77 Thoracic surgery and tracheostomy
Indications for thoracic surgery
Lung cancer
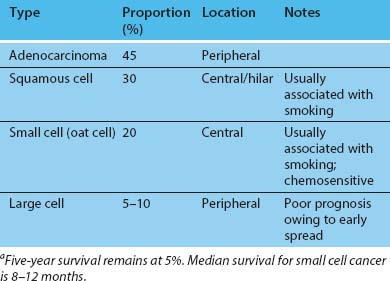
Only 10% of lung tumours are surgically resected because the disease presents late as there is no suitable test for screening (Table 3.77.1). Complete surgical resection is most effective for peripheral tumours away from the hilum, most commonly for stage I or II non-small cell lung cancer. Incomplete resection may palliate symptoms or ‘down-size’ the tumour for better response to adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Rib fractures and flail chest
A double fracture, usually caused by a compression force, results in a floating section of the rib (flail segment; Fig. 3.77.1), which may damage underlying contents and cause paradoxical respiration. Treatment depends upon the severity of the injury:
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree