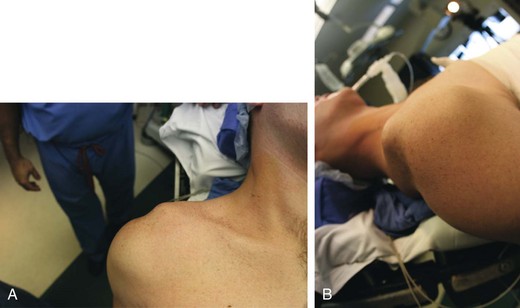
Chapter 34 • Acute traumatic event versus chronic instability • Current pain, physical limitations, and disability • Failure of at least 3 months of conservative treatment • Age of the patient (physeal fractures) • Prior surgical procedures (distal clavicle resection) • Status post–distal clavicular fracture (not always obvious) Figure 34-1 High-grade (type V) acromioclavicular separation. A, Anteroposterior view. B, Lateral view. – Anterior-posterior translation or mobility – Superior-inferior translation or mobility – Reduction of the distal clavicle with shoulder shrug differentiates type III from type V (distal clavicle buttonhole through deltotrapezial fascia)
Anatomic Acromioclavicular Joint Reconstruction
Preoperative Considerations
History
Physical Examination
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Anatomic Acromioclavicular Joint Reconstruction






