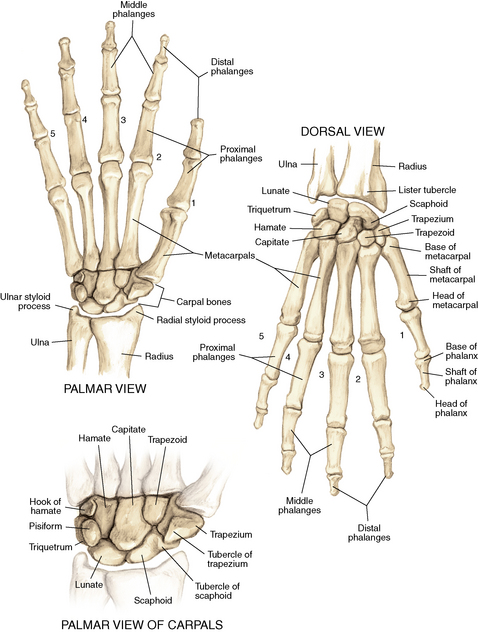
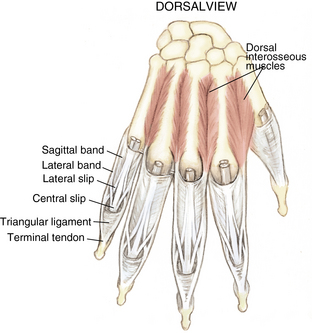
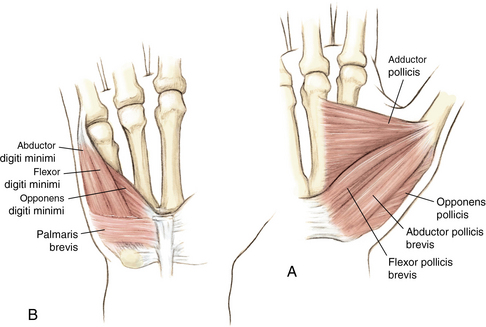
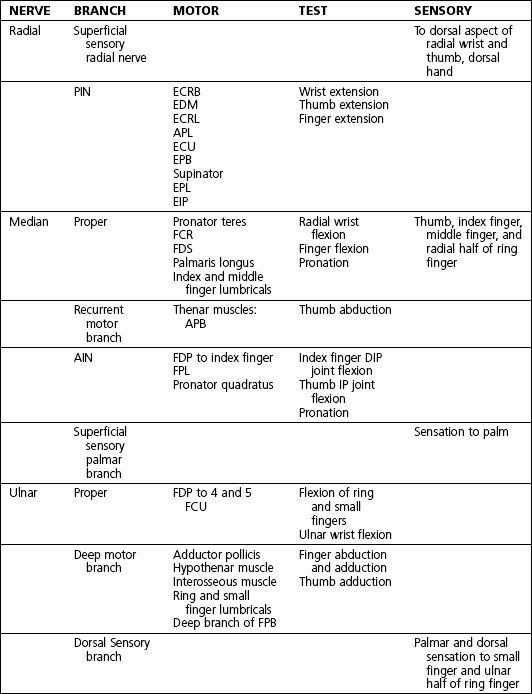
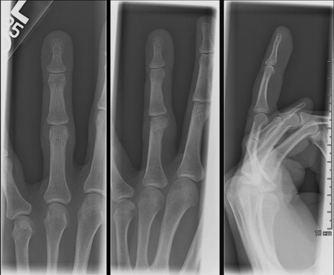
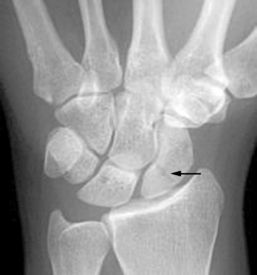
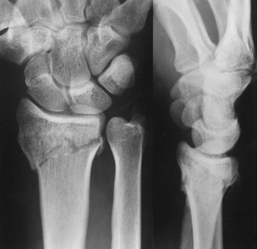
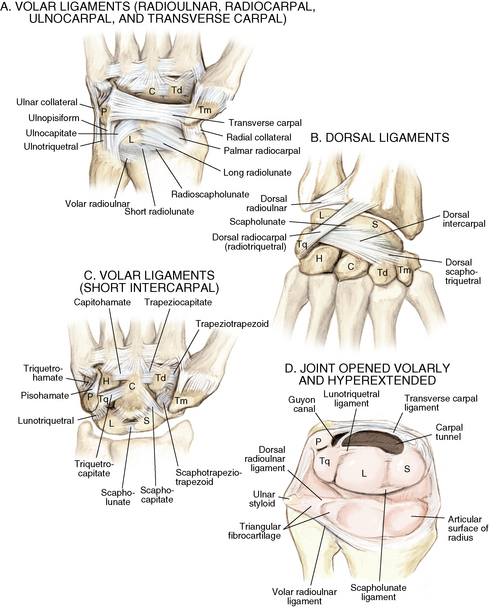
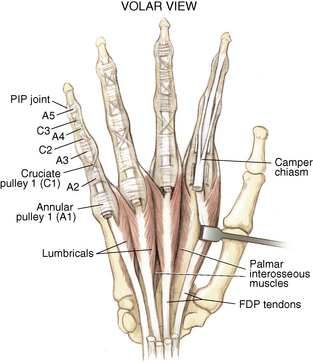
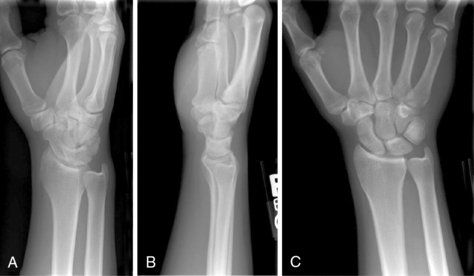
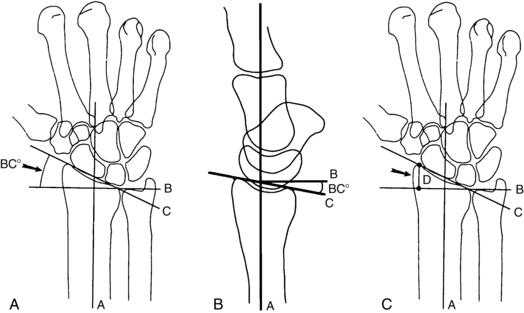
4 Wrist and hand Figure 4-2. A to D, Ligaments of the wrist. Ca, capitate; H, hamate; L, lunate; P, pisiform; S, scaphoid; Td, trapezoid; Tm, trapezium; Tq, triquetrum. (From Chhabra AB: Wrist and hand. In Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches, Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 150.) Figure 4-3. Flexor tendon pulley system. Figure 4-4. Volar muscles of the hand: lumbricals and palmar interossei. FDP, flexor digitorum profundus; PIP, proximal interphalangeal. (From Chhabra AB: Wrist and hand. In Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches, Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 154.) Figure 4-6. A and B, Extensor tendon compartments of wrist. APL, abductor pollicis longus; ECRB, extensor carpi radialis brevis; ECRL, extensor carpi radialis longus; ECU, extensor carpi ulnaris; EDC, extensor digitorum communis; EDM, extensor digiti minimi. (From Chhabra AB: Wrist and hand. In Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches, Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 157.) Figure 4-8. A and B, Nerves of the hand and wrist. (From Chhabra AB: Wrist and hand. In Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches, Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 159.) Figure 4-11. Surface anatomy of the hand and wrist. Figure 4-12. Normal radiographs of the hand. Figure 4-13. Normal radiographs of the wrist. Anteroposterior (A) views of the wrist (B), and oblique (C), lateral. Inspect for scars, muscle atrophy, edema, erythema or deformity. Palpate specific structures to evaluate complaint: • Distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) • Anatomic snuffbox, scaphoid tubercle • First extensor compartment, extensor carpi radialis ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi radialis longus • Scapholunate (SL) interval (approximately 1 to 3 cm distal from Lister tubercle) • First carpometacarpal (CMC) joint • Flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) tendon • Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) tendon • Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) Normal wrist range of motion (ROM): Table 4-2 Table 4-2. Neurovascular examination of the wrist and hand: Table 4-3 Table 4-3. Neurovascular Examination of the Wrist and Hand Table 4-4. Differential Diagnosis of Wrist Pain • Sutures are removed, and a wound check is performed. • Radiographs consist of wrist PA, lateral, oblique, and navicular views. • Immobilization: The patient is placed into a removable thumb spica splint. • Therapy referral: Start edema control and gentle finger and wrist ROM only. • Note: Some surgeons prefer cast immobilization in a thumb spica cast during the initial postoperative period, especially if the fracture was difficult to reduce or especially comminuted. • The patient returns for a motion check. • Radiographs consist of wrist PA, lateral, and scaphoid views. • Therapy: If healing is present, progress therapy to more aggressive wrist ROM, wean from the splint, and start gradual weight bearing. • If no healing is noted, continue gentle ROM and have the patient wear the brace at all times until healing is evident on radiographs. • The patient returns for a motion check. • Assess for tenderness at the anatomic snuffbox and scaphoid tubercle. • Radiographs consist of wrist PA, lateral, and scaphoid views. • If the injury is healed and no pain is noted on examination, release the patient to regular activities without restrictions. • If no evidence of healing is seen on radiographs, consider use of a bone stimulator and possibly obtain a CT scan to evaluate for healing. • Nonunion occurs if there has been no healing by 6 months postoperatively. Describe the fracture in terms of displacement, comminution, radial length, surface tilt, and articular step-off (Figure 4-18 and Table 4-6). Figure 4-18. How to determine whether a distal radius fracture meets operative criteria. A, Radial inclination. B, Volar tilt. C, Radial height. (Adapted from Baratz ME, Larsen CF. Wrist and hand measurements and classification schemes. In Gilula LA, Yin Y (eds). Imaging of the wrist and hand, Philadelphia, Saunders, 1996.) • Stable reduced fractures require 3 weeks in a sugar tong splint with weekly radiographs in the splint to ensure that fracture alignment is maintained. If the reduction is lost, surgery is recommended. If fracture reduction is maintained for 3 weeks, transition the patient to a short-arm cast with radiographs immediately following new cast placement to ensure alignment. • The fracture is considered healed if there is radiographic evidence of healing and the patient is nontender over the distal radius. This usually occurs in approximately 2 to 3 months, depending on the severity of the original injury. Figure 4-19. Surgical fixation of a displaced distal radius fracture with a volar locking plate. Posteroanterior (A) and lateral (B) views. • Sutures are removed, and a wound check is performed. • Possible radiographs include wrist PA, lateral, and oblique views. • Immobilization: The patient is placed into a removable spica splint. • Therapy referral: Start edema control and gentle finger and wrist motion only. Some clinicians start therapy at 3 to 5 days postoperatively. • Note: Some surgeons prefer cast immobilization in a short-arm cast during the initial postoperative period, especially if the fracture was difficult to reduce or especially comminuted. • The patient returns for a motion check. • Radiographs consist of wrist PA, lateral, and navicular views. • Therapy: If healing is present, progress therapy to more aggressive wrist motion, wean the patient from the splint, and start gradual weight bearing and strengthening.
Anatomy
Ligaments: Figure 4-2
Muscles and tendons: Figures 4-3 through 4-7
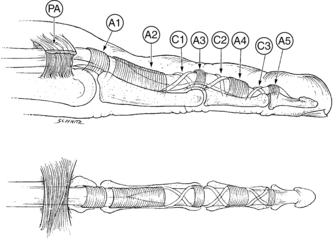
A1 to A5, annular pulleys; C1 to C3, cruciate pulleys; PA, palmar aponeurosis. (From Strickland JW: Flexor tendons: acute injuries. In Green DP, editor: Operative hand surgery, ed 4, New York, 1999, Churchill Livingstone, p 1853.)
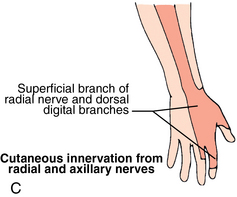
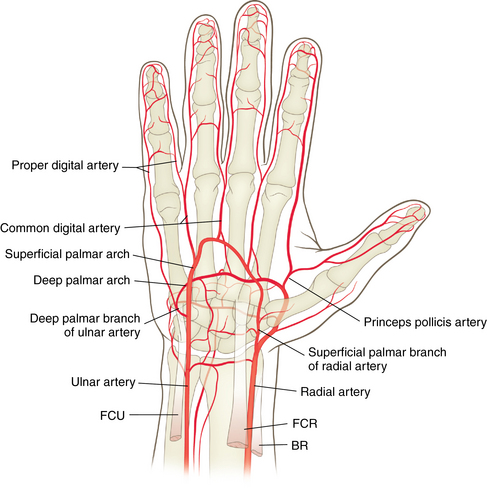
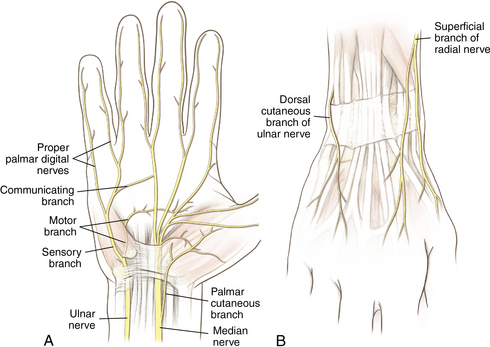
Nerves and arteries: Figures 4-8 through 4-10 and table 4-1
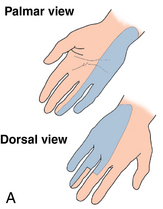
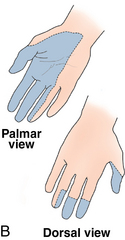
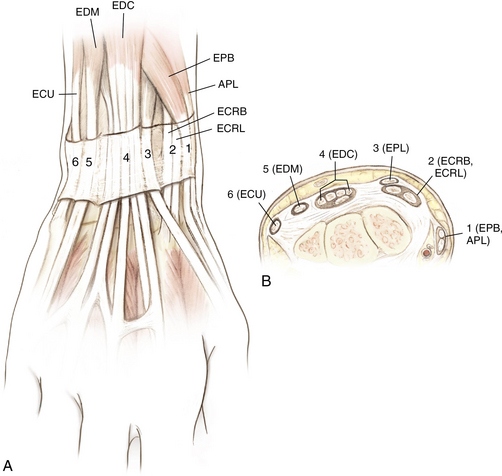
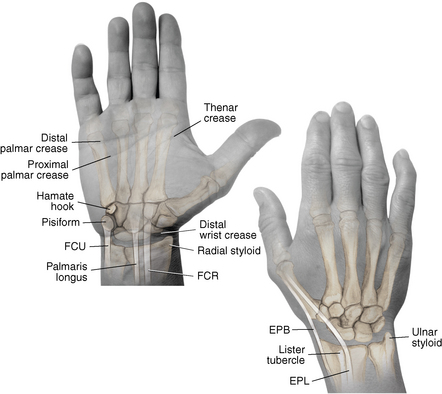
Surface anatomy: Figure 4-11
EPB, extensor pollicis brevis; EPL, extensor pollicis longus; FCR, flexor carpi radialis; FCU, flexor carpi ulnaris. (From Chhabra AB: Wrist and hand. In Miller MD, Chhabra AB, Hurwitz S, et al, editors: Orthopaedic surgical approaches, Philadelphia, 2008, Saunders, p 163.)
Normal radiographic appearance: Figures 4-12 through 4-14
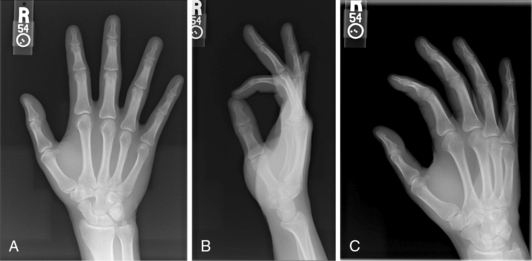
Anteroposterior (A), lateral (B), and oblique (C) views of the hand. (From Hart JA: Overview of the wrist and hand. In Miller MD, Hart JA, MacKnight JM, editors: Essential orthopaedics, Philadelphia, 2010, Saunders, p 303.)
Physical examination
Extension
80 degrees
Flexion
70 degrees
Supination
90 degrees
Pronation
90 degrees
Ulnar deviation
30 degrees
Radial deviation
20 degrees
NERVE
LOCATION OF TEST
TESTS
Median nerve
Carpal tunnel
Tinel, Phalen, Durkan test (see page 140)
Ulnar nerve
Guyon canal/medial epicondyle
Tinel test
Superficial sensory radial nerve
At radial styloid
Tinel test
Radial and ulnar artery
At volar wrist
Allen test for dominance or perfusion
Differential diagnosis of wrist pain: Table 4-4
Radial-sided wrist pain
Distal radius fracture
SLL tear
Arthritis
Scaphoid fracture
Extensor tendinitis
de Quervain tenosynovitis
Ulnar-sided wrist pain
TFCC tear
FCU tendinitis
Ulnar artery thrombosis
Cubital tunnel syndrome
Pisotriquetral arthritis
ECU tendinitis
Distal ulnar fracture
Lunotriquetral tear
Hook hamate fracture
Dorsal wrist pain
Extensor tendinitis
Arthritis
SLL tear
Scaphoid fracture
Volar wrist pain
FCU or FCR tendinitis
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Scaphoid fracture
Differential diagnosis
 SL ligament (SLL) injury (see page 129)
SL ligament (SLL) injury (see page 129)
 First extensor compartment tendinitis
First extensor compartment tendinitis
 Occult scaphoid fracture: If there is high level of suspicion for a scaphoid fracture but the initial radiographic findings are negative, place the patient into a thumb spica splint and obtain radiographs again at 3 weeks after injury. If follow-up radiographic findings are negative but patient is still symptomatic, order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to evaluate for occult scaphoid fracture or SLL tear.
Occult scaphoid fracture: If there is high level of suspicion for a scaphoid fracture but the initial radiographic findings are negative, place the patient into a thumb spica splint and obtain radiographs again at 3 weeks after injury. If follow-up radiographic findings are negative but patient is still symptomatic, order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to evaluate for occult scaphoid fracture or SLL tear.
Treatment options
 Conservative management is reserved for nondisplaced fractures in which patient declines surgery or for patients too ill for surgery.
Conservative management is reserved for nondisplaced fractures in which patient declines surgery or for patients too ill for surgery.
 Nondisplaced waist fractures have an 88% to 95% healing rate if treated within 3 weeks of injury.
Nondisplaced waist fractures have an 88% to 95% healing rate if treated within 3 weeks of injury.
 A short-arm thumb spica cast is used for a total of 8 to 12 weeks, depending on healing (some argue for long-arm cast).
A short-arm thumb spica cast is used for a total of 8 to 12 weeks, depending on healing (some argue for long-arm cast).
 See the patient in follow-up at 4-week intervals to change the cast, obtain repeat radiographs of the fracture, and assess healing.
See the patient in follow-up at 4-week intervals to change the cast, obtain repeat radiographs of the fracture, and assess healing.
 A computed tomography (CT) scan may be necessary to confirm healing after 8 to 12 weeks.
A computed tomography (CT) scan may be necessary to confirm healing after 8 to 12 weeks.
 The fracture is considered healed if there is radiographic evidence of healing and patient is nontender to palpation at the anatomic snuffbox and scaphoid tubercle or if a CT scan confirms healing.
The fracture is considered healed if there is radiographic evidence of healing and patient is nontender to palpation at the anatomic snuffbox and scaphoid tubercle or if a CT scan confirms healing.
Operative management of acute scaphoid fractures
Informed consent and counseling
 Even with appropriate treatment and good surgical fixation, the rate of nonunion is 5% because of the scaphoid’s tenuous blood supply. Proximal pole scaphoid fractures have the highest incidence of non-union.
Even with appropriate treatment and good surgical fixation, the rate of nonunion is 5% because of the scaphoid’s tenuous blood supply. Proximal pole scaphoid fractures have the highest incidence of non-union.
 Smoking cessation is imperative for fracture healing.
Smoking cessation is imperative for fracture healing.
 The patient can expect to be immobilized for approximately 6 weeks, although the type of immobilization depends on the surgeon’s preference and on fracture fixation.
The patient can expect to be immobilized for approximately 6 weeks, although the type of immobilization depends on the surgeon’s preference and on fracture fixation.
 The patient will require approximately 2 months of outpatient hand therapy to restore motion and strength.
The patient will require approximately 2 months of outpatient hand therapy to restore motion and strength.
Surgical procedures
 Dorsal approach for proximal pole fractures
Dorsal approach for proximal pole fractures
 Volar approach for distal pole and waist fractures
Volar approach for distal pole and waist fractures
 For either approach, placement of a forearm-based thumb spica splint
For either approach, placement of a forearm-based thumb spica splint
Open reduction, internal fixation
 Hardware consists of a cannulated headless compression screw and multiple wires.
Hardware consists of a cannulated headless compression screw and multiple wires.
 Dorsal approach: A small longitudinal incision is made over the proximal pole of the scaphoid. Avoid the superficial sensory radial nerve.
Dorsal approach: A small longitudinal incision is made over the proximal pole of the scaphoid. Avoid the superficial sensory radial nerve.
 Volar approach: A small incision is made over the scaphoid tubercle. Avoid the radial artery during exposure.
Volar approach: A small incision is made over the scaphoid tubercle. Avoid the radial artery during exposure.
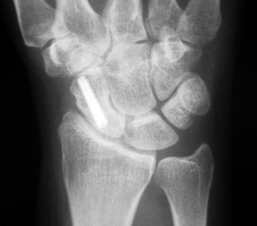
Percutaneous internal fixation: Figure 4-16
 This technique may be used preferentially for nondisplaced scaphoid fractures. The procedure is similar to the open technique, just performed percutaneously. With the patient’s wrist flexed, a guidewire is placed down the central axis of the scaphoid. The guidewire is also used to measure the appropriate screw length. After fluoroscopic confirmation of adequate reduction, a screw is placed for fixation. Place the patient in a thumb spica splint following surgery.
This technique may be used preferentially for nondisplaced scaphoid fractures. The procedure is similar to the open technique, just performed percutaneously. With the patient’s wrist flexed, a guidewire is placed down the central axis of the scaphoid. The guidewire is also used to measure the appropriate screw length. After fluoroscopic confirmation of adequate reduction, a screw is placed for fixation. Place the patient in a thumb spica splint following surgery.
Estimated postoperative course
Distal radius fractures
Classification
Initial treatment
 The distal radius is the most commonly fractured bone in the arm. The fracture pattern determines surgical versus nonsurgical treatment. If the fracture is nondisplaced or if the fracture has been successfully closed reduced and splinted and the fingers are sensate with good perfusion, then the injury can wait several days for evaluation by an orthopaedist. If the patient’s fingers are numb and/or not well perfused or the fracture is not able to be reduced, the patient should have an immediate surgical evaluation.
The distal radius is the most commonly fractured bone in the arm. The fracture pattern determines surgical versus nonsurgical treatment. If the fracture is nondisplaced or if the fracture has been successfully closed reduced and splinted and the fingers are sensate with good perfusion, then the injury can wait several days for evaluation by an orthopaedist. If the patient’s fingers are numb and/or not well perfused or the fracture is not able to be reduced, the patient should have an immediate surgical evaluation.
Treatment options
 Conservative management is reserved for nondisplaced fractures or stable reduced fractures or for patients too ill for surgery.
Conservative management is reserved for nondisplaced fractures or stable reduced fractures or for patients too ill for surgery.
 Nondisplaced fractures require casting for 6 to 8 weeks in a short-arm cast.
Nondisplaced fractures require casting for 6 to 8 weeks in a short-arm cast.
 Generally, after 6 weeks of immobilization, patients may progress with ROM.
Generally, after 6 weeks of immobilization, patients may progress with ROM.
Operative management of acute distal radius fractures
Codes
Informed consent and counseling
 Smoking cessation is important for fracture healing.
Smoking cessation is important for fracture healing.
 The patient can expect to be immobilized for approximately 6 weeks, but the type of immobilization depends on the surgeon’s preference and on fracture fixation.
The patient can expect to be immobilized for approximately 6 weeks, but the type of immobilization depends on the surgeon’s preference and on fracture fixation.
 The patient may require several sessions of outpatient hand therapy to restore motion and strength.
The patient may require several sessions of outpatient hand therapy to restore motion and strength.
Surgical procedures
Open reduction, internal fixation: See figure 4-19
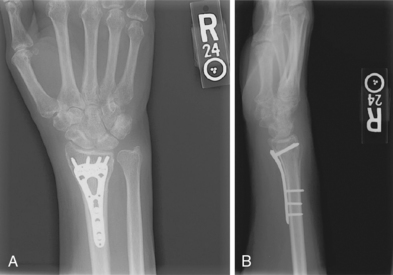
 Hardware consists of a volar plate and screws.
Hardware consists of a volar plate and screws.
 Volar approach: A longitudinal incision is made directly superficial to the flexor carpi radialis (FCR) tendon. An interval is developed between the FCR and the radial artery. Blunt deep dissection is carried down to the pronator quadratus muscle, which is sharply incised on the radial border and elevated off the periosteum of the radius to expose the fracture. Sometimes the brachioradialis tendon insertion must be released to decrease the deforming forces on the fracture. A volar plate and screws are used, and intraoperative fluoroscopy confirms reduction and hardware placement. The patient is placed in a volar short-arm splint postoperatively.
Volar approach: A longitudinal incision is made directly superficial to the flexor carpi radialis (FCR) tendon. An interval is developed between the FCR and the radial artery. Blunt deep dissection is carried down to the pronator quadratus muscle, which is sharply incised on the radial border and elevated off the periosteum of the radius to expose the fracture. Sometimes the brachioradialis tendon insertion must be released to decrease the deforming forces on the fracture. A volar plate and screws are used, and intraoperative fluoroscopy confirms reduction and hardware placement. The patient is placed in a volar short-arm splint postoperatively.
Estimated postoperative course
Wrist and hand