Chapter 17 Basic immunology
Cellular immunity
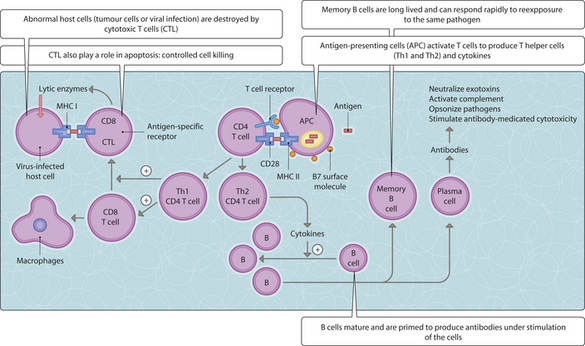
Cells that have become infected can be recognized by a subset of T-lymphocytes termed cytotoxic lymphocytes via presentation of processed viral antigens attached to MHC class I molecules on the surface of the infected cells, which are killed directly. Foreign antigen can be phagocytosed by antigen-presenting cells such as macrophages, which process the antigens before expressing modified fragments on the surface of their cytoplasmic membrane attached to class II molecules. Killing of these cells by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes is stimulated by interactions with helper T-lymphocytes, which themselves can recognize foreign antigens presented to them by MHC class II molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells and in association with the CD4 T-cell receptor. Two subsets of helper T-lymphocytes exist; Th1 cells secrete cytokines that help to induce cellular immunity (i.e. via the stimulation of CD8 T-lymphocytes) while Th2 cells secrete cytokines that promote humoral immunity. Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes recognize virally infected cells by class I molecules with antigen fragments on the surface of the infected cells in association with the CD8 T-cell receptor (Fig. 3.17.1).
Polymorphism within genes encoding the MHC
The genes encoding the HLA molecules are extremely polymorphic (i.e. have many potential forms) and this polymorphism particularly affects the amino acid sequences within the antigen-binding groove, resulting in subtle alterations in shape and, therefore, small differences in the efficiency of antigen presentation. This leads to small interindividual differences in modulation of the immune response to a wide range of antigens and to varying susceptibility to a range of diseases, both neoplastic and non-neoplastic, in which development and progression is affected by the immune system (e.g. autoimmune diseases; Ch. 18).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree