Section 4 Lower Limb Injections
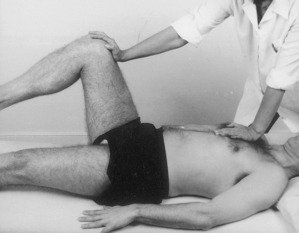
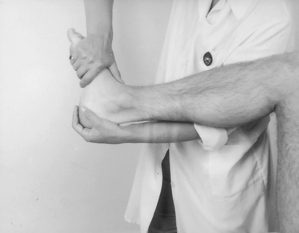
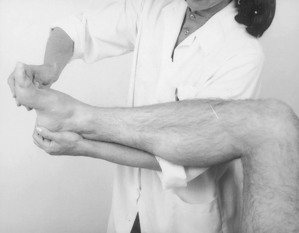
Examination of the lower limb
| Hip tests | ||
|---|---|---|
| In supine | In prone | |
| Passive lateral rotation | Passive extension | |
| medial rotation | Resisted lateral rotation | |
| flexion | medial rotation | |
| abduction | knee extension | |
| adduction | ||
| Resisted flexion | ||
| abduction | ||
| adduction | ||
| Hip capsular pattern: most loss of medial rotation, less of flexion and abduction, least of extension | ||
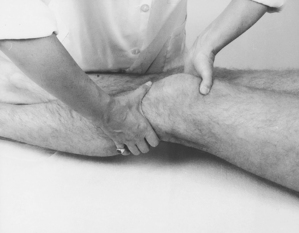
| Knee tests | ||
| Passive flexion | Draw test | |
| extension | Glide test | |
| valgus | Meniscal tests | |
| varus | Resisted extension | |
| rotation | flexion | |
| medial rotation | ||
| Knee capsular pattern: more loss of flexion than extension | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ankle and foot tests | ||
| Ankle | Subtalar | Forefoot |
| Passive dorsiflexion | Passive abduction | Passive abduction |
| plantarflexion | adduction | adduction |
| eversion | extension | |
| inversion | flexion | |
| Resisted dorsiflexion | ||
| plantarflexion | ||
| eversion | ||
| inversion | ||
| Ankle/foot capsular patterns: | ||
| Ankle: More loss of plantarflexion than dorsiflexion | ||
| Subtalar joint: More loss of adduction | ||
| Forefoot: Loss of adduction, dorsiflexion and supination | ||
| Big toe: More loss of extension than flexion | ||
| Toes: More loss of flexion than extension | ||
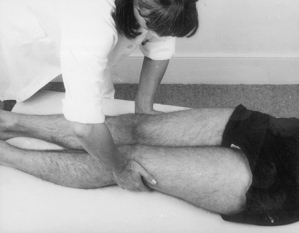
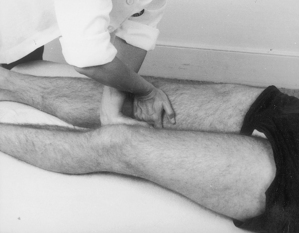
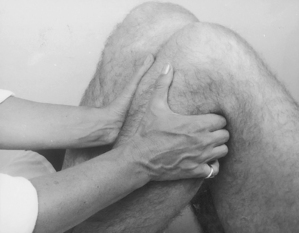
Hip joint
Acute or chronic capsulitis
Causes and findings
• Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis or traumatic capsulitis with night pain and severe radiating pain no longer responding to physiotherapy
Technique
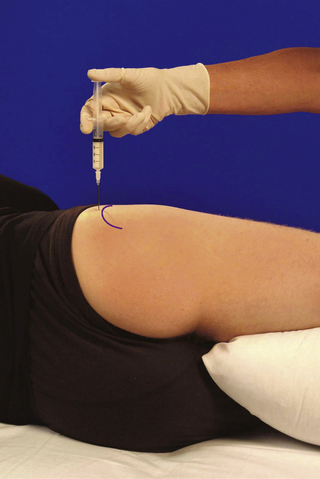
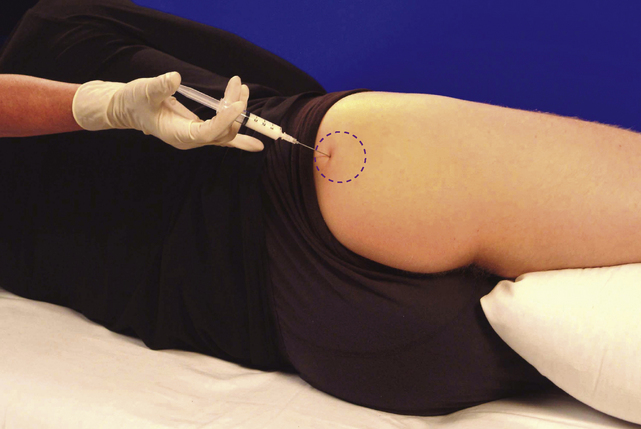
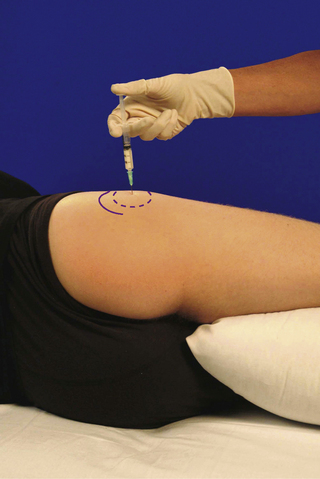
• Patient lies on pain-free side with lower leg flexed and upper leg straight resting horizontally on pillow
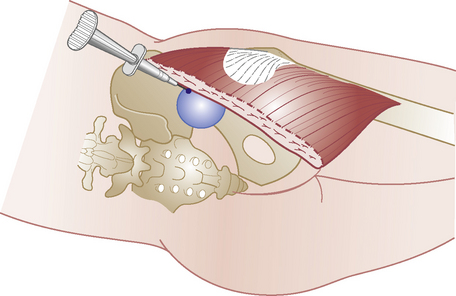
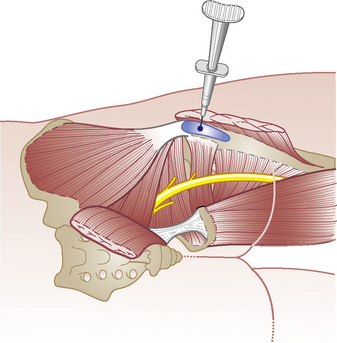
• Palpate the triangular greater trochanter with caudal thumb and middle finger placed either side of the base and identify the apex of the bone with index finger
• Insert needle perpendicularly about a thumb’s width proximal to palpable apex of trochanter until it touches the neck of femur
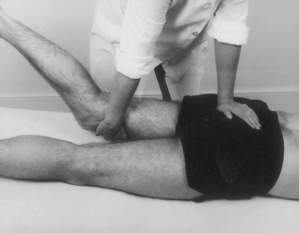
Psoas bursa
Chronic bursitis
Technique
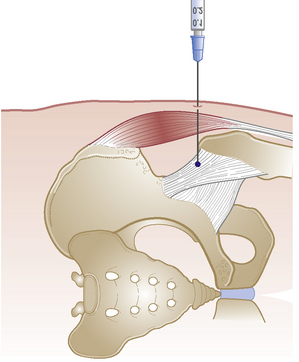
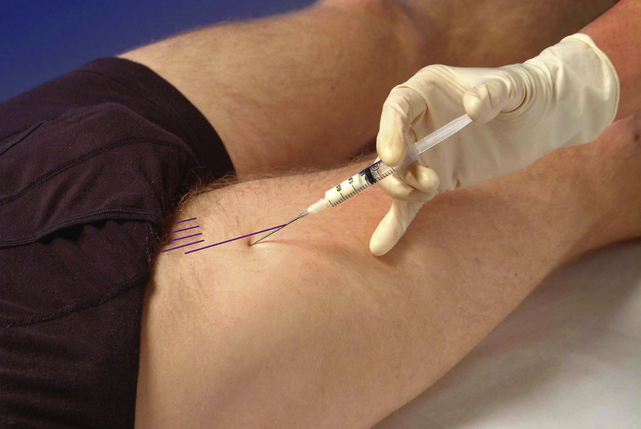
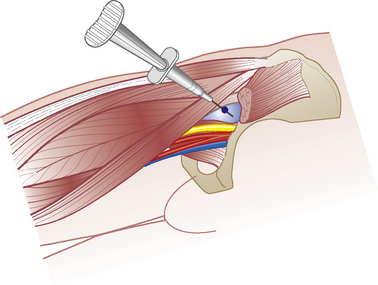
• Identify femoral pulse at mid-point of inguinal ligament. Mark a point three fingers distally and three fingers laterally, in line with the anterior superior iliac spine on medial edge of sartorius
• Insert needle at this point and aim 45° cephalad and 45° medially. Visualize the needle sliding under the three major vessels through the psoas tendon until point touches bone on anterior aspect of neck of femur