Fig. 32.1
Vertebral hemangioma. Roentgenogram (a), axial (b) and sagittal (c) CT, and MRI (d) show a lesion occupying the body of T2 vertebra, with intensification of vertical trabeculae in an otherwise lytic lesion. Cortex is preserved
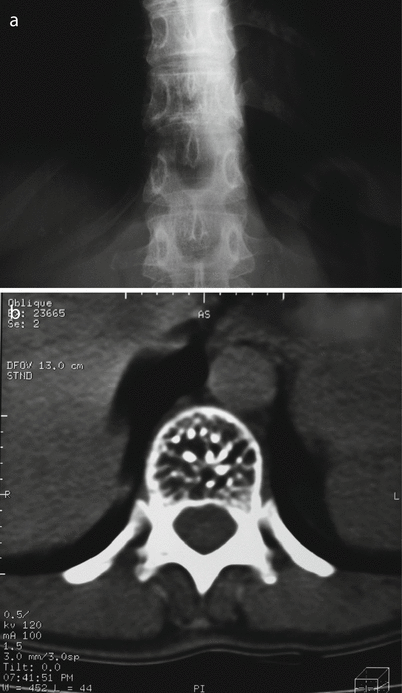
Fig. 32.2
Vertebral hemangioma. Roentgenogram (a) and CT (b) show characteristic vertical trabeculation and dotted image on axial CT
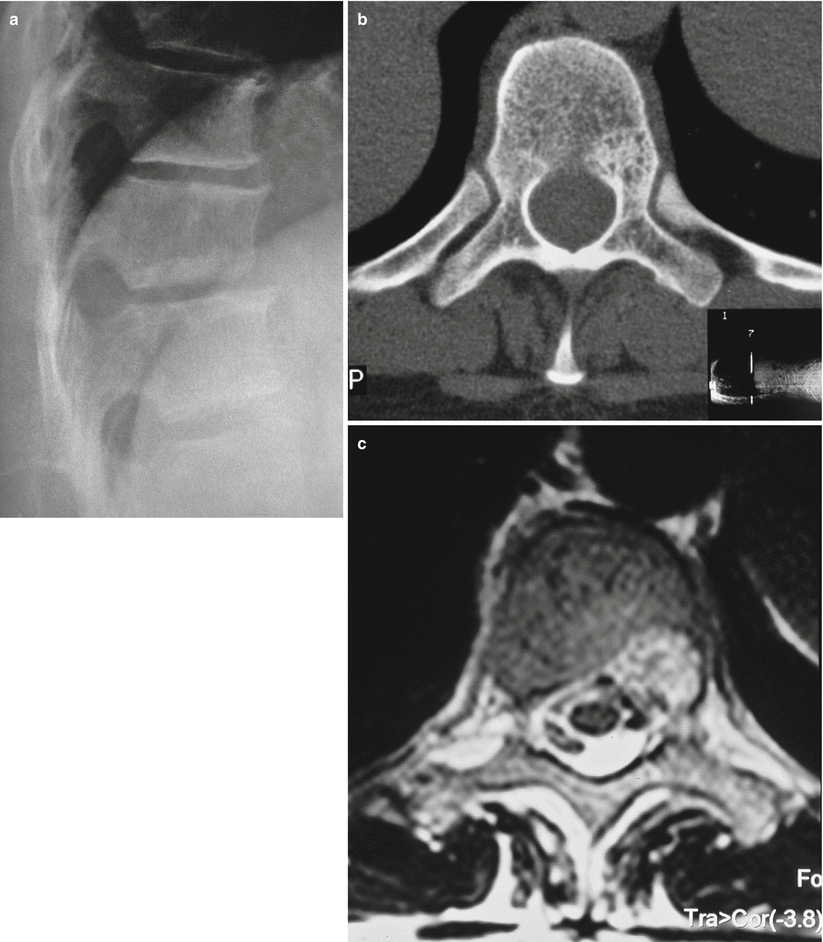
Fig. 32.3
Small vertebral hemangioma. Roentgenogram, (a) CT (b), and MRI (c) showing a small hemangioma in the vertebral body, next to the left pedicle
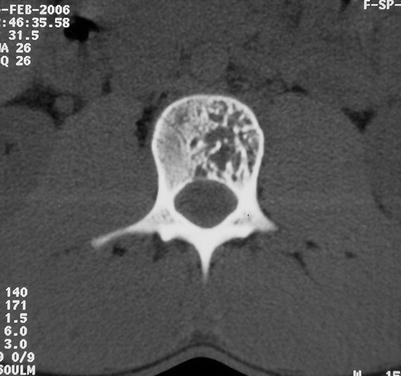
Fig. 32.4
Vertebral hemangioma. Axial CT image showing a hemangioma involving part of the vertebral body. The contour of the vertebra is preserved
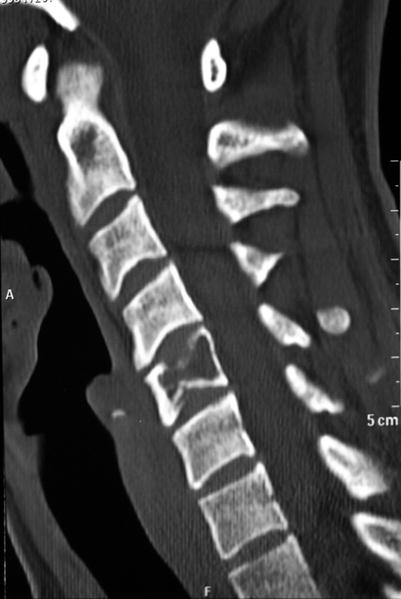
Fig. 32.5
Sagittal CT image of fractured vertebra with a hemangioma
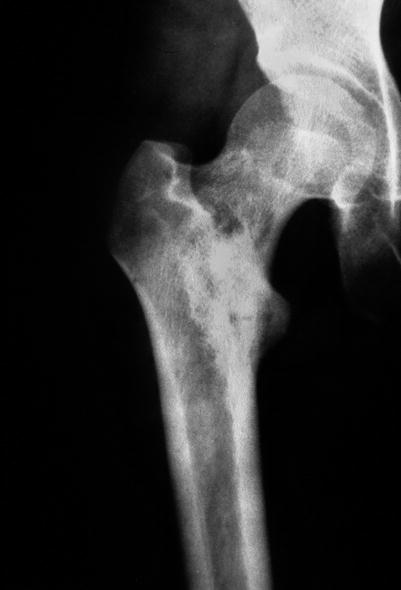
Fig. 32.6
Roentgenogram showing a hemangioma in the neck of the femur
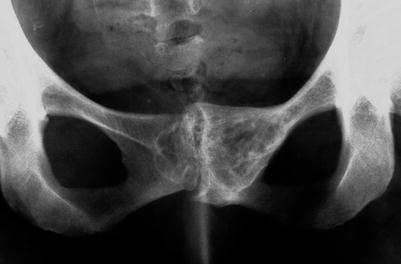
Fig. 32.7
Roentgenogram showing a hemangioma of the ischium
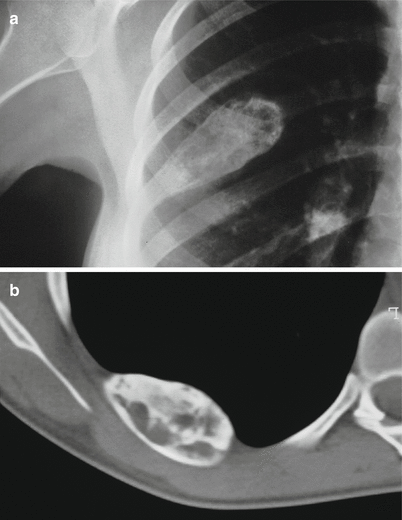
Fig. 32.8
Roentgenogram (a) and CT (b) of a hemangioma of a rib
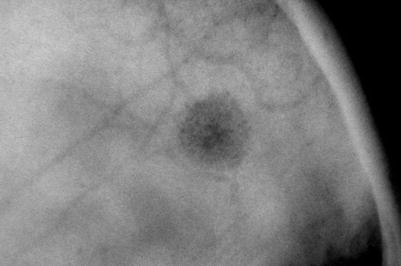
Fig. 32.9
Roentgenogram of a hemangioma in the skull. Differential diagnosis with eosinophilic granuloma
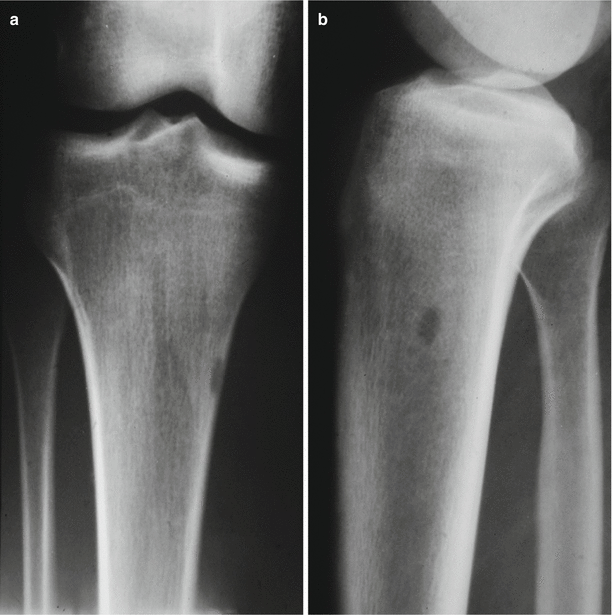
Fig. 32.10




AP (a) and lateral (b) radiographic view of a cortical hemangioma in the metaphysis of a tibia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








