrophin premessenger RNA splicing, enabling functional dystrophin protein to be produced (49).
Medication Treatments.
A number of medications have been tried to improve strength and function and prolong time to disability in Duchenne dystrophy. Steroids, such as prednisone and deflazacort, have been shown to preserve or improve strength, prolong ambulation, and slow the progression of scoliosis (50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58 and 59). Thus, this has become a mainstay of therapy in many neuromuscular clinics. Unfortunately, the side effects-weight gain, osteoporosis with vertebral fractures, and myopathy-limit their usefulness (37, 52, 53 and 54, 56, 60). Alternate day therapy, or pulse therapy with steroid treatment on the first 10 days of each month, may limit the side effects, slow deterioration of muscle function and not impact on patient quality of life (61, 62). Although prednisone and deflazacort appear to be equally efficacious, deflazacort appears to cause fewer side effects, especially related to weight gain (63). Creatinine supplementation has been evaluated and demonstrated an increase in handgrip strength and fat-free mass, but no improvement in functional tasks or activities of daily living (64). It did demonstrate a significant improvement in resistance to fatigue (65). Perhaps more promising is treatment with extended release albuterol, which has demonstrated increase in lean body mass, decrease in fat mass, and improved functional measures in short-term treatment of dystrophinopathy patients (66, 67). Azathioprine has also been evaluated in Duchenne muscular dystrophy but has not shown beneficial effects (68). Aminoglycoside therapy with intravenous gentamicin administration has been studied in two trials (69, 70). A decrease in serum CPK levels was demonstrated, but there was no effect on muscle strength.
Gene therapy for muscular dystrophies has proven difficult, primarily because of the size of the viral vectors and also because of the complications of immune reactions that may occur. Therefore, gene therapy is still very much in the early investigational stages. This treatment has been reviewed in detail by Chamberlain (71). Dystrophin delivery to muscle has been attempted with four primary vectors: adenovirus, retroviruses, adeno-associated viruses, and plasmids. Complications of this technology included triggering of a cellular immune response, poor integration of the vector into the host gene, and lack of a sustained response, to name only a few (72). Stem cell therapy may be a promising intervention for the dystrophinopathies. In the mdx mouse, bone marrow transplantation and injection of normal muscle-derived stem cells led to partial restoration of dystrophin expression (73).
Treatment.
Orthopaedic problems in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy include decreasing ambulatory ability, softtissue contractures, and spinal deformity (5, 6, 18, 74). The goals of treatment should be to improve or maintain the functional capacity of the affected child or adolescent.
The treatment modalities in Duchenne muscular dystrophy include medical therapy, physical therapy, functional
testing, use of orthoses, fracture management, surgery, use of wheelchair, cardiopulmonary management, and genetic and psychological counseling.
testing, use of orthoses, fracture management, surgery, use of wheelchair, cardiopulmonary management, and genetic and psychological counseling.
Medical Therapy.
Recently, the use of steroids has shown promise in preserving strength, prolonging ambulation, and slowing the progression of scoliosis. However, this therapy is not in wide use because of the attendant complications as described in the earlier text.
Physical Therapy.
Physical therapy is directed toward prolongation of functional muscle strength, prevention or correction of contractures by passive stretching, gait training with orthoses and transfer techniques, ongoing assessment of muscle strength and functional capacity, and inputs regarding wheelchair and equipment measurements.
After the diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy has been established and before muscle strength has deteriorated, a program of maximum-resistance exercises should be commenced, to be performed several times a day. This may help preserve strength and delay the onset of soft-tissue contractures. Physical therapy is more effective in preventing or delaying contractures than in correcting them. Contractures develop in the ambulatory patient because the progression of muscle weakness results in the development of adaptive posturing to maintain lower extremity joint stability. A home exercise program can be effective in minimizing hip and ankle soft-tissue contractures. Exercises should be performed twice a day on a firm surface, and should include stretching of the tensor fascia lata, hamstrings, knee flexors, and ankle plantar flexors. Occasionally, serial casting may be useful in correcting existing deformities before physical therapy. Kneeflexion contractures of <30 degrees may benefit from serial or wedge casting. This enhances the use of knee-ankle-foot orthoses (KAFOs). Unless orthoses are used after casting and in conjunction with physical therapy, these contractures rapidly recur.
Functional Testing.
Functional testing predominantly involves periodic muscle testing. Muscle strength is tested by measurement of the active range of motion of a joint against gravity. This type of testing allows assessment of the rate of deterioration as well as the functional capacity of the individual.
Orthoses.
Lightweight molded plastic ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs) or KAFOs are used in independently ambulatory patients when gait becomes precarious, when early soft-tissue contractures of the knees and ankle are developing, and after surgical correction of these deformities (75, 76, 77 and 78). AFOs can also be helpful in improving tendo-Achilles contractures, especially when worn both during the day and at night (79). KAFOs are usually supplemented with a walker because of the excessive weight on the orthoses and the risk of falling. Important prescription components include partial ischial weight-bearing support, posterior thigh cuff, and a spring-loaded, drop-lock knee joint with an ankle joint set at a right angle. Ambulation may be extended for up to 3 years by the combined use of surgery and orthoses. The maintenance of a straight lower extremity also enables the nonwalking patient to stand with support, and thereby assists in transfers.
Spinal orthoses are usually of no value in progressive spinal deformities, but wheelchair-bound patients, especially those with severe cardiopulmonary compromise and severe scoliosis, may benefit from the use of a custom wheelchair, a thoracic suspension orthosis, or a custom-made thoracic-lumbar spinal orthosis (TLSO). A mobile arm-support orthosis attached to the wheelchair may help the patient in performing personal hygiene tasks and self-feeding (80).
Fracture Management.
Fractures of the lower extremities occur frequently in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. This is due to decreased bone mineral density from disuse osteoporosis, steroid induced osteoporosis, or both (81, 82, 83 and 84). Fractures can result in a permanent loss of function (81, 83, 84). This occurs predominantly after ambulation has ceased and the child is wheelchair bound. These fractures are best treated by closed reduction and cast immobilization. Occasionally, open reduction and internal fixation may be needed. In children who are still ambulatory, it is important that they be placed on a program of early mobilization to allow weight bearing. This may require the use of an electrically powered circle bed. Once early healing is present, the child can be returned to the KAFO to decrease weight and enhance mobility.
Surgery.
Contractures of the lower extremities and progressive weakness impair ambulation. Surgery is indicated when independent ambulation becomes precarious and when contractures are painful or interfere with essential daily activities. The major contractures that are amenable to surgical intervention include equinus and equinovarus contractures of the ankle and foot, knee-flexion contractures, and hip-flexion and abduction contractures. In thin individuals, these contractures may be released by percutaneous techniques (74, 85). For ambulatory patients, orthotic measurements should be obtained before surgery. This allows the orthoses to be applied shortly after surgery to assist in rapid restoration of ambulation. Correction of contractures and the use of orthoses can prolong effective ambulation and assisted standing ability by a period of 1 to 3 years (5, 18, 22, 75, 76, 77 and 78, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89 and 90). Hsu and Furumasu (22) reported a mean prolongation of walking of 3.3 years in 24 patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy ranging in age from 8 to 12 years at the time of surgery. It is usually not possible to restore functional ambulation once the patient has been unable to walk for more than 3 to 6 months (75). Each patient must be individually assessed to determine the functional needs and the best procedures. Common contraindications for correction of lower extremity contractures include obesity, rapidly progressive muscle weakness, or poor motivation (those who prefer to use a wheelchair rather than attempt ambulation) (6).
Foot and Ankle.
Equinus contractures occur first, followed by equinovarus contractures. This is because of a combination of tendo-Achilles contracture and muscle imbalance induced by the stronger tibialis posterior muscle. This latter muscle retains
good function despite the progression of muscle weakness in other areas. These equinovarus deformities can be managed by a combination of tendo-Achilles lengthening by means of percutaneous open tenotomy (18, 74, 77, 78, 86, 87) with or without resection, or by Vulpius (5) or open Z-lengthening (89), and tibialis posterior lengthening, tenotomy, or transfer through the interosseous membrane to the dorsum of the foot (5, 6, 18, 25, 74, 76, 77 and 78, 86, 87, 91, 92 and 93). Scher and Mubarak have also recommended toe flexor tenotomies (94). Tibialis posterior transfer prevents recurrence of equinovarus deformities and maintains active dorsiflexion of the foot. Some orthopaedists, however, have questioned the necessity of a transfer, because it is a more extensive procedure. They prefer tenotomy, recession, or lengthening (74, 76, 86). Postoperative gait analysis has shown that the transferred tibialis posterior muscle is electrically silent (95). Greene (91) has reported that tibialis posterior myotendinous junction recession in six patients (12 ft) resulted in an increased recurrence rate when compared with transfer in nine patients (18 ft), making the former a less desirable procedure. Percutaneous tendo-Achilles lengthening under local anesthesia is usually reserved for nonambulatory patients, who typically have an equinus deformity and cannot wear shoes. The nonambulatory patient with a moderately severe equinovarus deformity may require open tenotomies of the tendo-Achilles, the tibialis posterior, and long toe flexors. Severe equinovarus contractures have been managed effectively by talectomy. Leitch et al. (96) recently studied 88 Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients and found no difference in the long-term results of those treated surgically and those who did not.
good function despite the progression of muscle weakness in other areas. These equinovarus deformities can be managed by a combination of tendo-Achilles lengthening by means of percutaneous open tenotomy (18, 74, 77, 78, 86, 87) with or without resection, or by Vulpius (5) or open Z-lengthening (89), and tibialis posterior lengthening, tenotomy, or transfer through the interosseous membrane to the dorsum of the foot (5, 6, 18, 25, 74, 76, 77 and 78, 86, 87, 91, 92 and 93). Scher and Mubarak have also recommended toe flexor tenotomies (94). Tibialis posterior transfer prevents recurrence of equinovarus deformities and maintains active dorsiflexion of the foot. Some orthopaedists, however, have questioned the necessity of a transfer, because it is a more extensive procedure. They prefer tenotomy, recession, or lengthening (74, 76, 86). Postoperative gait analysis has shown that the transferred tibialis posterior muscle is electrically silent (95). Greene (91) has reported that tibialis posterior myotendinous junction recession in six patients (12 ft) resulted in an increased recurrence rate when compared with transfer in nine patients (18 ft), making the former a less desirable procedure. Percutaneous tendo-Achilles lengthening under local anesthesia is usually reserved for nonambulatory patients, who typically have an equinus deformity and cannot wear shoes. The nonambulatory patient with a moderately severe equinovarus deformity may require open tenotomies of the tendo-Achilles, the tibialis posterior, and long toe flexors. Severe equinovarus contractures have been managed effectively by talectomy. Leitch et al. (96) recently studied 88 Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients and found no difference in the long-term results of those treated surgically and those who did not.
Knee.
Knee-flexion contractures coexist with hip-flexion contractures and develop rapidly when the patient is wheelchair bound. These contractures limit proper positioning in bed and may lead to the development of hamstring spasm, causing considerable discomfort when the patient attempts to transfer. A Yount procedure (97) (release of the distal aspect of the tensor fascia lata and iliotibial band) is the most common procedure used in correcting knee-flexion contractures (18, 74, 76, 77 and 78). Hamstring tenotomies, recession or Vulpius-type lengthening, and formal Z-lengthening may also be necessary. These procedures enhance quadriceps power and function and also relieve symptoms. Postoperatively, KAFOs are necessary in order to prevent recurrence.
Hip.
Hip-flexion and -abduction contractures increase lumbar lordosis and interfere with the ability to stand and to lie comfortably supine. Patients with hip-flexion contractures may experience low back pain. Correction of flexion contractures involves release of the tight anterior muscles, including the sartorius, rectus femoris, and tensor fascia femoris (6, 18, 74). Abduction contractures are improved by release of the tensor fasciae lata proximally with use of the Ober procedure (98), modified Soutter release, the Yount procedure distally (97), or by complete resection of the entire iliotibial band.
Chan et al. (99) studied 54 patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and found that 15 had unilateral subluxation, 1 had bilateral subluxation, and 3 had a unilateral dislocation. They recommended serial pelvic radiographs in patients with this disorder. They also felt that any pelvic obliquity should be corrected at the time of spinal stabilization.
Upper Extremity.
Upper extremity contractures are common in adolescents with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, but usually do not require treatment. These contractures include shoulder adduction, elbow flexion, forearm pronation, wrist flexion, metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joint flexion, and others. These usually do not preclude the use of wheelchairs. Muscle weakness is the most devastating aspect of upper extremity involvement. Wagner et al. (100) demonstrated wrist ulnar deviation and flexion contractures in addition to contractures of the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the fingers in adolescents with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. These contractures produce boutonniere and swan neck deformities and hyperextension of the distal interphalangeal joints. The treatment of upper extremity contractures involves physical therapy with daily passive range-of-motion exercises. When passive wrist dorsiflexion is limited to neutral, a nighttime extension orthosis may be helpful. Surgery is rarely indicated for these contractures.
Spinal Deformity.
Approximately 95% of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy develop progressive scoliosis (27, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107 and 108). This typically begins to occur when ambulation ceases, and it is rapidly progressive. Approximately 25% of older ambulating patients, however, have mild scoliosis (23, 109). Prolongation of ambulation by appropriate softtissue releases of the lower extremity contractures, thereby maintaining accentuated lumbar lordosis, can delay the onset of scoliosis (88). The curves are usually thoracolumbar, associated with kyphosis, and lead to pelvic obliquity. Scoliosis cannot be controlled by orthoses or wheelchair seating systems (102, 110, 111, 112, 113 and 114). Although orthotic management may slow curve progression, it does not slow the systemic manifestations of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (e.g., decreasing pulmonary function and cardiomyopathy). These may complicate spinal surgery at a later time. As the scoliosis progresses, it can result in a loss of sitting balance, produce abnormal pressure, and occasionally cause the patient to become bedridden. Heller et al. (114) reported improved sitting support with an orthosis in 28 patients who either refused surgery or were considered to be inoperable.
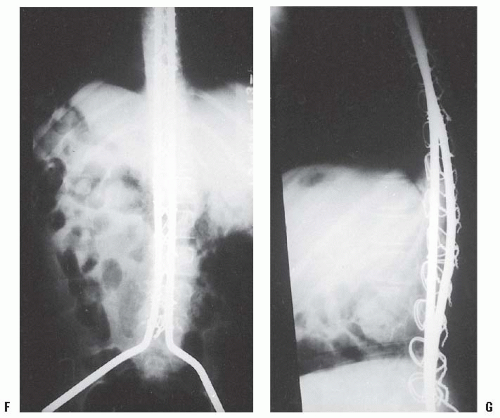
Surgical correction of scoliosis both improves sitting balance and minimizes pelvic obliquity (102, 109, 113, 114, 115 and 116). It is usually recommended that a posterior spinal fusion be performed once the curve is >20 degrees (102, 109, 112, 113 and 114, 117, 118 and 119). Fusion extends from the upper thoracic spine (T2 or T4) to L5 or the pelvis. It is important to center the patient’s head over the pelvis in both the coronal and sagittal planes. This usually allows complete or almost complete correction of the deformity, maintains sitting balance, improves head control, and allows more independent hand function. Although autogenous bone grafting is used in most patients, there appears to be no difference in fusion rates when allograft
bone is used (120, 121, 122 and 123). Segmental spinal instrumentation techniques using Luque rod instrumentation are most commonly used (18, 74, 102, 109, 112, 116, 120, 121, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128 and 129) (Fig. 16-2). Other modern segmental instrumentation systems, can also be used (120, 121, 125, 130). The use of pedicle screws and iliac bolts can improve results (131, 132) (see Fig. 16-2). All of these techniques allow sufficient fixation so that postoperative immobilization is not necessary (Fig. 16-2). Fixation to the pelvis is achieved using the Galveston or other techniques (117, 120, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132 and 133).
bone is used (120, 121, 122 and 123). Segmental spinal instrumentation techniques using Luque rod instrumentation are most commonly used (18, 74, 102, 109, 112, 116, 120, 121, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128 and 129) (Fig. 16-2). Other modern segmental instrumentation systems, can also be used (120, 121, 125, 130). The use of pedicle screws and iliac bolts can improve results (131, 132) (see Fig. 16-2). All of these techniques allow sufficient fixation so that postoperative immobilization is not necessary (Fig. 16-2). Fixation to the pelvis is achieved using the Galveston or other techniques (117, 120, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132 and 133).
These techniques are thought to maintain better correction of pelvic obliquity. Some authors believe that fusion to L5 is sufficient, and that there will be no spinopelvic deformity throughout the remainder of the patient’s life (122, 134, 135 and 136). However, a postoperative spinopelvic deformity can occur and progress, and most authors recommend fusion to the pelvis (127, 129, 137). Mubarak et al. (133) recommend fusion to L5 if the curve is >20 degrees, the FVC is >40%, and the patient is using a wheelchair full time, except for occasional standing. If the patient’s curve is >40 degrees or if there is pelvic obliquity >10 degrees, then fusion to the sacropelvis is recommended. In severe deformities, vertebral osteotomies may be beneficial to improve postoperative correction (138).
Careful preoperative evaluation, including pulmonary function studies and cardiology consultation, is mandatory because of the associated pulmonary and cardiac abnormalities and the risk of malignant hyperthermia (2, 3, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143 and 144). Children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy have a decreased FVC, commencing at approximately the age of 10 years, because of weakness of the intercostal muscles and associated contractures. There is a linear decrease over time (14, 103, 106, 119, 139). Kurz et al. (14) observed a 4% decrease in FVC for each year of age or each 10 degrees of scoliosis. It stabilizes at approximately 25% of normal until death. The presence of severe scoliosis may increase the rate of decline in the FVC. Jenkins et al. (137) reported that when the FVC is 30% or less, there is an increased risk of postoperative complication such as pneumonia and respiratory failure. Smith et al. (105) found that most patients with curves of more than 35 degrees had FVC <40% of predicted normal values. They therefore recommend that spinal arthrodesis be considered for all patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy when they can no longer walk. Nevertheless, successful surgery can be performed in many patients with FVC as low as 20% of predicted normal valves (121). Marsh et al. (139) recently reported similar results in 17 patients with FVC >30% and 13 patients with FVC <30%. They concluded that spinal fusion could be offered to patients in the presence of a low FVC.
It is debatable whether spinal stabilization increases longevity, although it definitely increases the quality of the remaining life (102, 120, 140). In a study of 55 patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, of whom 32 underwent spinal fusion and 23 did not, Galasko et al. (102) found that FVC remained stable in the operated group for 36 months postoperatively and then fell slightly. In the nonoperated group, it progressively declined. The survival data showed that a significantly higher mortality rate was seen in the nonoperated group. This study indicated that spinal stabilization can increase survival for several years if it is done early, before significant progression has occurred. Velasco et al. (141) in 2007 showed that posterior spinal fusion in 56 Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients was associated with a significant decrease in the rate of respiratory decline compared with preoperative rates. Other studies, however, have shown that posterior spinal fusion has no effect on the steady decline in pulmonary function when compared with unoperated patients (118, 121, 145, 146 and 147). In addition to correction and stabilization of the spine, patients experience improved quality of life, as measured by ability to function, self-image, and cosmesis (118, 124, 125, 148). Parents also reported improvement in their ability to provide care to their child.
Complications are common during and following surgery (103, 112, 113 and 114, 118, 125, 134). These include excessive intraoperative blood loss, neurologic injury, cardiopulmonary compromise, postoperative infection, poor wound healing, curve progression, hardware problems, and late pseudarthrosis. Intraoperative blood loss can be minimized by early surgery and the use of hypotensive anesthesia (121). The increased intraoperative blood loss in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy appears to result from inadequate vasoconstriction caused by the lack of dystrophin in the smooth muscle (149). Malignant hyperthermia has been thought to be a potential complication. A recent systematic analysis by Gurnaney et al. (150) on patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Becker muscular dystrophy, and other types of muscular dystrophy did not find an increased risk for malignant hyperthermia compared to the general population. Succinylcholine administration was associated with life-threatening hyperkalemia and should be avoided in those patients; tranexamic acid and epsilon aminocaproic acid (amicar) can be beneficial in decreasing intraoperative and perioperative blood loss (151, 152).
The role of intraoperative spinal cord monitoring in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy is controversial. Noordeen et al. (149) reported that a 50% decrease in amplitude was suggestive of neurologic impairment.
Wheelchair.
A wheelchair is necessary for patients who are no longer capable of independent ambulation. This is typically a motorized wheelchair that allows the patient to be independent of parents or aides, especially while attending school. The wheelchair may be fitted with a balanced mobile arm orthosis for the purpose of facilitating personal hygiene and self-feeding (80).
Cardiopulmonary Management.
Respiratory failure in Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a constant threat and is the most common cause of death early in the third decade of life. Kurz et al. (14) found that the vital capacity peaks at the age when standing ceases, then declines rapidly thereafter. The development of scoliosis compounds the problems and leads to further diminution of the vital capacity (146). The complication rate in spinal surgery increases when the FVC is <30% of the normal value. Programs of vigorous respiratory therapy and the use of home negative-pressure and positive-pressure ventilators may allow patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy to survive into the third and fourth decades of life (153, 154, 155 and 156).
Cardiac failure may occur in the second decade of life. After initially responding to digitalis and diuretics, the involved cardiac muscle becomes flabby, and the patient goes into congestive heart failure. Myocardial infarction has been reported in boys as young as 10 years. There is no correlation between the severity of pulmonary dysfunction and cardiac function, or between age and cardiac function (157). The cardiomyopathy of Duchenne muscular dystrophy exists clinically as a separate entity.
Genetic and Psychological Counseling.
Proper diagnosis and early genetic counseling may help prevent the birth of additional male infants with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. It must be remembered that approximately 20% of families have already conceived and delivered a second affected male infant before the diagnosis is made in the first (78, 158). Genetic counseling with parents and family groups is important in the management of psychological problems arising when the genetic nature of the diagnosis becomes known.
Becker Muscular Dystrophy.
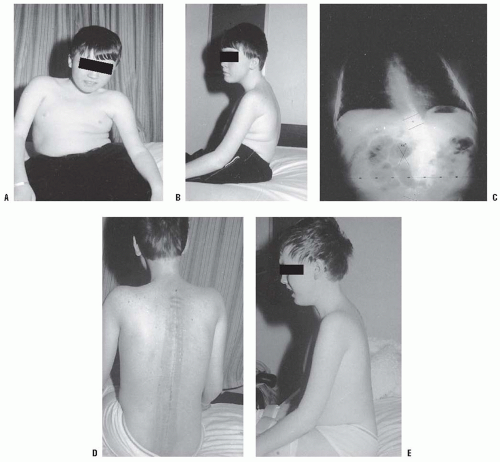
Becker muscular dys trophy is similar to Duchenne muscular dystrophy in clinical appearance and distribution of weakness, but it is less severe (159, 160). Onset is generally after the age of 7 years and the rate of progression is slower. The patients usually remain ambulatory until adolescence or the early adult years. The Gower maneuver may occur as the weakness progresses (Fig. 16-3). Pseudohypertrophy of the calf is common, and eventually equinus and cavus foot deformities develop (Fig. 16-4). Cardiac involvement is frequent. There may be a family history of atypical muscular dystrophy. Pulmonary problems are less severe and the patient’s life expectancy is greater.
Treatment.
The treatment of the musculoskeletal deformities associated with Becker muscular dystrophy is essentially the same as in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Steroid therapy (prednisone) has recently been shown to decrease serum creatine kinase levels and improve strength (161). Ankle and forefoot equinus occur commonly. Shapiro and Specht (6) have reported good outcome with the Vulpius tendo-Achilles lengthening in patients with equinus contractures. A tibialis posterior tendon transfer is performed if necessary. Forefoot equinus may require a plantar release and possibly a midfoot dorsal-wedge osteotomy for correction. The use of orthotics is also beneficial because the rate of progression is slower and the remaining muscle strength greater than in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The incidence of scoliosis is high, especially in those adolescents who have ceased walking. These patients require careful evaluation and periodic spinal radiographs. Posterior spinal fusion and segmental instrumentation, usually Luque, are useful for patients in whom there is progression (162).
Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy.
Emery Dreifuss muscular dystrophy is an uncommon sex-linked recessive disorder characterized by early contractures and cardiomyopathy (12). The typical phenotype is seen only in the male sex, although milder or partial phenotypes have been reported in female carriers (163, 164, 165 and 166). Affected boys show mild muscle weakness in the first 10 years of life and a tendency for toe walking. The Gower maneuver may be present in young children. The distinctive clinical criteria occur in late childhood or early adolescence. These include tendo-Achilles contractures, elbowflexion contractures, neck-extension contracture, tightness of the lumbar paravertebral muscles, and cardiac abnormalities involving brachycardia and first-degree, and eventually complete, heart block (165, 167). The muscle weakness is slowly progressive, but there may be some stabilization in adulthood.
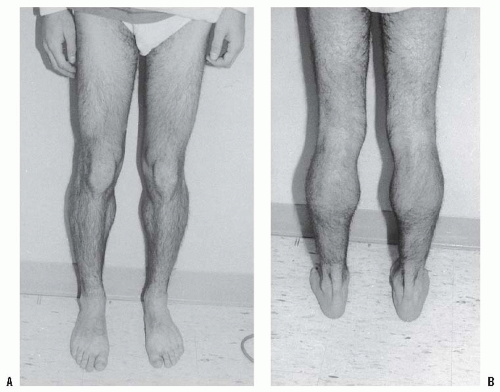 FIGURE 16-4. A: Pseudohypertrophy of the calves in an 18-year-old man with Becker muscular dystrophy. He is a brace-free ambulator. B: Posterior view. |
Most patients are able to ambulate into the fifth and sixth decades of life. Obesity and untreated equinus contractures can lead to the loss of ambulatory ability at an earlier age (6).
The CPK level in patients with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy is only mildly or moderately elevated. EMG and muscle biopsy reveal myopathy. The diagnosis of this form of muscular dystrophy should be considered in patients with a myopathic phenotype, after Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies have been ruled out (usually by testing for dystrophin) (6). The condition should also be distinguished from scapuloperoneal muscular dystrophy and the rigid spine syndrome (167).
Genetic and Molecular Biology Studies.
The gene locus for the most common variant of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, the X-linked recessive form, has been localized, in linkage studies, to the long arm of the × chromosome at Xq28 (168, 169 and 170). Rarely, an autosomal dominant form and, even less frequently, an autosomal recessive form may be seen. The autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive forms have an identified gene mutation on the lamin A/C gene on chromosome 1q21 (170). The specific type of gene testing depends on the family history and sex of the affected individual.
Treatment.
The treatment for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy is similar to what is used in other forms of muscular dystrophy. The goals are to prevent or correct deformities and maximize function. Treatment modalities include physical therapy, correction of soft-tissue contractures, spinal stabilization, and cardiologic intervention.
Physical Therapy.
This can be useful in the management of neck-extension contractures, elbow-flexion contractures, and tightness of the lumbar paravertebral muscles. Decreased neck flexion, which is characteristic of this disorder, can begin as early as the first decade of life, but is usually not present until the second decade. This is due to contracture of the extensor muscles and the ligamentum nuchae. According to Shapiro and Specht (6), this contracture does not progress past neutral. Lateral bending and rotation of the neck also become limited as the extensor contractures progress. Physical therapy can be helpful in maintaining limited flexion of the neck.
Soft-tissue Contractures.
Tendo-Achilles lengthening and posterior ankle capsulotomy, combined with anterior transfer of the tibialis posterior tendon, can be helpful in providing longterm stabilization of the foot and ankle (6, 165). Elbow-flexion contractures usually do not require treatment. These contractures can be as severe as 90 degrees, although most do not exceed 35 degrees (6). Full flexion from this position and normal forearm pronation and supination are preserved. Physical therapy may be helpful in slowing the progress of the elbow-flexion contractures. Surgery has not been shown to be beneficial.
Spinal Stabilization.
Scoliosis is common in this form of muscular dystrophy, but it shows a lower incidence of progression. This has been attributed to contractures at the lumbar and ultimately the thoracic paravertebral muscles, which seem to prevent progression (6, 165). Patients with scoliosis need to be followed closely, but most do not require treatment. Curves that progress beyond 40 degrees may require surgical stabilization.
Cardiologic Intervention.
Severe brachycardia caused by complete heart block has been a major cause of sudden death in these patients. Most of them do not have cardiac symptoms preceding death. Merlini et al. (166) reported that 30 out of 73 patients with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy died suddenly, of whom only four were symptomatic. It is recommended that a cardiac pacemaker be inserted shortly after confirmation of the diagnosis (166, 171).
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree