43. Antifungal therapy
 Describe the mechanism of action for three different groups of antifungal agents and give an example for each
Describe the mechanism of action for three different groups of antifungal agents and give an example for eachThere are a number of antifungal agents that can be used topically (e.g. creams) or systemically (e.g. oral, intravenous) depending on the type, site and severity of fungal infection. The choice of antifungal treatment also depends on the antifungal drug sensitivity of the agent (Fig. 3.43.1). Fungal infections (mycoses) may be:
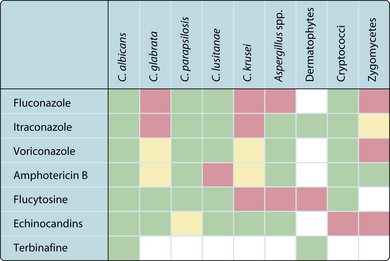
Fig. 3.43.1 Spectrum of antifungal drug activity. Green, good activity; yellow, some activity; red, poor activity.
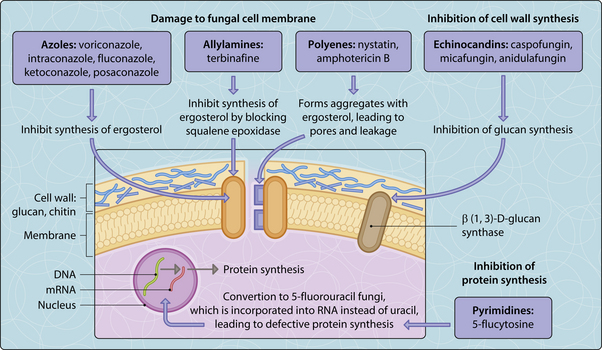
As with antibacterial drugs, many antifungal agents are derived from the fermentation products of certain fungi (e.g. Streptomyces and Penicillium). The principal targets and mode of action of antifungal drugs are through the disruption of the cell membrane or inhibition of cell wall or protein synthesis (Fig. 3.43.2).
< div class='tao-gold-member'>