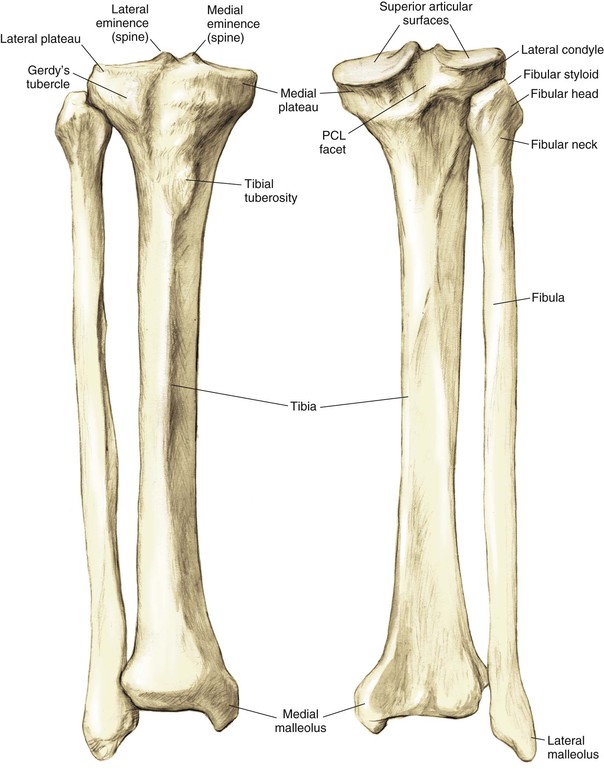
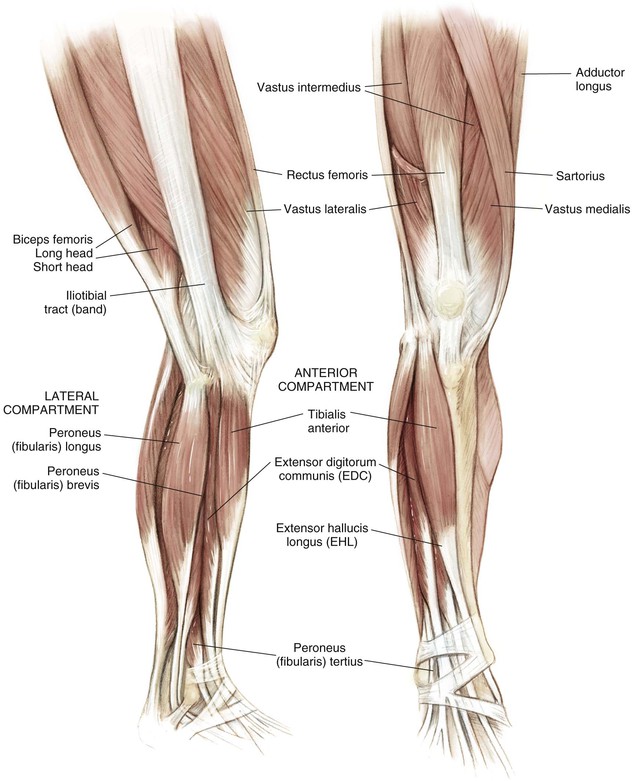
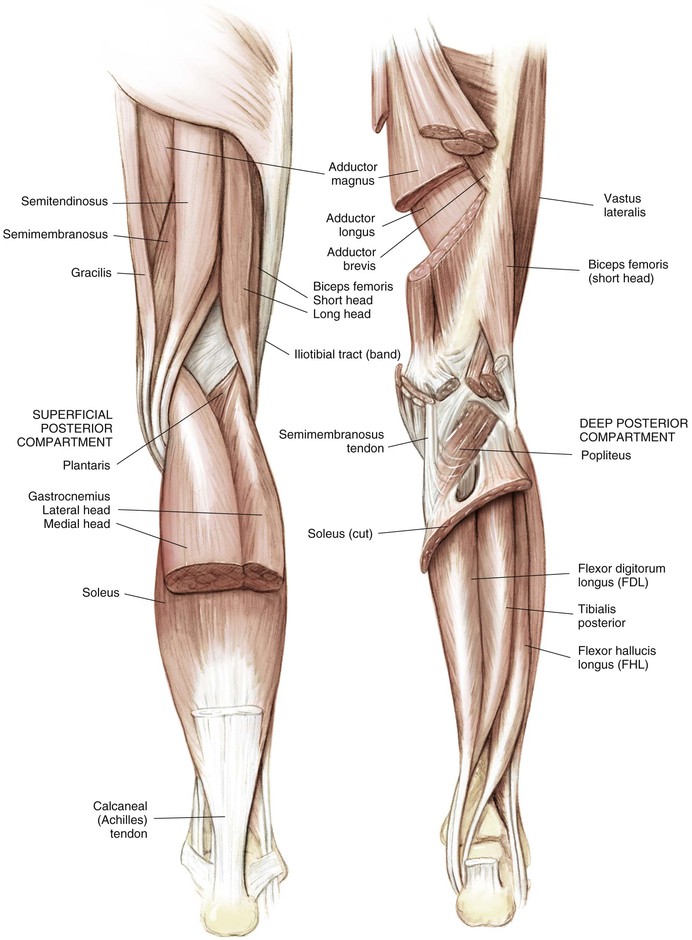
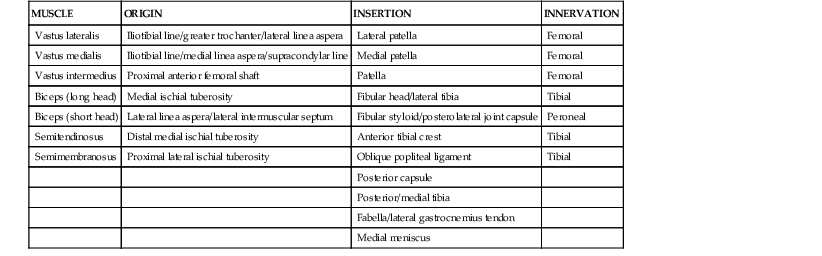
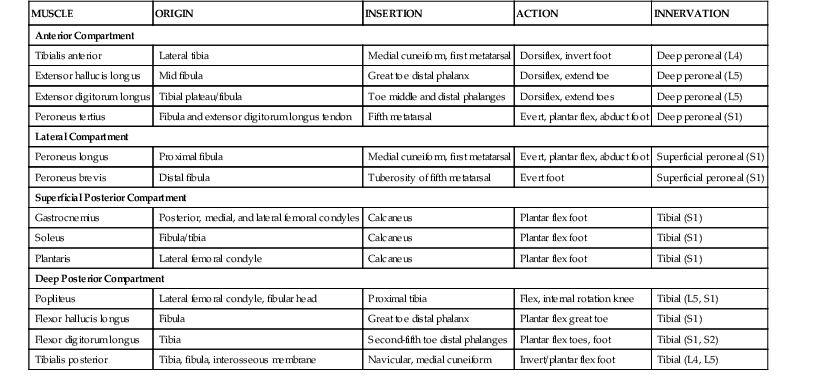
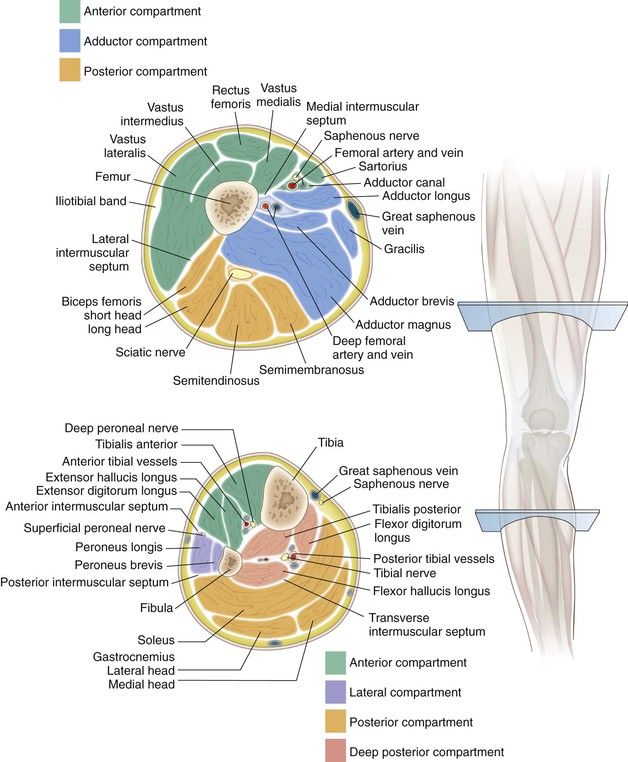
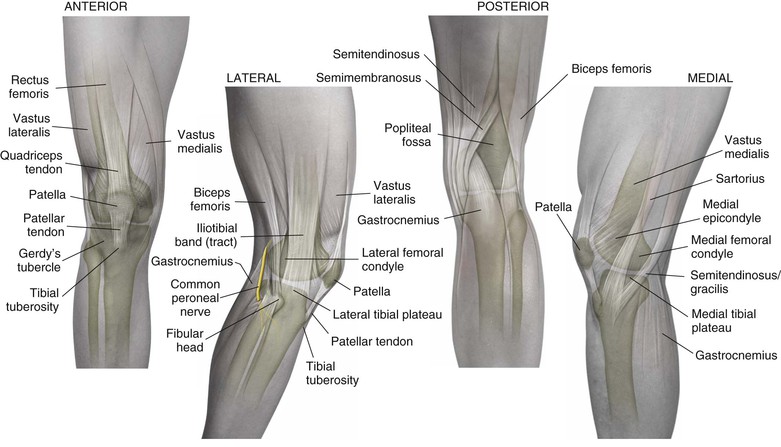
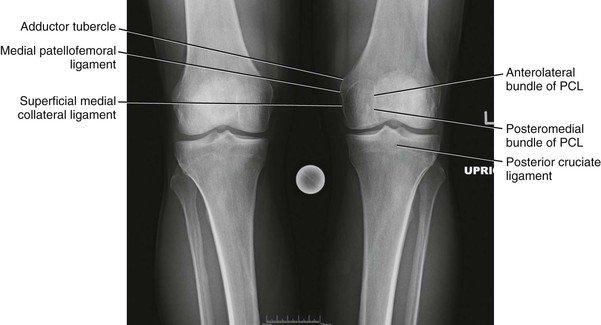
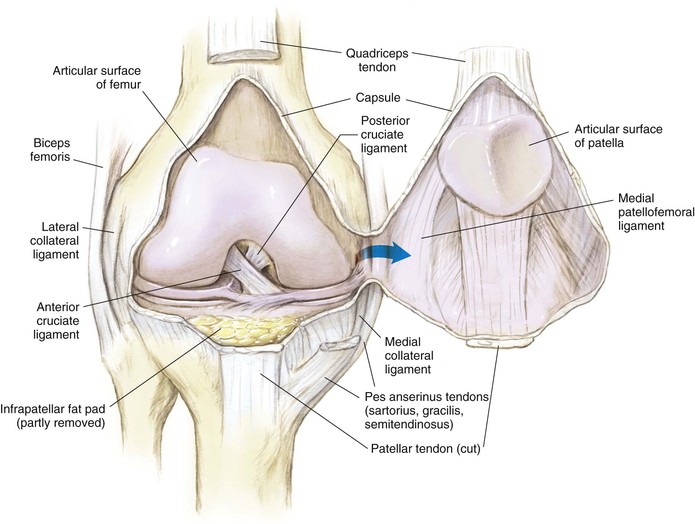
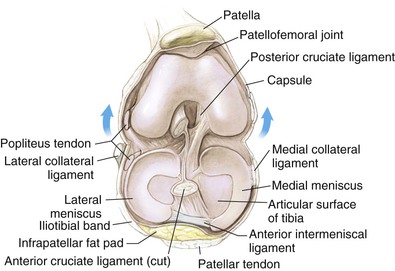
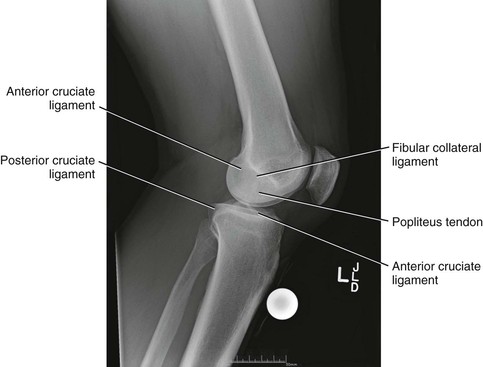
Robert F. LaPrade, Nicholas I. Kennedy The tibia is the second longest bone in the body The plateau areas match the corresponding femoral condyle • The medial tibial plateau is broad and concave • The lateral tibial plateau is smaller and convex The tibial eminences (spines) define the borders of the cruciate ligament insertions • The ACL lies between the eminences The tubercles serve as attachments for tendons • The tibial tubercle (or tuberosity) serves as the patellar tendon attachment The knee joint is the largest joint in the body The knee joint is a ginglymus (hinge) joint that allows rolling and sliding • ACL—resists anterior translation • PCL—resists posterior translation • MCL—resists valgus displacement • LCL—resists varus displacement • Popliteus tendon—resists external rotation • Posteromedial and posterolateral capsular structures—resist rotation • Menisci • Medial—semicircular and broader posteriorly • Lateral—more circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface (Figs. 7-12 through 7-15)
Knee and Lower Leg
Regional Anatomy
Osteology
Distal Femur (Fig. 7-1)
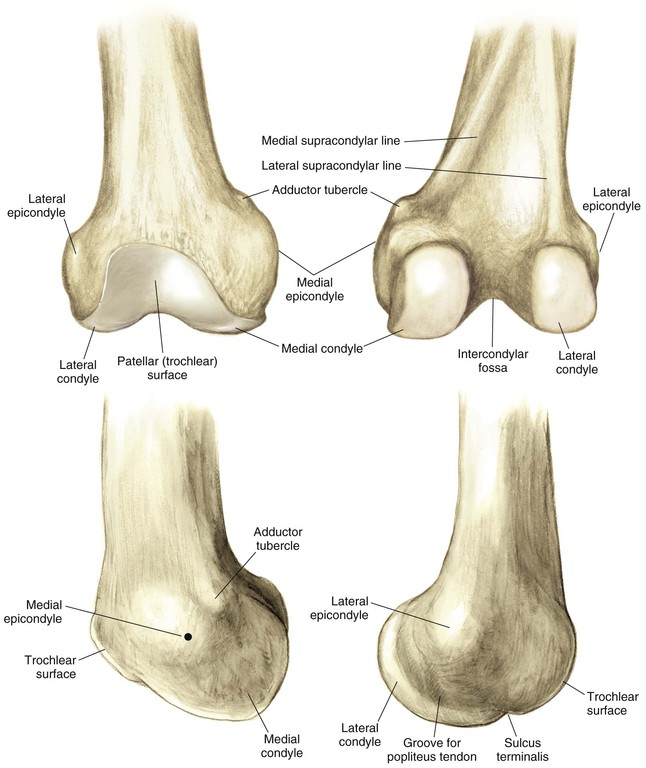
Proximal Tibia (Fig. 7-2)
Arthrology
Knee Joint (Figs. 7-4 and 7-5)
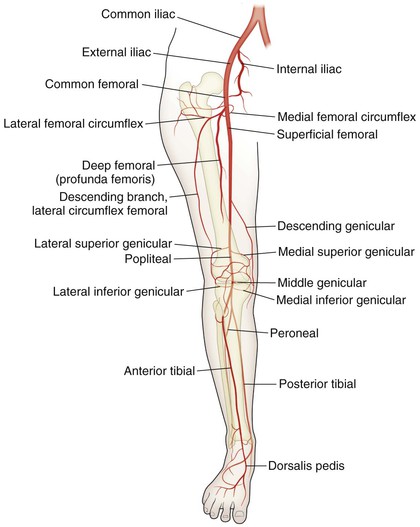
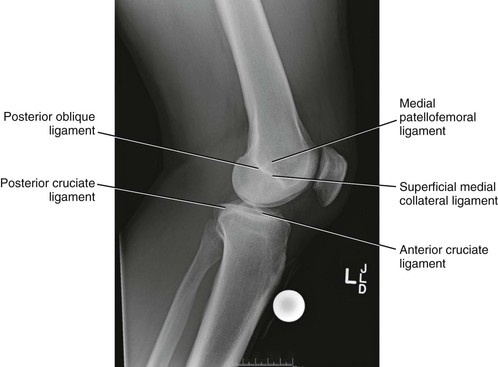
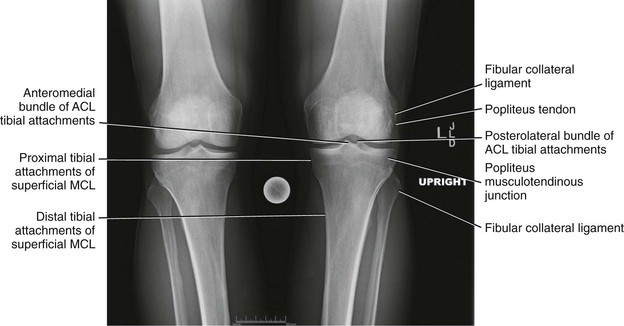
Radiologic Landmarks
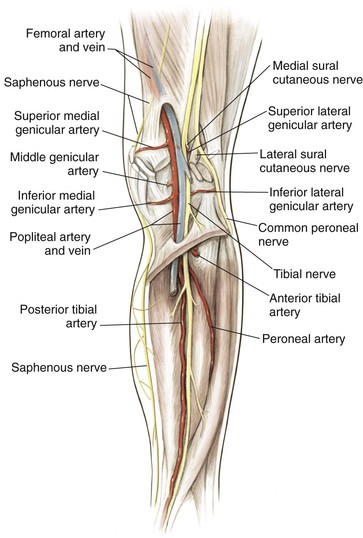
Hazards (Fig. 7-16)
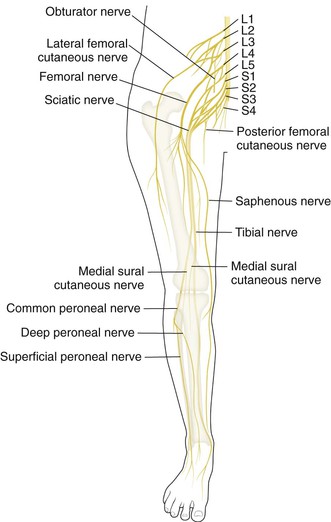
Sciatic Nerve

Knee and Lower Leg
Chapter 7