FIGURE 5.3 Suboccipital region. (From Tank PW, Gest TR. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Atlas of Anatomy. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009.)
PATIENT POSITION
- Sitting on an exam stool with neck flexed and leaning forward with arms resting on the exam table.
LANDMARKS
1. With the patient seated on the exam stool, the clinician stands directly behind the patient.
2. Find the external occipital protuberance of the occipital bone in the midline.
3. The point of injection of the greater occipital nerve is 2 cm lateral to the external occipital protuberance along the superior nuchal line and then 2 cm inferior (caudal).4 At the point where the greater occipital nerve courses over the occipital bone, pressure over the nerve will elicit pain. Mark that spot with an ink pen.
4. At that site, press firmly on the skin with the retracted tip of a ballpoint pen. This indention represents the entry point for the needle.
5. After the landmarks are identified, the patient should not move the neck.
ANESTHESIA
- Local anesthesia of the skin with topical vapocoolant spray may be used but is not necessary in most patients.
EQUIPMENT
- 3-mL syringe
- 25-gauge, 1-in. needle
- 1 mL of 1% lidocaine without epinephrine
- 1 mL of the steroid solution (40 mg of triamcinolone acetonide)
- One alcohol prep pad
- Two povidone–iodine prep pads
- Sterile gauze pads
- Sterile adhesive bandage
TECHNIQUE
1. Part the hair and prep the insertion site with alcohol followed by the povidone–iodine pads.
2. Achieve good local anesthesia by using topical vapocoolant spray (optional).
3. Position the needle and syringe perpendicular to the skin with the tip of the needle directed anteriorly toward the nuchal line of the occiput.
4. Using the no-touch technique, introduce the needle at the insertion site (Fig. 5.4).
5. Advance the needle toward the location of the greater occipital nerve until the needle tip contacts the occiput at the superior nuchal line. Back up the needle 1 to 2 mm.
6. Inject the steroid solution as a bolus around the greater occipital nerve. The injected solution should flow smoothly into the tissues. If increased resistance is encountered, advance or withdraw the needle slightly before attempting further injection.
7. Following injection of the corticosteroid solution, withdraw the needle.
8. Apply a sterile adhesive bandage.
9. Instruct the patient to gently massage the area with a piece of gauze. This movement distributes the steroid solution around the nerve.
10. Reexamine the greater occipital nerve in 5 min to confirm pain relief.
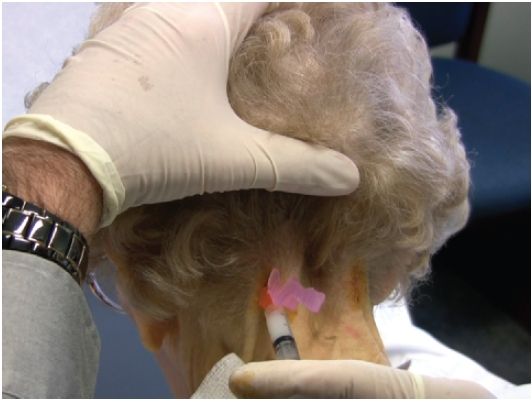
FIGURE 5.4 Greater occipital neuralgia injection.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




