A. Bobby Chhabra, Aaron M. Freilich
Wrist and Hand
Regional Anatomy and Surgical Intervals
Regional Anatomy
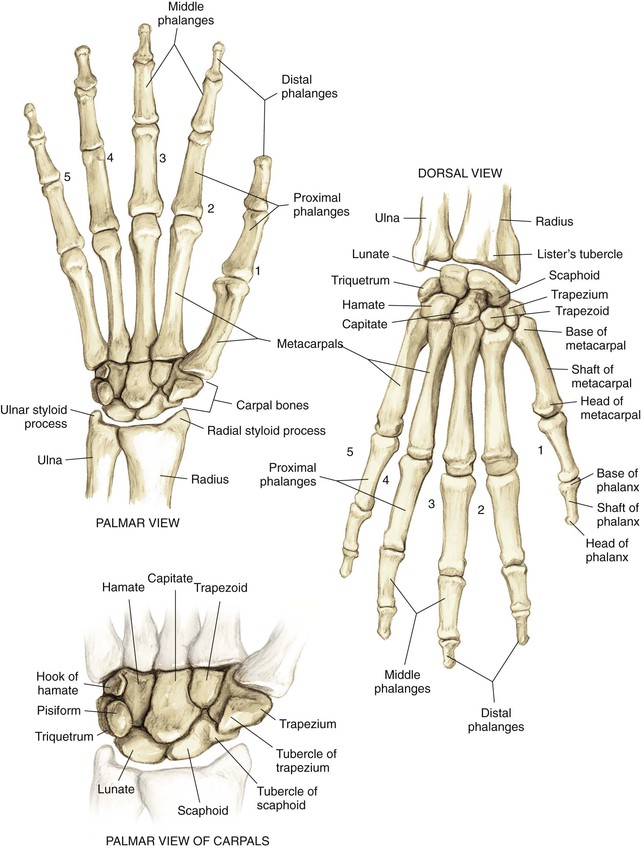
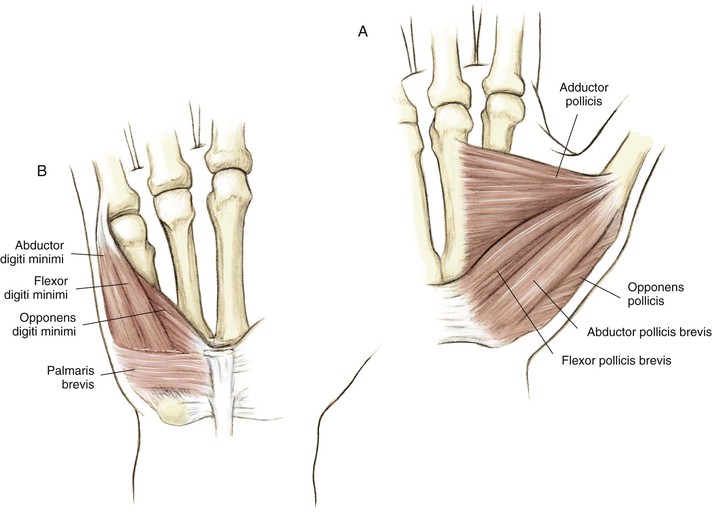
Osteology (Fig. 4-1)
Distal Radius
Phalanges
• Insertion of the flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) on the volar surface at the base
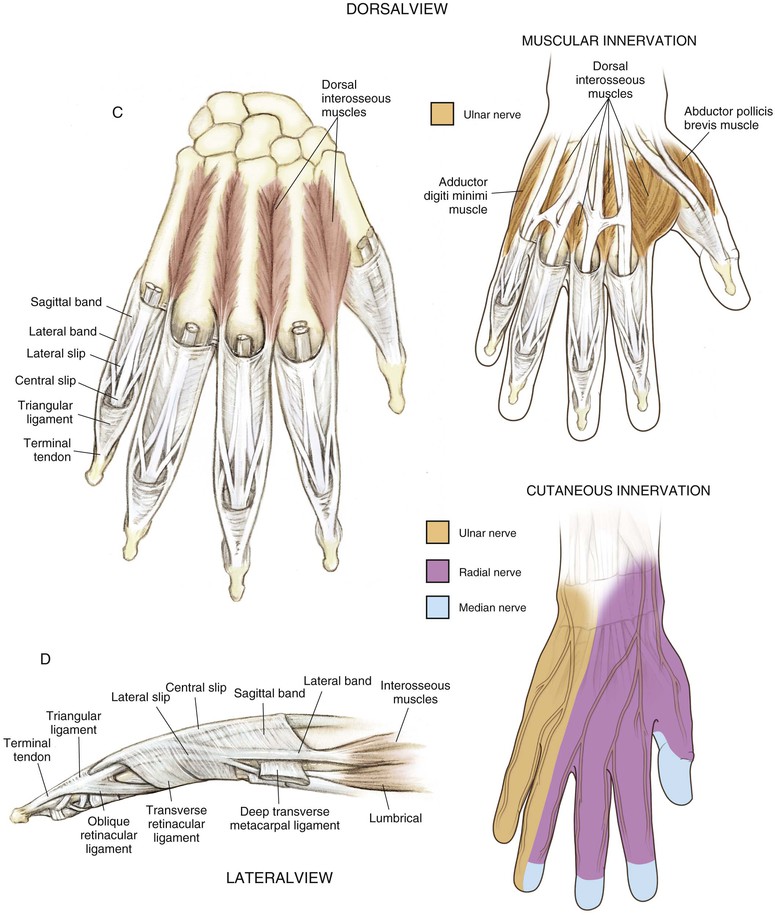
• Insertion of the central slip of the extensor hood on the dorsal surface
• Insertion of the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) on the volar surface
• Insertion of the terminal extensor tendon on the dorsal surface
Arthrology
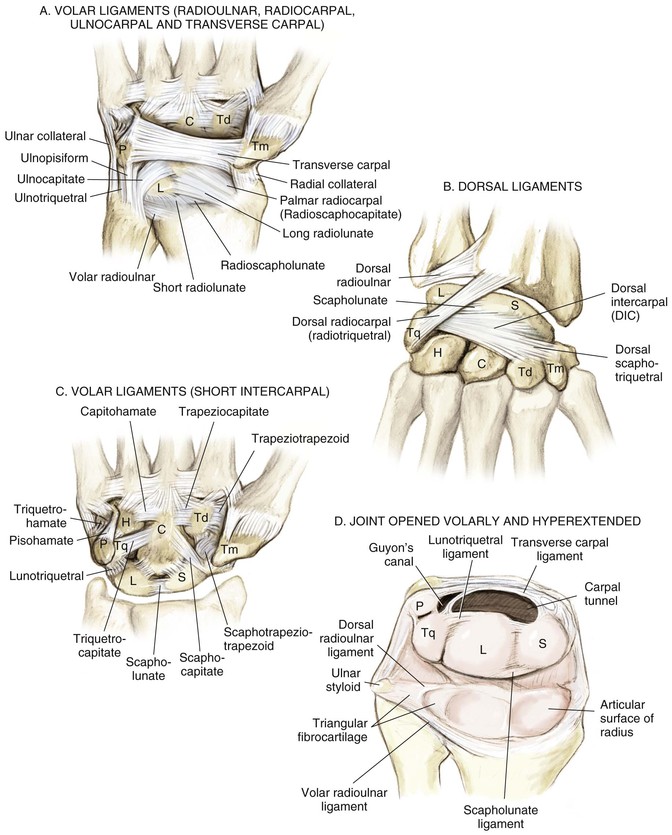
Radiocarpal Joint (Fig. 4-2, A and B)
The distal radius articulates with the proximal carpal row
Extrinsic volar and dorsal ligaments
Radioscaphocapitate, long and short radiolunate, ulnar collateral ligaments (part of the TFCC)
Dorsal ligaments (dorsal intercarpal and dorsal radiocarpal)
Distal Radioulnar Joint
The ulna articulates with the radius in the sigmoid notch
Distal radioulnar ligaments of the TFCC are the major stabilizers of the distal radioulnar joint
• Located on the articular surface of the distal ulna and the very ulnar aspect of the distal radius
• The central portion of the triangular fibrocartilage is thin and avascular
• The periphery is vascularized and amenable to repair
• Volar and dorsal distal radioulnar ligaments
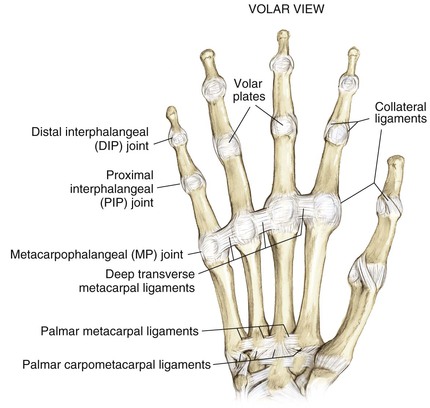
Carpometacarpal Joints (Fig. 4-3)
Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints
Proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints
Distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints
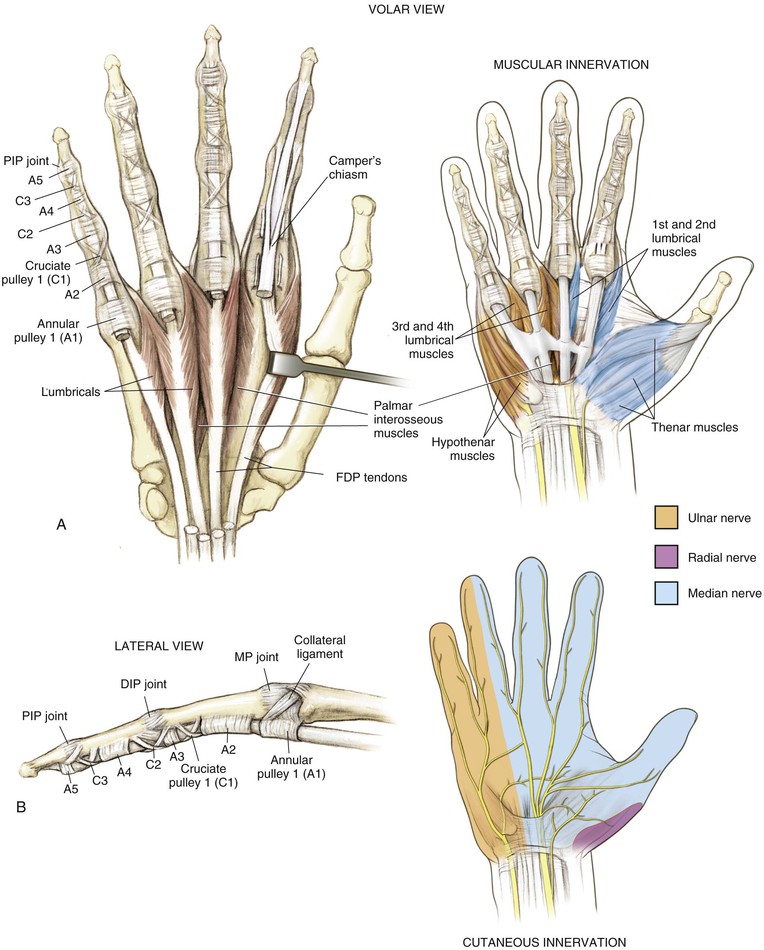
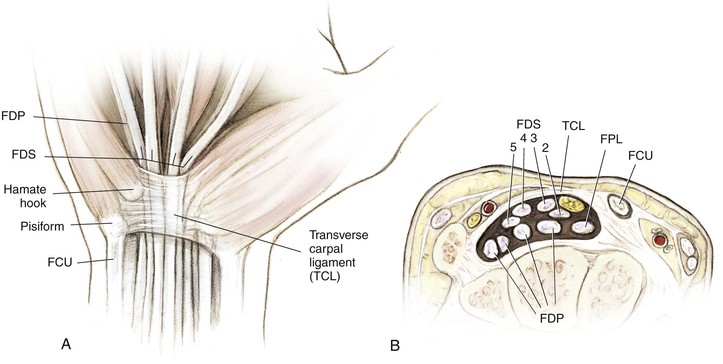
• Flexor tendon relationship in carpal tunnel
• The FDS to digits 3 and 4 lies volar to tendons 2 and 5 (Fig. 4-5, A and B)
• The FDP lies dorsal to the FDS in the forearm
• Camper’s chiasm—crossing of the FDS and FDP tendons at the level of the proximal phalanx; from the forearm to Camper’s chiasm, the FDS lies volar to the FDP; in the finger, the FDS splits and attaches onto the middle phalanx; the FDP emerges from between the chiasm volarly and continues to its attachment on the distal phalanx (see Fig. 4-4, A)
• Finger flexor pulley system (see Figure 4-4, B)
• Five annular ligaments and four cruciate ligaments
• A2 and A4 are crucial and prevent bowstringing of the flexor tendon
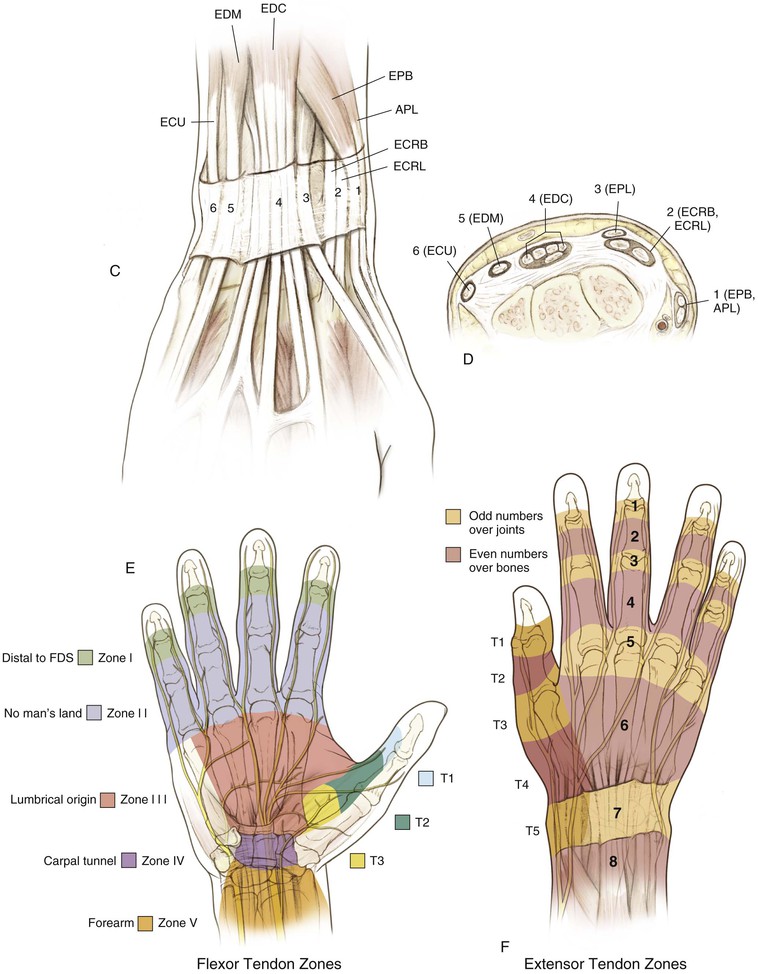
• Extensor tendon compartments (Table 4-1; see Fig. 4-5, C and D)
Table 4-1
Extensor Tendon Compartments
| COMPARTMENT | TENDONS |
| 1 | EPB |
| APL | |
| 2 | ECRL |
| ECRB | |
| 3 | EPL |
| 4 | EIP |
| EDC | |
| 5 | EDM |
| 6 | ECU |
APL, Abductor pollicis longus; ECRB, extensor carpi radialis brevis; ECRL, extensor carpi radialis longus; ECU, extensor carpi ulnaris; EDC, extensor digitorum communis; EDM, extensor digiti minimi; EIP, extensor indicis proprius; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis; EPL, extensor pollicis longus.
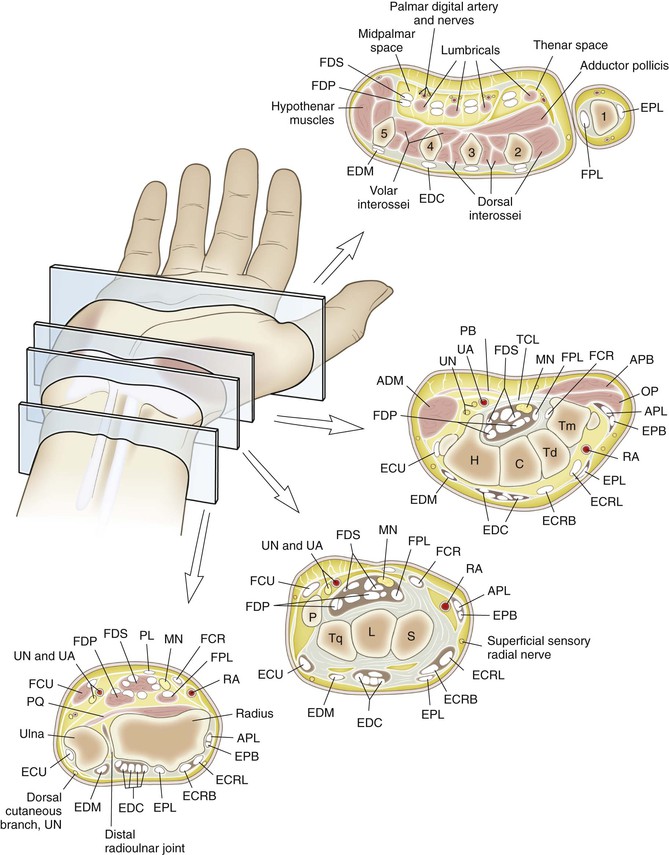
Cross-sectional anatomy (see Fig. 4-9) at the following levels: (1) distal radioulnar joint, (2) proximal carpal row, (3) distal carpal row, and (4) proximal metacarpal.
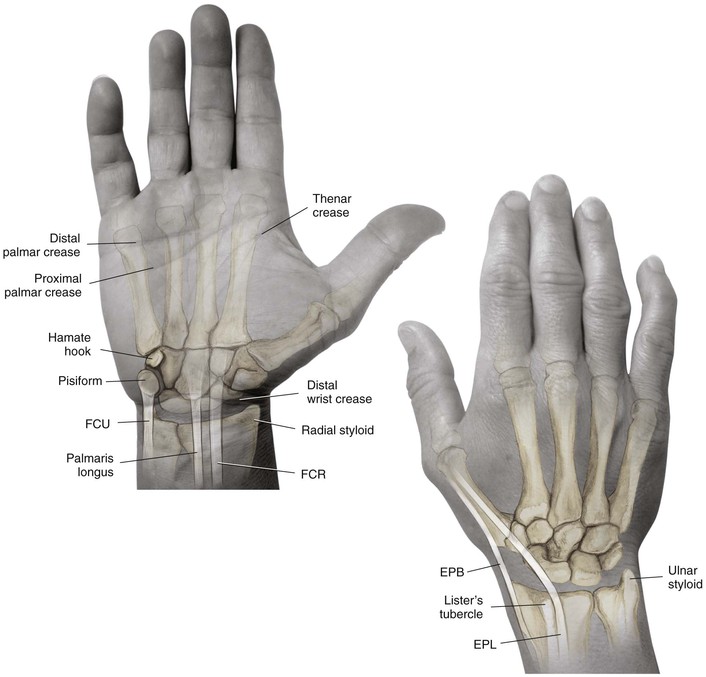
Landmarks (see Fig. 4-10): palpable anatomic landmarks: the pisiform, the hook of the hamate, Lister’s tubercle, and the palmaris.
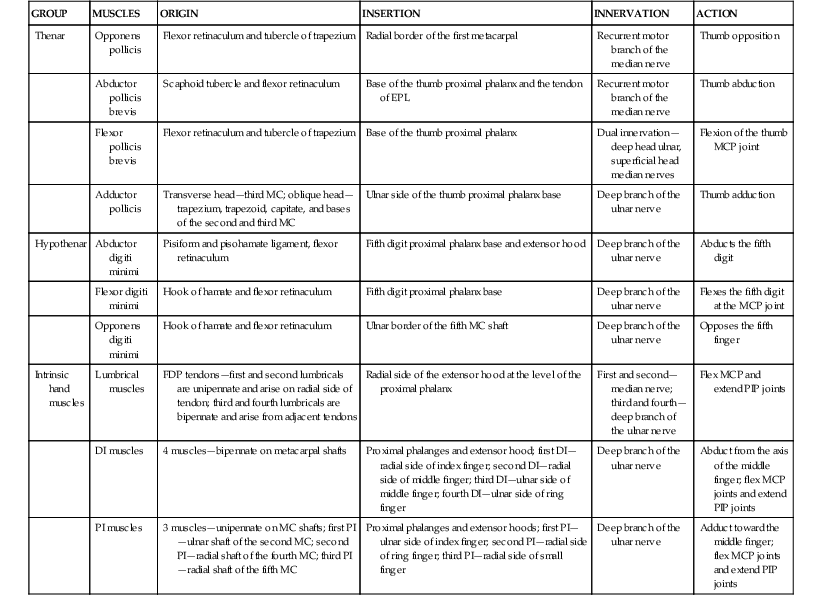
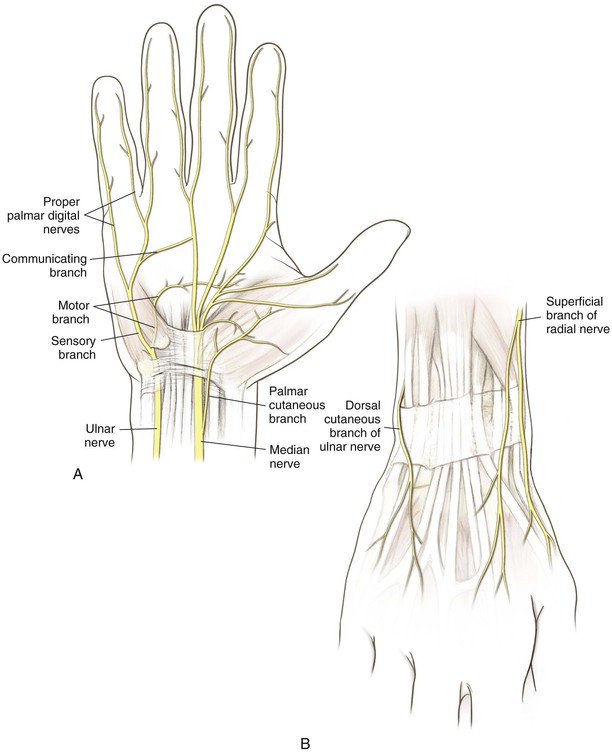
Nerves (Fig. 4-7, A)
Median Nerve
Gives off a sensory palmar branch approximately 6 cm proximal to the radial styloid
The median nerve enters the hand through the carpal tunnel
Gives off a recurrent motor branch with a variable course
• 80% branches distal to the TCL and enters the thenar musculature in a recurrent manner
• 15% branches subligamentously
• 5% branches transligamentously
Hazards
Nerves
The palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve is at risk during the Henry approach
The dorsal sensory ulnar nerve branch is at risk during TFCC repairs
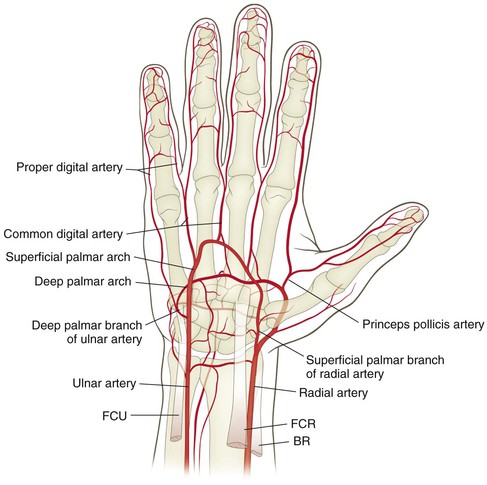
Vascular
The radial artery is at risk during the distal volar Henry approach
The ulnar artery is at risk during exposure of the ulnar distal forearm and the distal ulnar shaft
The superficial palmar arch is at risk during carpal tunnel release and exposures in palm
Proper digital arteries are at risk during midlateral approaches to finger and volar exposures
Palpable Anatomic Landmarks of the Hand and Wrist
Surgical Approaches to the Wrist
Dorsal Approach to the Forearm, Wrist, and Carpus (Video 4-1)
Indications
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree