Surgical Treatment of Deep Space Infections of the Hand
Jennifer Etcheson
Jeffrey Yao
DEFINITION
Deep space infections occur in one of three anatomically defined potential spaces within the hand.
Thenar, midpalmar, and hypothenar spaces
Interdigital subfacial web space
Parona space—a potential forearm space
Thenar space infections are the most common deep space infections. Midpalmar and hypothenar space infections are much more rare.
Deep space infections usually result from direct penetrating trauma or spread from an adjacent infection such as a superficial abscess or a flexor tenosynovitis (in the case of thenar and midpalmar space infections).
The single most common infecting organism is Staphylococcus aureus, although most of these infections are mixed. Other common pathogens include streptococci and coliforms.2
ANATOMY
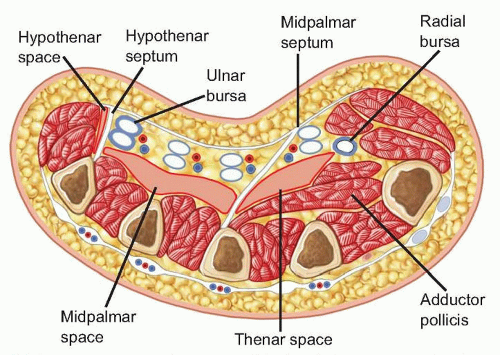
The thenar space (FIG 1) is defined by the fascia of the adductor pollicis muscle dorsally and the tendon sheath of the index finger and palmar fascia volarly.
The radial border is defined by the insertion of the adductor pollicis tendon and fascia on the thumb proximal phalanx.
The ulnar border is the midpalmar (oblique) septum, which extends from the third metacarpal to the palmar fascia.
The midpalmar space (see FIG 1) is bordered radially by the midpalmar septum and bordered ulnarly by the hypothenar septum, which extends from the fifth metacarpal to the palmar fascia.
The dorsal border of the midpalmar space is the fascia of the second and third palmar interosseous muscles, and the volar border is the flexor sheaths of the long, ring, and small fingers and the palmar fascia.
The hypothenar space (see FIG 1) is bordered radially by the hypothenar septum and dorsally by the periosteum of the fifth metacarpal. The fascia of the hypothenar muscles forms the ulnar and palmar borders.
The interdigital subfacial web spaces are three interdigital spaces at the distal end of the palm containing loose subcutaneous fat. These spaces are located near the metacarpophalangeal joints, just proximal to the deep transverse ligaments.
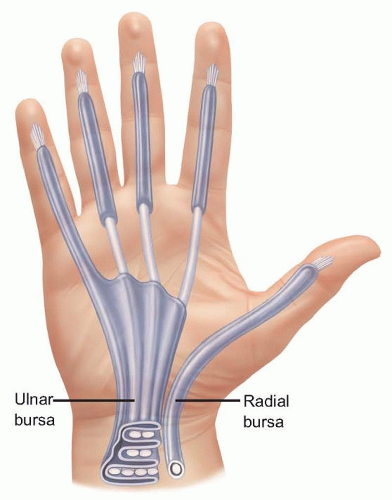
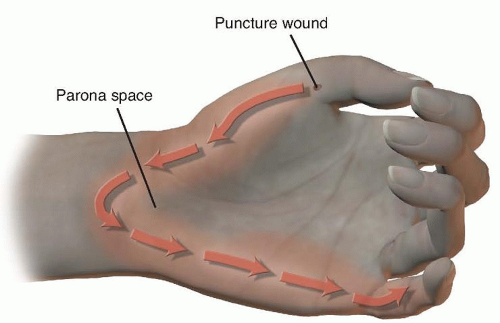
Parona space is a deep potential space in the distal forearm superficial to pronator quadratus and deep to the flexor digitorum profundus tendons. It is continuous with the midpalmar space.
PATHOGENESIS
Thenar space infections may result from penetrating injury or local spread from adjacent flexor tenosynovitis or a subcutaneous abscess.
If not treated early, the infection may spread to the dorsal side of the hand after destroying the fascia of the adductor pollicis muscles and traveling between the transverse and oblique heads.
Midpalmar space infections usually result from direct penetrating trauma but may also result from spread of an adjacent flexor tenosynovitis or superficial abscess.
Hypothenar space infections usually result from direct penetrating trauma but may also result from spread of a superficial abscess.
Interdigital subfacial web space infections usually result from penetrating injury but may also result from spread of an adjacent lumbrical canal infection or infected palmar blister.1
Parona space infection may result from direct penetrating trauma, in which case the infection may be isolated to Parona space.
PATIENT HISTORY AND PHYSICAL FINDINGS
The patient may recall a history of a penetrating injury in the vicinity of the involved deep space.
In the case of a thenar space infection, the patient will present with swelling and tenderness in the thenar region.
The patient will hold the thumb in an abducted position to minimize the pressure for comfort.
If the infection has been present for some time, it may have spread dorsally, in which case swelling and tenderness will be found dorsally in the first web space.
In the case of a midpalmar space infection, there will be tenderness and swelling in the midpalm, although dorsal swelling may be more impressive due to the strength of the palmar aponeurosis.
The fingers will be held in a semiflexed posture.
This condition is distinguished from flexor tenosynovitis by relative lack of pain with passive motion of the fingers and with direct palpation of the flexor sheath along the digit.
In the case of interdigital subfacial web space infection, the patient will present with swelling and tenderness in the dorsum of the hand and maximal tenderness on the palmar aspect of the web space.
If the infection is severe, the fingers may be abducted on either side of the infected web space.1
Infection of Parona space is characterized by swelling in the distal volar forearm and pain with digital flexion.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree