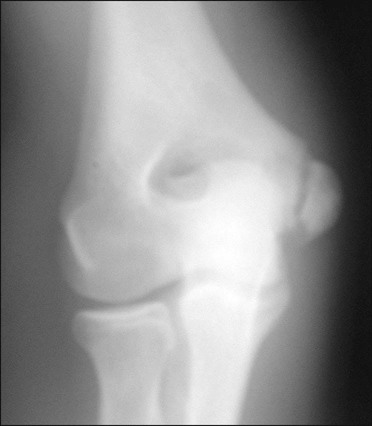
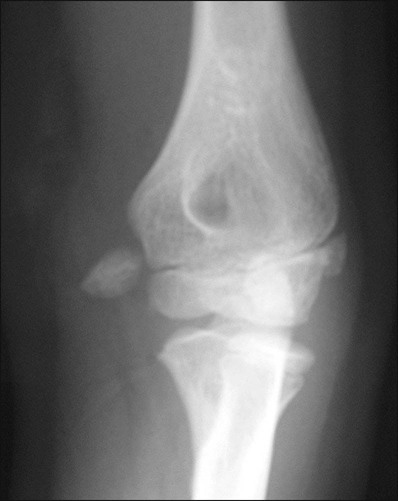
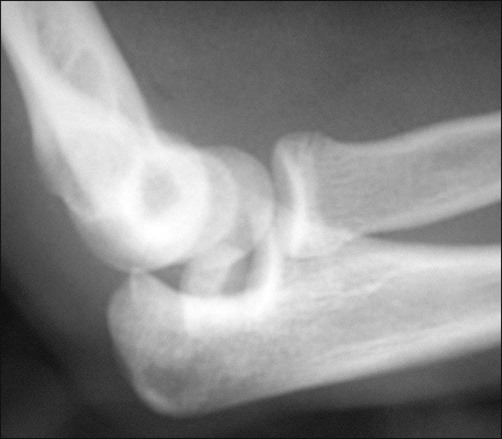
• The AP radiograph is best for determining the amount of displacement of the medial epicondyle fracture (Fig. 2). • The lateral radiograph is examined to be certain that the elbow joint is reduced and that the medial epicondyle fragment is not in the joint (Fowles et al., 1984) (Fig. 3). • The valgus stress view (Fig. 4) can be utilized to demonstrate valgus instability of the elbow. This can be done prior to surgery with a gravity valgus stress test, or under anesthesia prior to making the skin incision (Case and Hennrikus, 1997; Schwab et al., 1980; Woods and Tullos, 1977).
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Medial Epicondyle Fracture Using a Screw and Washer
Examination/Imaging
 The skin is examined for abrasions or open injuries.
The skin is examined for abrasions or open injuries.
 The sensory and motor function of the ulnar nerve, the radial pulse, and capillary refill of the hand are evaluated.
The sensory and motor function of the ulnar nerve, the radial pulse, and capillary refill of the hand are evaluated.
 The wrist and shoulder are also examined for possible additional injuries.
The wrist and shoulder are also examined for possible additional injuries.
 Plain radiographs should be obtained in anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and valgus stress views.
Plain radiographs should be obtained in anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and valgus stress views.
Surgical Anatomy
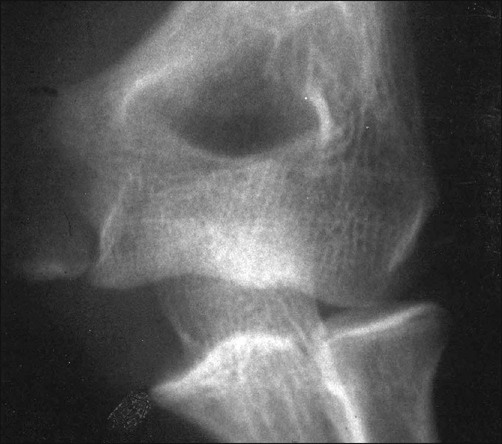
 The medial epicondyle is the last growth plate to fuse in the elbow (Fig. 5). Fusion occurs between the ages of 14 and 18. Fusion occurs later in males.
The medial epicondyle is the last growth plate to fuse in the elbow (Fig. 5). Fusion occurs between the ages of 14 and 18. Fusion occurs later in males.
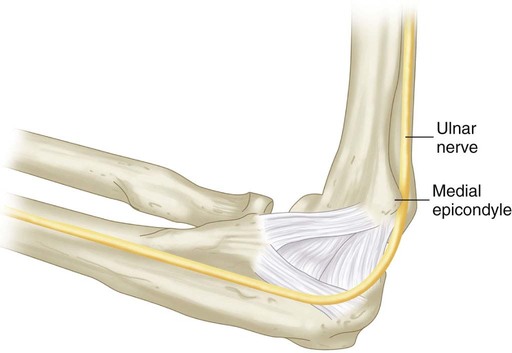
 The ulnar collateral ligament originates on the inferior surface of the medial epicondyle.
The ulnar collateral ligament originates on the inferior surface of the medial epicondyle.
 Muscles in the flexor-pronator mass, including the pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor digitorum superficialis, and flexor carpi ulnaris, originate from the medial epicondyle.
Muscles in the flexor-pronator mass, including the pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor digitorum superficialis, and flexor carpi ulnaris, originate from the medial epicondyle.
4: Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Medial Epicondyle Fracture Using a Screw and Washer