Arthroscopic Dorsal Radiocarpal Ligament Repair
David J. Slutsky
DEFINITION
Tears of the dorsal radiocarpal ligament (DRCL) are more common than previously suspected. They are best seen through a volar radial portal and are amenable to arthroscopic repair.
DRCL tears appear to be part of a spectrum of radial- and ulnar-sided carpal instability, as evidenced by the frequent association with scapholunate and lunotriquetral ligament injuries as well as triangular fibrocartilage (TFC) tears.
Isolated DRCL tears can be solely responsible for wrist pain.
Good results are obtained after arthroscopic repair of isolated DRCL tears. Results of DRCL repairs are less predictable when seen in combination with other types of carpal pathology.8
Recognition of this condition and further research into treatment methods is needed.
ANATOMY
The DRCL (FIG 1) is an extracapsular ligament on the dorsum of the wrist. It originates on the tubercle of Lister and moves obliquely in a distal and ulnar direction to attach to the tubercle of the triquetrum. Its radial fibers attach to the lunate and lunotriquetral interosseous ligament.2
The dorsal intercarpal (DIC) ligament originates from the triquetrum and extends radially to attach onto the lunate, the dorsal groove of the scaphoid, and then the trapezium.
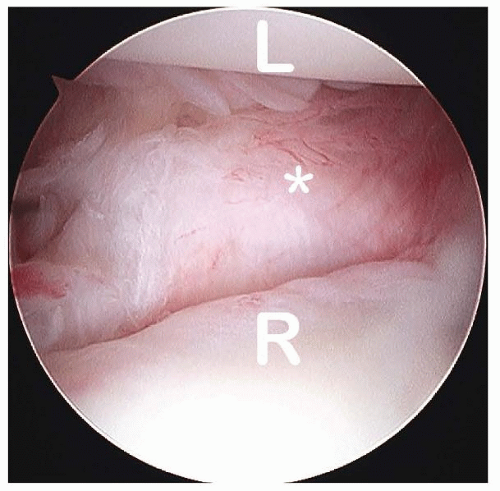
FIG 1 • View of a normal DRCL (asterisk) from the volar radial (VR) portal. L, lunate; R, radius. (Copyright David J. Slutsky MD.)
The lateral V configuration of the DRCL and the DIC functions as a dorsal radioscaphoid ligament.
It can vary its length by changing the angle between the two arms while maintaining its stabilizing effect on the scapholunate joint during wrist flexion and extension.
This would require changes in length far greater than any single fixed ligament could accomplish.9
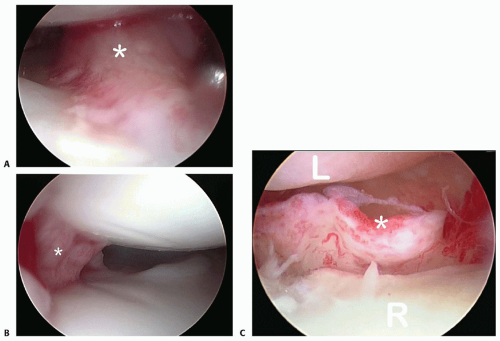
When viewed from a volar radial portal, a DRCL tear can be seen immediately ulnar to the 3-4 portal, just underneath the lunate.
The DRCL tear can also be seen tangentially from the 6R portal (FIG 2 A-C).
PATHOGENESIS
The wrist has a number of primary and secondary stabilizers.
The scapholunate interosseous ligament (SLIL), the lunotriquetral interosseous ligament (LTIL), and the triangular fibrocartilaginous complex (TFCC) are the primary stabilizers.
The capsular ligaments, including the radioscaphocapitate, radiolunotriquetral, ulnolunate, ulnotriquetral, dorsal radiocarpal, and DIC ligaments, can be thought of as secondary stabilizers.3
A chronic tear of a primary stabilizer may culminate in the attenuation or tearing of the secondary stabilizer.
This is seen in patients with a triquetrolunate dissociation of more than 6 months’ duration, in whom arthroscopy often reveals fraying of the ulnolunate ligaments and ulnotriquetral ligaments.12
DRCL tears appear to be part of a spectrum of radial- and ulnar-sided carpal instability, as evidenced by the frequent association with SLIL, LTIL, or TFC tears. They have also been associated with midcarpal instability.4
The DRCL tear may occur after or precede these injuries.
In a recent study, 35 of 64 patients who underwent arthroscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of refractory wrist pain were noted to have associated DRCL tears, for an overall incidence of 55%.7
Five patients had an isolated DRCL tear.
Thirteen patients in this series had SLIL instability, tear, or both; 7 of 13 (54%) also had a DRCL tear. Of this subgroup, 4 patients had Geissler stage 1 or 2 instability and 3 had a Geissler stage 3 or 4 tear.
Seven patients had LTIL instability, tear, or both; 2 of 7 (28%) also had a DRCL tear. Of this subgroup, 1 patient had Geissler stage 2 instability and 1 had a Geissler stage 3 or 4 tear.
Two patients had a capitohamate ligament tear; one of these patients also had a DRCL tear.
Seven patients had a solitary TFCC tear; 6 of 7 (86%) were in association with a DRCL tear. One patient had a chronic ulnar styloid nonunion and a DRCL tear. There was TFCC fraying but no tear or detachment.
Two or more lesions were present in 23 patients; DRCL tears were present in 12 patients (52%). Sixty-two percent of the combined lesions that were associated with a DRCL tear also included a TFCC tear.
NATURAL HISTORY
The natural history of DRCL tears is not completely certain.7
Unrecognized DRCL tears may be a cause for treatment failures in patients with persistent dorsal wrist pain.
In nondissociative carpal instability, the pain is believed to be caused by dynamic joint incongruity.1 Chronic detachment of the ulnar sling on the triquetrum has been implicated as a cause of wrist pain in these cases.11 It is plausible that impingement of the torn edge of the DRCL against the lunate can have a similar effect.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree