Chapter 11 Tissue degenerations
Calcification
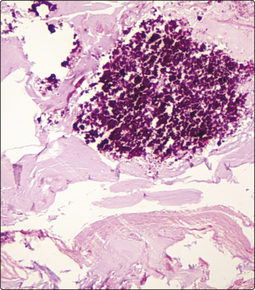
Pathological calcification is abnormal deposition of calcium salts plus small quantities of other minerals. Macroscopically, calcification is white or pale grey, and it produces a hard or gritty feeling to palpation. Calcium is opaque to X-rays and can be seen radiologically. Histologically, calcium is basophilic with haematoxylin stain (Fig. 3.11.1); it also takes up other dyes. Heavily calcified tissues cannot be processed in the laboratory using routine paraffin wax methods so the tissue must be embedded in a hard medium such as acrylic or epoxy resin, or decalcified so it becomes soft. In long-standing calcification, osseous metaplasia can produce heterotopic bone within the calcified tissue.
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree