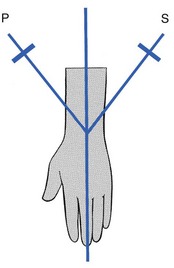
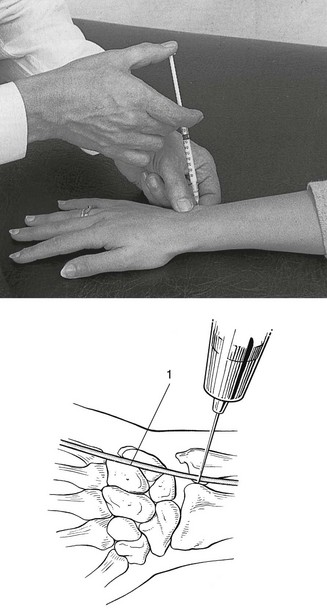
22 Pain felt at the wrist during pronation and supination movements of the forearm inculpates the distal radioulnar joint. The source can be the joint capsule,1 the ligaments2–4 or the articular disc. The capsular pattern of the lower radioulnar joint presents with pain at the end of range of the two movements (pronation and supination, Fig. 22.1) and indicates arthritis. Usually there is only pain at end-range but sometimes there may be equal limitation, or slightly more limitation of supination than of pronation. When a fracture of the distal part of the radius fails to unite properly, arthrosis at the distal radioulnar joint may follow. Mal-union of the distal part of the ulna does not give rise to persistent problems5 and painless ulnar styloid non-union is a frequent incidental radiographic finding.6 Arthritis may develop without a provable cause such as rheumatoid or traumatic arthritis. Furthermore, the condition will worsen when attempts are made to mobilize the joint. Such a condition responds particularly well to intra-articular triamcinolone.7 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) involves the wrist in up to 95% of cases. The distal radioulnar joint is affected in 31–75% of these patients and is frequently the first compartment of the wrist involved,8 often bilaterally.9 Triamcinolone suspension injected intra-articularly once or twice a year may keep the joint free from symptoms.10 Long-standing rheumatoid arthritis results in ligamentous laxity. At the distal radioulnar joint this leads to the so-called ‘caput ulnae syndrome’: dorsal subluxation of the distal part of the ulna, supination of the carpus on the forearm, and palmar dislocation of the tendon of the extensor carpi ulnaris.11–14 Technique: intra-articular injection The patient sits at the couch with the arm lying in pronation. A 1 mL syringe filled with triamcinolone acetonide and fitted with a 2 cm needle is used. The joint line, which is very short, is identified just radially to the head of the ulna. Gliding movements between the ulna and radius may help to find it. As the extensor digiti minimi tendon lies just dorsal to the joint line, care must be taken to avoid puncturing it (Fig. 22.2). After a mal-united Colles’ fracture, shortening of the radius may be responsible for an irreversible limitation of supination only, with the end-feel of a bony block.15,16 The movement may be painful in recent cases but should become painless in due course. A dorsal dislocation of the ulna also presents with a block to supination and a visible dorsoulnar prominence. The mechanism for dorsal subluxation and dislocation is extreme pronation and extension, which pull the ulnar head out through the dorsal capsule. Triangular fibrocartilage complex avulsion and attenuation of the palmar radioulnar ligament will allow this dislocation.17 In tenosynovitis of the extensor carpi ulnaris, passive supination may be painful at the end of the range. This is a localizing sign, indicating that the lesion lies in the groove at the base of the ulna. The tenosynovitis will, of course, be diagnosed by interpreting resisted movements at the wrist (see p. 345). A block to pronation is present in palmar dislocations of the ulna. On inspection–palpation there will be a volar–ulnar prominence and a palpable radial sigmoid notch.18
Disorders of the lower radioulnar joint
Disorders of the inert structures
Capsular pattern
Arthrosis
Monoarticular steroid-sensitive arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
![]()
Non-capsular pattern
Limited supination
Painful supination
Limited pronation
Disorders of the lower radioulnar joint