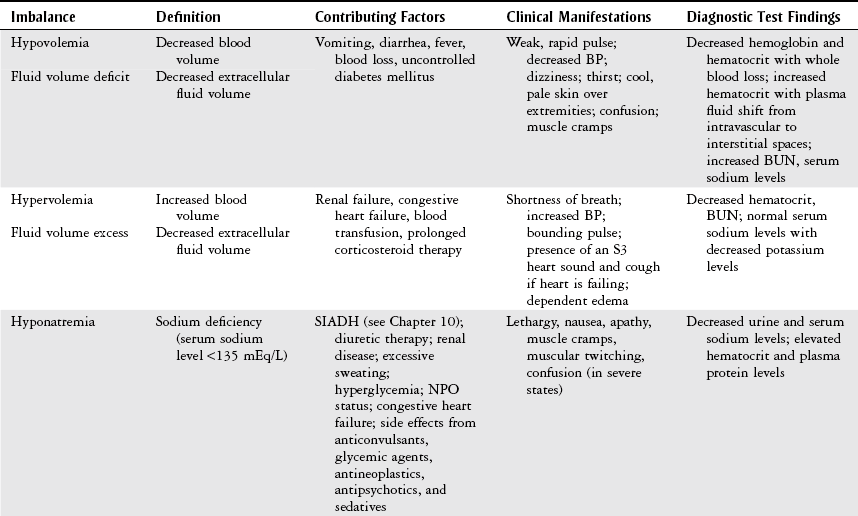
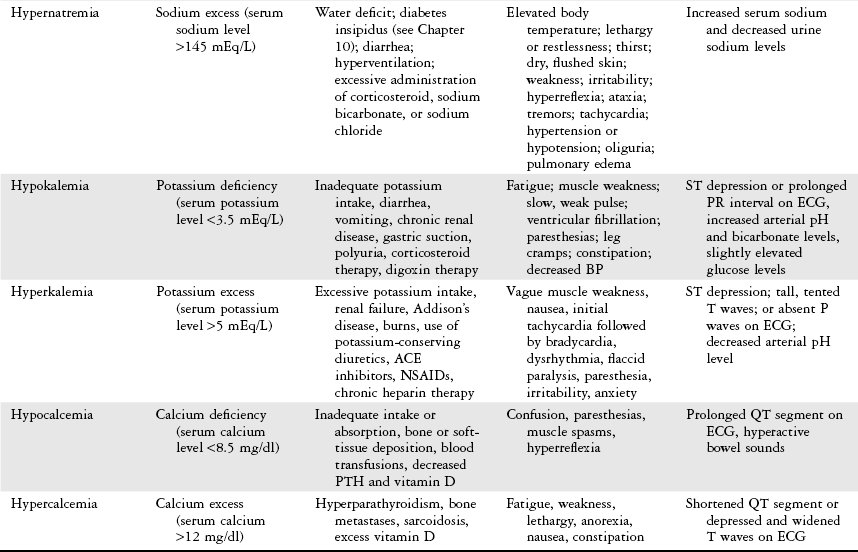
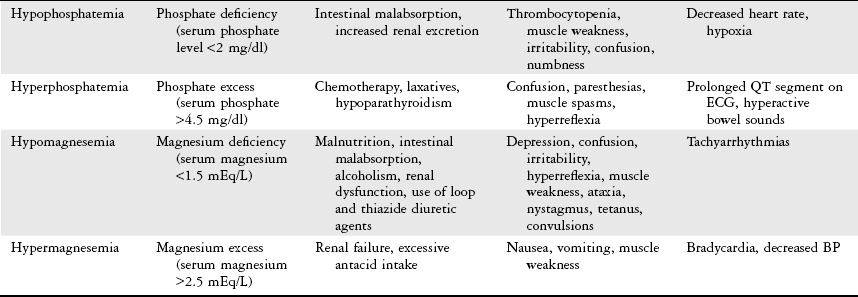
Chapter 15 Provide a description of fluid and electrolyte imbalance including: 1 Clinical manifestations and diagnostic studies 2 Contributing health conditions Please refer to Appendix A for a complete list of the preferred practice patterns in order to best delineate the most applicable practice pattern for a given patient with fluid and electrolyte imbalance. • Concentration of intracellular and extracellular fluids • Type and concentration of electrolytes • Permeability of cell membranes The total amount of fluid in the body is distributed between the intracellular and extracellular compartments. Intracellular fluid contains approximately two-thirds of the body’s fluid. Extracellular fluid is further made up of interstitial fluid and intravascular fluid, which is the blood and plasma.1–3 Fluid imbalance occurs when there is a deficit or an excess primarily in extracellular fluid.1–6 Table 15-1 provides an overview of fluid imbalances. TABLE 15-1 Data from Huether SE: The cellular environment: fluids and electrolytes, acids and bases. In McCance KL, Huether SE, Brashers VL et al, editors: Pathophysiology, the biologic basis for disease in adults and children, ed 6, St Louis, 2010, Mosby, pp 96-125; The body fluid compartments: extracellular and intracellular fluids; edema. In Hall JE, editor: Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology, ed 12, Philadelphia, 2011, Saunders, pp 285-301; Porth CM: Alterations in fluids and electrolytes. In Porth CM, editor: Pathophysiology, concepts of altered health states, ed 6, Philadelphia, 2002, Lippincott, pp 693-734; Gorelick MH, Shaw KN, Murphy KO: Validity and reliability of clinical signs in the diagnosis of dehydration in children, Pediatrics 99(5):E6, 1997; Mulvey M: Fluid and electrolytes: balance and disorders. In Smeltzer SC, Bare BG, editors: Brunner and Suddarth’s textbook of medical-surgical nursing, ed 8, Philadelphia, 1996, Lippincott; Goodman CC, Kelly Snyder TE: Problems affecting multiple systems. In Goodman CC, Boissonnault WG, editors: Pathology: implications for the physical therapist, Philadelphia, 1998, Saunders; Fall PJ: Hyponatremia and hypernatremia: a systematic approach to causes and their correction, Postgrad Med 107(5):75-82, 2000; Marieb EN editor: Human anatomy and physiology, ed 2, Redwood City, CA, 1992, Benjamin Cummings, p 911.
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
Preferred Practice Patterns
Fluid Imbalance
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






