Chapter 23. Disorders of the wrist and hand
Rheumatoid arthritis
Wrist
Rheumatoid arthritis affects synovium and the large amount of synovium around the wrist and inferior radioulnar joints makes them especially vulnerable to the disease.
Clinical features
The disease follows the usual pattern. The joint is painful and swollen in the acute attack but then subsides. If the disease cannot be controlled, the mass of synovium on the dorsum of the hand engulfs the extensor tendons and all may rupture (Fig. 23.1).
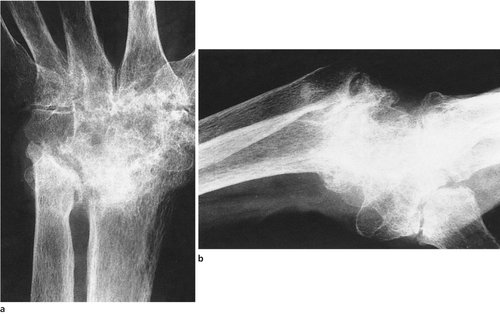 |
| Fig. 23.1 Late rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist and carpus. Note that the carpal bones have fused and the wrist is ankylosed in flexion. |
The tendons which cross the joint also become eroded and eventually rupture. The extensor tendon of the little finger is usually the first to go, but the extensor pollicis longus can also rupture where it runs around Lister’s tubercle at the lower end of the radius (Fig. 23.2 and Fig. 23.3). Later the ligaments stretch, bone collapses, the joint becomes unstable and a characteristic deformity develops, with the wrist radially deviated and supinated on the forearm and the fingers in ulnar deviation.
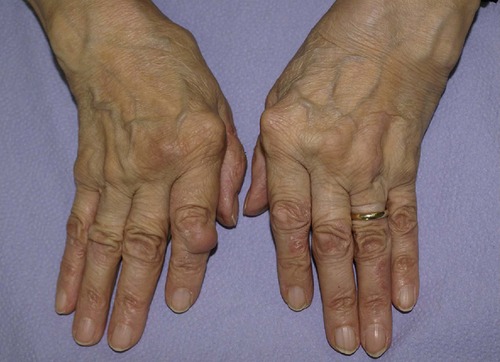 |
| Fig. 23.2 Rheumatoid of the hands with synovial swellings and ulnar deviation. |
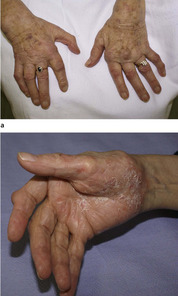 |
| Fig. 23.3 Rheumatoid of the hand: (a) postoperative with correction of m.c.p. joints, synovectomy of wrist; (b) with associated psoriasis in palm. |
Treatment
Conservative treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs and rest is usually effective but if the synovitis cannot be controlled medically, surgery is needed for the following indications:
1. Synovectomy to remove painful and inflamed synovium if it cannot be controlled by conservative means.
3. If the lower end of the ulna is unstable it must be excised before it damages the tendons that cross the wrist.
4. Arthrodesis if the wrist joint is unstable. Note: Arthrodesis limits flexion and extension of the wrist only, leaving pronation and supination unaffected.
5. Replacement arthroplasty.
Although arthrodesis is contraindicated in multiple joint disease (p. 298), arthrodesis of the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis produces a good result. If both wrists are to be arthrodesed, care should be taken not to fix them both in extension. With both wrists dorsiflexed it is difficult to fasten buttons and personal hygiene is almost impossible. Hold both your own wrists in dorsiflexion and see how inconvenient it is.
Hand
Rheumatoid arthritis of the hand presents many problems and much disability. The disease usually presents with symmetrical painful swelling of the metacarpophalangeal joints caused by synovial proliferation, and is often first visible as in-filling of the valleys between the metacarpal heads (Fig. 23.4). The small joints are destroyed later and fixed deformities develop (Fig. 23.5).
 |
| Fig. 23.4 Filling of the ‘valleys’ between the metacarpal heads in rheumatoid arthritis. |
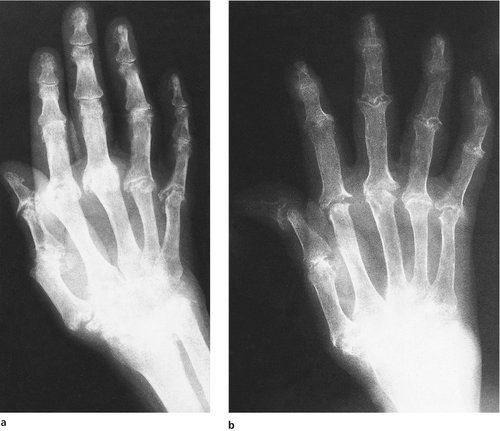 |
| Fig. 23.5 (a) Rheumatoid arthritis of the hand with destruction of the small joints. (b) Late rheumatoid arthritis of the hand with fixed hyperextension of the first interphalangeal joint and fixed adduction of the first m.c.p. joint. |
Treatment
Management of the rheumatoid hand is almost a specialty in its own right.
Initial treatment is conservative, with resting splints, occupational therapy and drugs, and is best conducted by a rheumatologist. If rest, night splints and anti-inflammatory drugs do not control symptoms or induce remission, surgical synovectomy may be necessary to remove exuberant synovium from the metacarpophalangeal joints. This will relieve pain but there is no evidence that it minimizes joint destruction.
If conservative measures fail, operation must be considered. This entails a careful and thorough assessment of the patient’s disability and a critical estimate of the likely benefit from operation.
Operation is done neither because the disease is there nor because the operation is possible, but to produce a specific improvement in function.
There are several indications for operation:
1. To repair ruptured tendons by using a ‘spare’ tendon, such as the extensor indicis proprius, or by attaching the ruptured tendons to those that remain intact to produce a common extensor action.
2. To salvage destroyed metacarpophalangeal joints by replacement arthroplasty.
3. To correct other deformities, including the swan-neck deformity that results from tightness of the intrinsic muscles and damage to the volar plate and flexor digitorum sublimis. Dislocation of the extensor tendons may also need correction (Fig. 23.6).
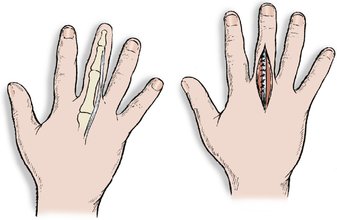 |
| Fig. 23.6 Tendon displacement in rheumatoid arthritis. The extensor tendon can slip off the back of the m.c.p. joint and may need to be replaced. |
Osteoarthritis
Wrist
Osteoarthritis of the wrist is usually the late result of trauma, often a fractured scaphoid, and causes pain and stiffness of the wrist after use (Fig. 23.7).
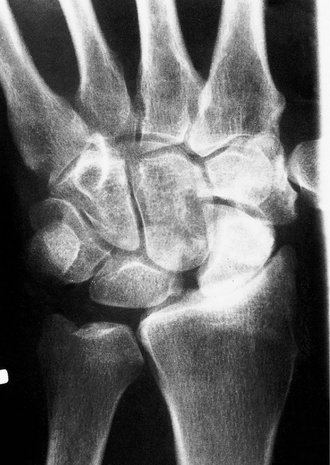 |
| Fig. 23.7 Osteoarthritis of the wrist with narrowing of the radiocarpal joint following perilunate dislocation. |
Treatment
If the symptoms only occur when the patient is working, a firm wrist support may be sufficient. If this is not effective, arthrodesis is needed. A trial period in plaster before operation will allow the patient to assess the likely result and be convinced that pronation and supination really are possible with the wrist fused.
Hand
The trapeziometacarpal joint is affected by osteoarthritis and causes pain on gripping and twisting movements (Fig. 23.8). The joint is tender on palpation, abduction of the thumb is limited, and longitudinal pressure reproduces the symptoms.
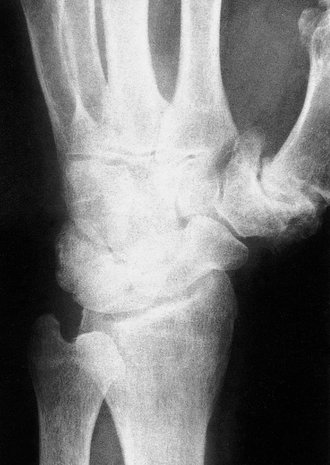 |
| Fig. 23.8 Advanced osteoarthritis of the first carpometacarpal joint. |
Treatment
Conservative treatment includes a support to splint the thumb, anti-inflammatory drugs and restriction of activity. If these measures are unsuccessful, operation may be required.
Fingers
Generalized osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joints produces unsightly osteophytic lumps at the margins of the interphalangeal joints (Fig. 23.9). These are called Heberden’s nodes if they involve the distal interphalangeal joints and Boucher’s nodes if they involve the proximal interphalangeal joints. They are different from the swelling of the interphalangeal joints seen in rheumatoid arthritis.
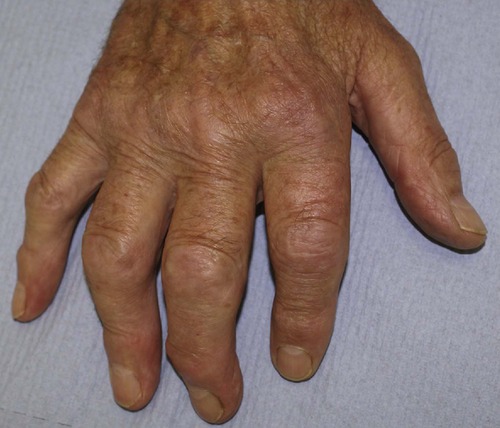 |
| Fig. 23.9 Osteoarthritis of the hand. |
Treatment
No operative treatment is helpful but physiotherapy may improve function.
Disorders of tendons
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
The extensor pollicis brevis and the abductor pollicis longus pass beneath a tight fibrous bridge just proximal to the radial styloid process and repeated stressing of these tendons by wringing out dish cloths or other twisting movements can cause a localized tenosynovitis (Fig. 23.10). The tendon swells, movements become painful and the fibrous bridge becomes thickened and forms a firm swelling on the lateral side of the radius just proximal to the wrist, which can be alarming. The tendon sheaths sometimes become inflamed above and below the fibrous bridge and make a soft creaking sound with movement.
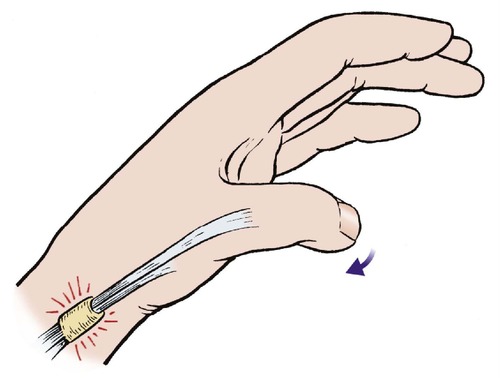 |
| Fig. 23.10 De Quervain’s disease. The extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons are irritated as they pass beneath a fibrous bridge proximal to the radial styloid. |
The diagnosis can be confirmed by stressing the tendons. Ask the patient to grasp the thumb with the other fingers and then push the hand gently into flexion and ulnar deviation. This stretches the affected tendons and reproduces the pain.
Treatment
If elimination of the activity which caused the condition does not produce relief, steroid injection into the tendon sheaths can be helpful. If this is ineffective, the fibrous bridge must be divided surgically.
Extensor tenosynovitis
The extensor tendons, which do not have a tendon sheath, are less vulnerable to tenosynovitis than the flexors but the paratenon can become inflamed. Affected tendons produce the creaking, leathery sensation of muffled crepitus as they move.
Treatment
Rest and splintage are usually effective but steroid injection is sometimes necessary.
Trigger finger
The flexor profundus longus tendon is subjected to friction where it enters its tendon sheath and swelling can occur on the tendon at this point (Fig. 23.11). As the swelling enters the tendon sheath it irritates the opening of the sheath and this can narrow it still further. A vicious circle is therefore established, with the swelling aggravating the constriction and vice versa.
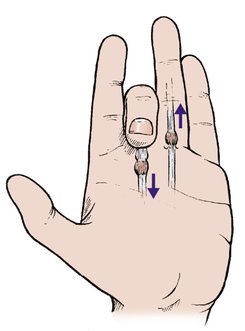 |
| Fig. 23.11 Trigger finger. Triggering is caused by a swelling on the flexor tendon catching as it moves in and out of the opening into the fibrous flexor sheath. |
Clinical features
The swelling on the tendon prevents the tendon moving easily and causes a ‘pop’ as it enters the tendon sheath. The flexors are stronger than the extensors and the tendon becomes stuck in the flexed position. Extension is only possible passively, when it will straighten with a click.
This phenomenon is known as ‘triggering’ and is usually worse first thing in the morning after sleeping with the fingers flexed but improves during the day as soft tissue swelling subsides.
Treatment
The symptoms usually follow unaccustomed repetitive activity and settle with rest and elimination of the cause. If this is ineffective a steroid injection into the tendon sheath is needed.
If the symptoms persist after three injections, the fibrous opening of the flexor tendon sheath must be incised to ease the passage of the tendon swelling. The operation is effective, but only required if all conservative measures have failed.
Trigger thumb
The same phenomenon can occur at the thumb, which can become locked in flexion. The lesion is also seen in infancy, usually before the age of 2.









