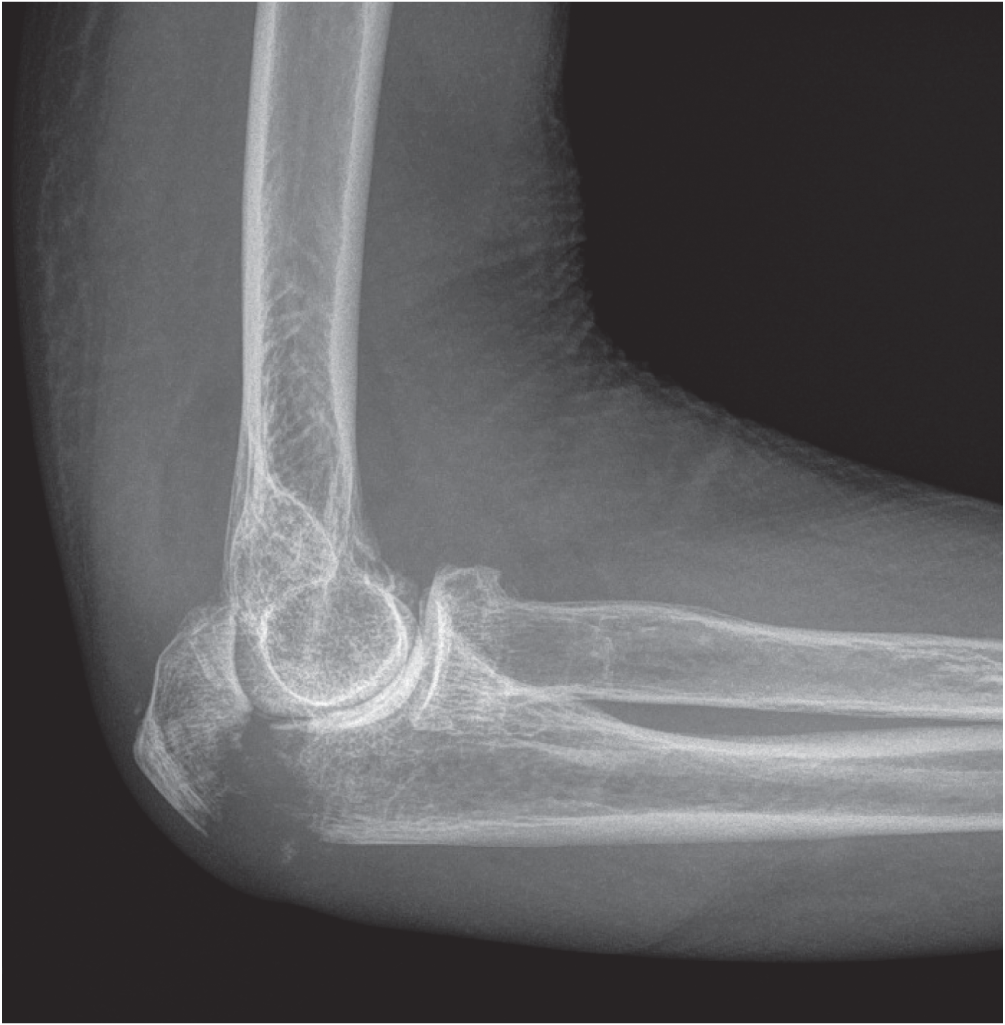
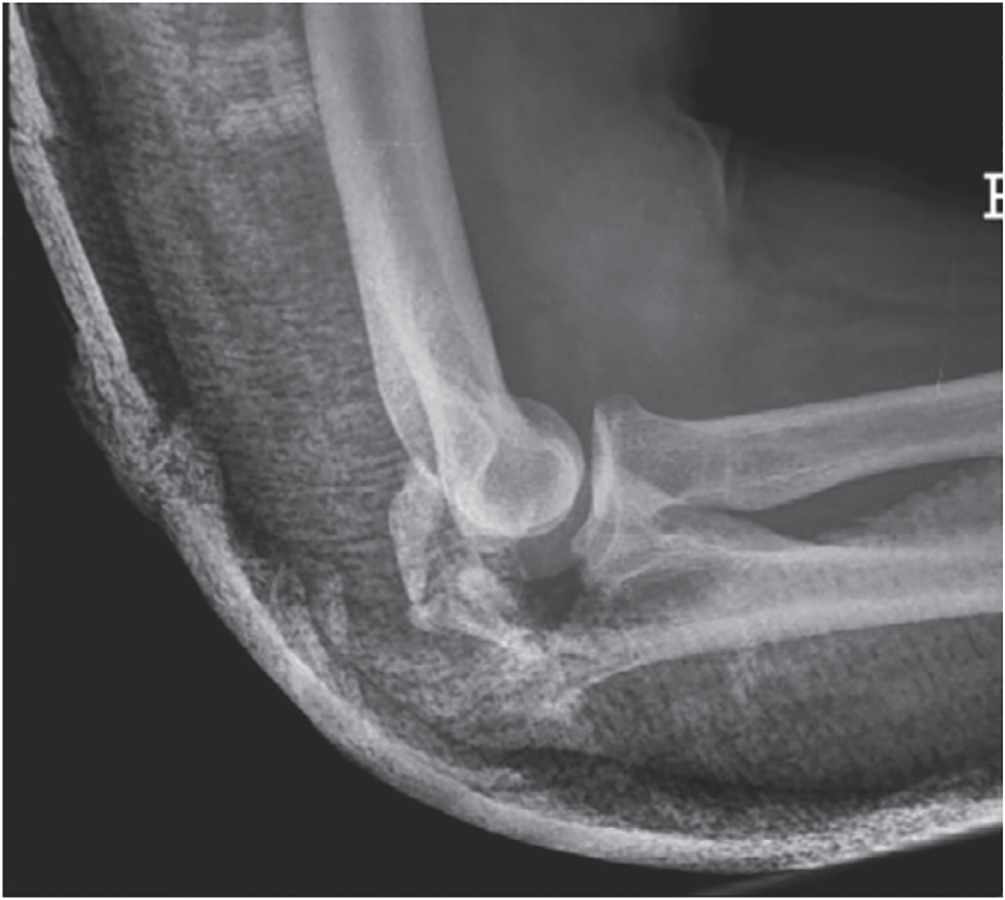
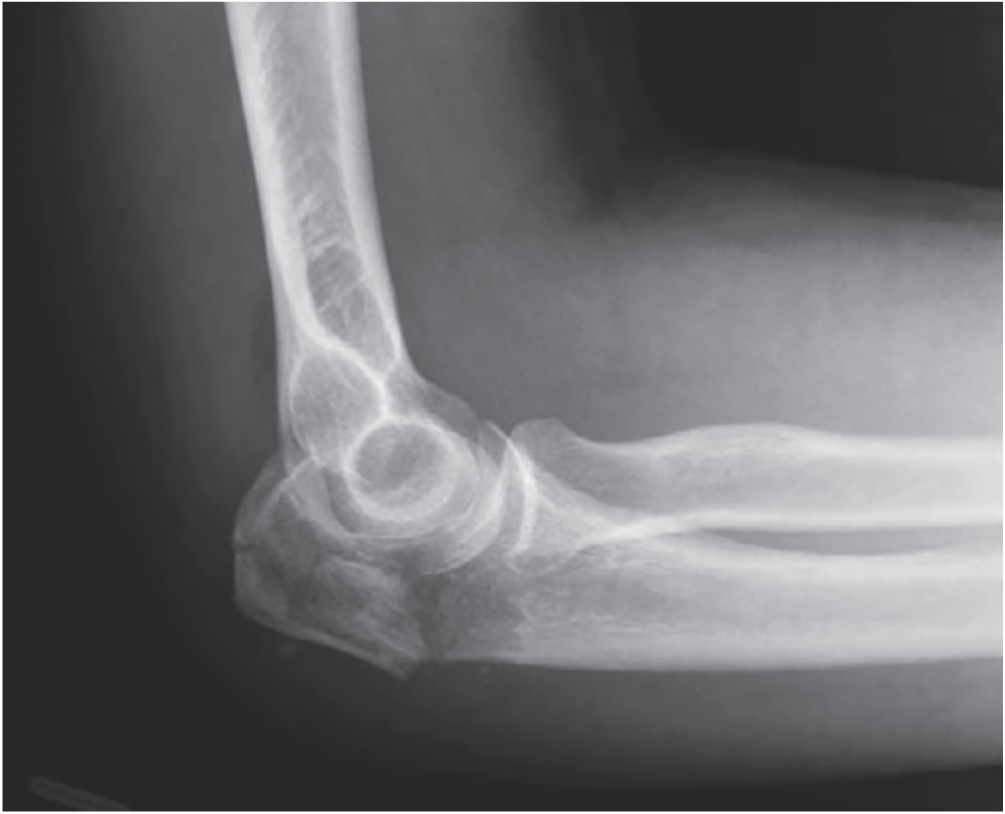
Michael C. Daly MD1 and Jesse B. Jupiter MD2 1Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA 2Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA Figure 85.1 Case 1. As internal fixation implants and surgical techniques have been refined, our ability to achieve stable fixation constructs in comminuted fracture patterns has improved. As a result, more fractures are being treated with open reduction and internal fixation, including olecranon fractures that may have previously been treated with fragment excision. Figure 85.2 Case 2. Figure 85.3 Case 3. Fragment excision with triceps advancement is usually now reserved for elderly patients with low functional demands and olecranon fractures with small proximal fragments and/or extensive comminution not amenable to internal fixation. Otherwise, internal fixation is typically the treatment of choice for acute displaced olecranon fractures. Since the 1940s, fragment excision with triceps advancement has been considered in the management of select olecranon fractures, especially in low‐demand elderly patients and injuries with extensive comminution not amenable to internal fixation.1–6 As the olecranon process contributes to the osseous constraint and stability of the ulnohumeral articulation,7 partial excision of the olecranon raises concern for creating iatrogenic elbow instability. There are conflicting reports in the literature as to how much of the olecranon may be excised. Clinical studies suggest that up to 50%2 (or perhaps as much as 60%,8 70%,6 or 80%4) of the semilunar notch of the olecranon may be safely excised without causing clinically relevant instability of the elbow, assuming an intact coronoid, radial head, and collateral ligaments.2,4,6,8 Cadaver studies of sequential olecranon resection have demonstrated increasing elbow angular and rotational laxity with increasing olecranon resection.9,10 While the landmark study by An and Morrey suggests up to 50% of the olecranon may be removed without adversely affecting ulnohumeral joint stability,7,9 a subsequent biomechanical study by Bell et al. suggested up to 75% of the olecranon articular surface can probably be removed, provided there are no concurrent injuries to the coronoid, radial head, or collateral ligaments.10 In the same study, however, Bell et al. also demonstrated that elbow instability became evident following even small amounts of olecranon resection. The authors therefore cautioned against olecranon resection if internal fixation is possible or alternative reconstructive options exist.10 Rettig et al. reported comparable range of motion (ROM) among four patients treated with excision and 34 patients treated with internal fixation, and a higher rate of complications (15% reoperation rate) with internal fixation. Despite these findings, the authors recommended excision only when internal fixation is not possible.1 Gartsman et al. compared primary excision (n = 53) with internal fixation (n = 54) for olecranon fractures.2 Excision was used for all severely comminuted and small avulsion fractures; patients with two‐part fractures were equally distributed between the excision and internal fixation groups. Twenty‐nine patients were reviewed at minimum two‐year follow‐up (range 2–15 years); of the 15 patients who underwent primary excision, nine had 33–50% of the articular surface excised, and the six had ≥50% of the articular surface excised. Comparing patients treated with primary excision versus internal fixation at two years’ minimum follow‐up, there was no difference in pain, instability, ROM, or elbow extension strength.2 In Case 2, a low‐demand elderly patient presented with a stable displaced olecranon fracture with small proximal fragments and extensive comminution (Figure 85.2). Key takeaways: The literature regarding the management of displaced olecranon fractures is replete with studies debating the virtues of various surgical fixation constructs. Yet the more fundamental question has remained largely unanswered: which patients do better with surgery as compared with no surgery? Although displaced olecranon fractures are typically treated surgically, a recent prospective randomized trial comparing operative with no‐operative care suggested comparable outcomes and fewer complications with nonsurgical management in low‐demand elderly patients.11
85
Olecranon Fractures
Clinical scenarios
Cases 1 and 2
Case 3
Top three questions
Question 1: In patients with displaced olecranon fractures treated surgically, how do the outcomes compare between those treated with internal fixation vs fragment excision and triceps advancement?
Rationale
Clinical comment
Available literature and quality of the evidence
Findings
Resolution of clinical scenario
Question 2: In low‐demand elderly patients with displaced olecranon fractures, does surgery result in improved outcomes compared with nonsurgical treatment?
Rationale
Clinical comment
Available literature and quality of the evidence
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





