Distal Femur Allograft Prosthe Composite
D. Luis Muscolo
Miguel A. Ayerza
Luis A. Aponte-Tinao
Distal femur osteoarticular allografts are utilized for reconstruction of the proximal side of the knee after tumor resection. Osteoarticular allografts do not sacrifice the side of the joint that is not compromise by the tumor and have the possibility of attaching soft-tissues. Reconstruction of the ligaments, tendons, and joint capsule must be meticulous and precise, since the longevity of these grafts is related in part to the stability of the joint. Care must be taken to avoid malalignment that will put greater stress on the allograft cartilage.
INDICATIONS
The procedure is indicated for the treatment of massive osteoarticular defects after tumor resections or traumatic bone losses.
The major neurovascular bundle must be free of tumor.
Patient with degenerative arthritis or cartilage defects of the proximal tibia
Inadequate host soft tissues to reconstruct and obtain a stable joint with an osteoarticular allograft
Inadequate anatomical matching between the receptor and potential available donors
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients in whom preoperative imaging studies demonstrate evidence of intra-articular compromise of the tumor
Patients who received previous or will receive postoperatively high doses of radiotherapy
Gross tissue deficiencies, particularly of the extensor mechanism, irreparable from soft tissues provided by the allograft
PREOPERATIVE PREPARATION: ALLOGRAFT SELECTION
Fresh-frozen allografts are obtained and stored according to a technique that has been previously described (1). In allograft prosthetic composite anatomical matching of both size and shape is not critical as in osteoarticular allograft. However, it is critical that the bone transplanted is the same as the resected (e.g., distal femur for distal femur) in order to reproduce as much normal biomechanical loading as possible at the construct.
TECHNIQUE
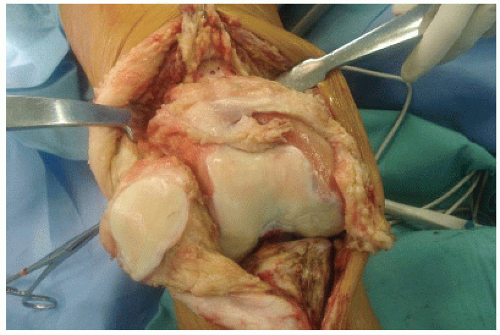
All operations are performed in a clean-air enclosure with vertical airflow and usually with spinal anesthesia. The patient is placed on the operating table in the supine position. A sandbag is placed under the ipsilateral buttock. A long midline incision is made, beginning in the middle part of the thigh, and a medial parapatellar arthrotomy is performed with the eversion of the patella in a similar way as in a total knee replacement to enable a wide exposure of the distal part of the femur and the knee joint (Figs. 18.1 and 18.2). The biopsy track is left in continuity with the specimen. The collateral ligaments are identified and, if they are not affected
by the tumor, sectioned near the femur insertion to ensure that there is enough host tissue to reconstruct these ligaments with the donor. The cruciate ligaments are resected with the specimen. The distal part of the femur is approached through the interval between the rectus femoris and the vastus medialis. If there is an extraosseous tumor component, a cuff of normal muscle must be excised. Femoral osteotomy is performed at the appropiate location as determined on the basis of the preoperative imaging studies. All remaining soft tissues at the level of the transection are cleared. After the posterior and medial structures have been protected and retracted, the osteotomy is performed perpendicular to the long axis of the femur (Fig. 18.3). Following the osteotomy, the distal part of the femur is pulled forward in order to expose the soft tissue attachments of the popliteal space. The popliteal artery is mobilized, and the geniculate vessels are ligated and transected. Boths heads of the gastrocnemius are released, and the posterior capsule is sectioned near the femoral insertion. The distal femur is then passed off the operative field (Fig. 18.4).
by the tumor, sectioned near the femur insertion to ensure that there is enough host tissue to reconstruct these ligaments with the donor. The cruciate ligaments are resected with the specimen. The distal part of the femur is approached through the interval between the rectus femoris and the vastus medialis. If there is an extraosseous tumor component, a cuff of normal muscle must be excised. Femoral osteotomy is performed at the appropiate location as determined on the basis of the preoperative imaging studies. All remaining soft tissues at the level of the transection are cleared. After the posterior and medial structures have been protected and retracted, the osteotomy is performed perpendicular to the long axis of the femur (Fig. 18.3). Following the osteotomy, the distal part of the femur is pulled forward in order to expose the soft tissue attachments of the popliteal space. The popliteal artery is mobilized, and the geniculate vessels are ligated and transected. Boths heads of the gastrocnemius are released, and the posterior capsule is sectioned near the femoral insertion. The distal femur is then passed off the operative field (Fig. 18.4).
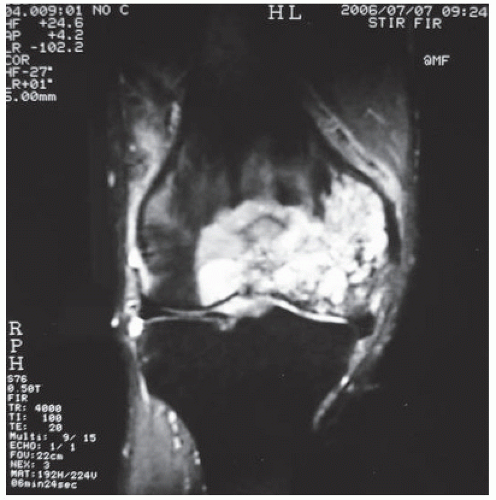 FIGURE 18.1 Coronal magnetic resonance image that illustrates the preoperative tumor growing assessment with extension to the medial collateral ligament. |
Simultaneous with the tumor resection, the allograft specimen is prepared in the back table. The graft is taken out of the plastic packaging and placed directly in a warm normal saline solution. After being thawed, the donor bone is cut to the proper length and soft tissue structures such as the collateral ligaments and posterior capsule are prepared for implantation. It is crucial for joint reconstruction to have these adequate soft tissue structures in order to repair them to correspondent host tissues. The femoral cuts are done in the back table in order to place the prosthesis in the allograft (Figs. 18.5, 18.6, 18.7). After the appropriate size of the prosthesis is




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree