FIGURE 6.20 Right lateral elbow joint. (From Tank PW, Gest TR. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Atlas of Anatomy. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009.)
PATIENT POSITION
- Supine on the examination table with the head of the bed elevated 30 degrees.
- The elbow is positioned at 45 degrees of extension.
- The wrist is in a neutral position.
- The elbow is supported with the placement of chucks pads or towels.
- Rotate the patient’s head away from the side that is being injected. This minimizes anxiety and pain perception.
LANDMARKS
1. With the patient supine on the examination table, the clinician stands lateral to the affected elbow.
2. Locate the radial head by palpating over the lateral aspect of the elbow while supinating and pronating the wrist.
3. Find the depression immediately proximal to the radial head and mark it with ink.
4. At that site, press firmly on the skin with the retracted tip of a ballpoint pen. This indention represents the entry point for the needle.
5. After the landmarks are identified, the patient should not move the elbow.
ANESTHESIA
- Local anesthesia of the skin using topical vapocoolant spray.
EQUIPMENT
- 3-mL syringe
- 10-mL syringe—for optional aspiration
- 25-gauge, 1-in. needle
- 20-gauge, 1-in. needle—for optional aspiration
- 0.5 mL of 1% lidocaine without epinephrine
- 0.5 mL of the steroid solution (20 mg of triamcinolone acetonide)
- One alcohol prep pad
- Two povidone–iodine prep pads
- Sterile gauze pads
- Sterile adhesive bandage
- Nonsterile, clean chucks pad
TECHNIQUE
1. Prep the insertion site with alcohol followed by the povidone–iodine pads.
2. Achieve good local anesthesia by using topical vapocoolant spray.
3. Position the needle and syringe perpendicular to the skin with the needle tip directed medially toward the elbow joint.
4. Using the no-touch technique, introduce the needle at the insertion site (Fig. 6.21).
5. Advance the needle into the elbow joint. This places the needle tip between the humeral lateral condyle and the radial head.
6. If aspirating, withdraw fluid using a 20-gauge, 1-in. needle with the 10-mL syringe.
7. If injection of corticosteroid is to follow the aspiration, grasp the needle firmly, remove the 10-mL syringe from the 20-gauge needle, and then attach the 3-mL syringe filled with the steroid–lidocaine mixture.
8. If only injecting the steroid mixture, use a 25-gauge, 1-in. needle with the 3-mL syringe.
9. Inject the steroid solution as a bolus into the elbow joint. The injected solution should flow smoothly into the space. If increased resistance is encountered, advance or withdraw the needle slightly before attempting further injection.
10. Following injection of the corticosteroid solution, withdraw the needle.
11. Apply a sterile adhesive bandage.
12. Instruct the patient to move his or her elbow through its full range of motion. This movement distributes the steroid solution throughout the elbow joint.
13. Reexamine the elbow in 5 min to confirm pain relief.
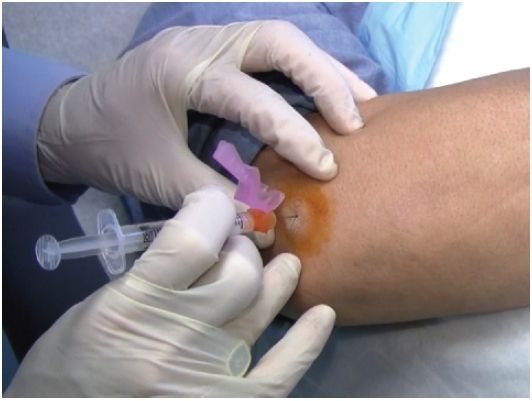
FIGURE 6.21 Left elbow joint injection.





