Procedure 31 Interspinous Process Motion-Sparing Implant
Indications
 Lumbar stenosis at one or two levels
Lumbar stenosis at one or two levels
 Patient must report a resolution of symptoms when seated or flexed forward (i.e., “shopping cart” sign) when upright.
Patient must report a resolution of symptoms when seated or flexed forward (i.e., “shopping cart” sign) when upright.
Indications Pitfalls
• Symptoms unresolved with lumbar flexion
• Axial back pain as the main complaint (versus buttock and/or leg pain)
• Osteoporosis with recent history of fragility fracture (severe osteoporosis)
• Spondylolisthesis greater than 25% on static or dynamic radiographs
• Significant scoliosis (greater than 25 degrees at the level of stenosis)
Indications Controversies
• “Mild to moderate” stenosis indication for ISP implantation refers to patients’ symptoms (able to walk at least 50 feet), not the MRI findings.
• Three-level implantation of the device is not currently approved. Some surgeons have had success with treatment of three-level stenosis with ISP implantation.
Figures 31-3, 31-5, 31-6, and 31-8 © 2011 Medtronic Spine, LLC. Used with permission.
Examination/Imaging
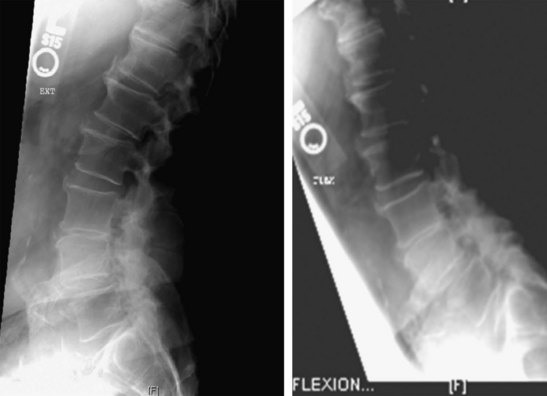
 Standing anteroposterior (AP), lateral (neutral, extension [left] and flexion [right]) views (Figure 31-1)
Standing anteroposterior (AP), lateral (neutral, extension [left] and flexion [right]) views (Figure 31-1)
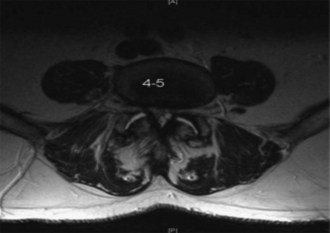
 MRI with axial, sagittal, and coronal imaging to assess disk herniation, canal stenosis, and Modic changes (Figure 31-2)
MRI with axial, sagittal, and coronal imaging to assess disk herniation, canal stenosis, and Modic changes (Figure 31-2)
Surgical Anatomy
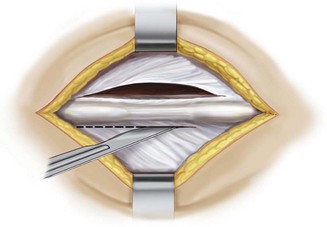
 Midline skin incision with bilateral fascial incision exposing the inferior and superior aspects of the spinous processes at the selected interspinous segment (Figure 31-3)
Midline skin incision with bilateral fascial incision exposing the inferior and superior aspects of the spinous processes at the selected interspinous segment (Figure 31-3)
 Careful preservation of the supraspinous ligament
Careful preservation of the supraspinous ligament
Positioning
 Lateral positioning on radiolucent table (Figure 31-4)
Lateral positioning on radiolucent table (Figure 31-4)
 Prone positioning on a Jackson table with a Wilson frame for maximal flexion at the index level
Prone positioning on a Jackson table with a Wilson frame for maximal flexion at the index level