13 Vessels of the breast
13.3 Anatomy
13.3.1 Container
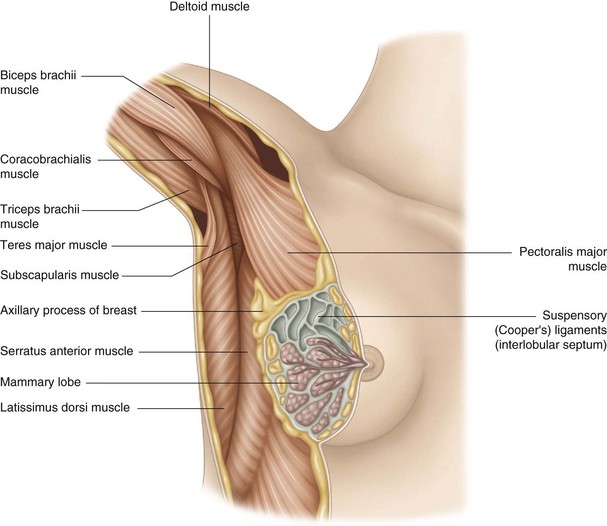
The breasts, located between the third and seventh ribs, are supported by collagen fibers called the suspensory mammary ligaments (of Astley Cooper) (Fig. 13.1). The ligaments are found between the dermis and the connective tissue of the breast. They can extend towards the axillary fossa, overlying the pectoral muscle. The suspensory ligaments of the breast are comprised of numerous septa, joining the pre- and post-mammary fascia. These fibrous strands of connective tissue are more developed in the upper part of the breast.
• In the superficial plane, two-thirds of the mammary gland rests on the pectoralis major muscle, and the remaining third on the external oblique and rectus abdominis muscles. The superolateral quadrant is related to the axillary fascia by its lateral process, where it contacts the fifth and sixth digitations of the serratus anterior muscle.
• The deep plane is made up of the subclavian and pectoralis minor muscles, which are ensheathed in the clavipectoral aponeurosis.
13.3.2 Contents
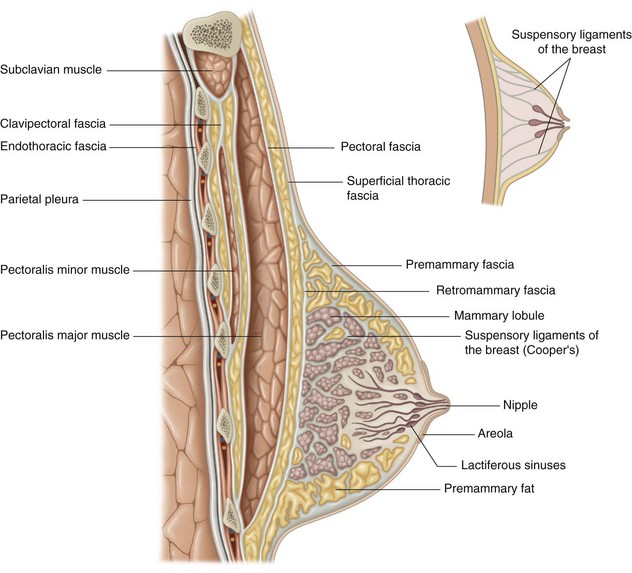
The breast is composed of glandular lobes and adipose tissue surrounded by connective tissue (Fig. 13.2).
13.3.3 Innervation
Intercostal nerves
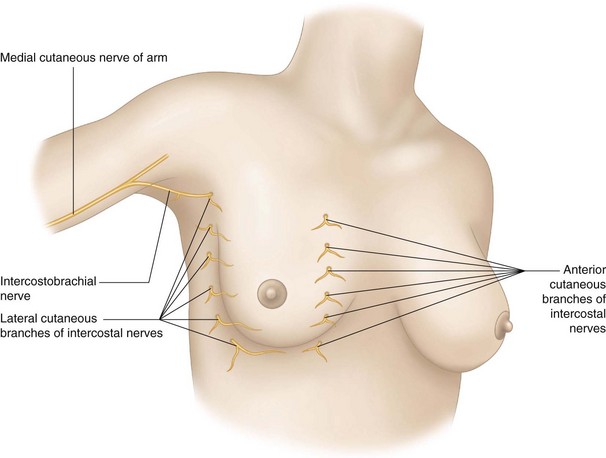
The breast is innervated by the third to the sixth intercostal nerves (Fig. 13.3). The lateral cutaneous branches innervate the lateral breast, whereas the anterior cutaneous branches pass through the pectoralis major muscle to reach the medial breast.
13.3.4 Vascularization
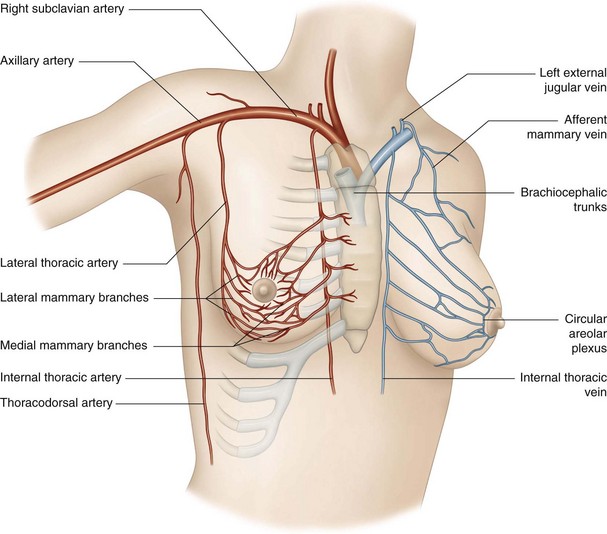
We emphasize again the fact that vascular manipulations will involve the venous system. The breast has a rich venous supply (Fig. 13.4).
Arteries of the breast
Internal thoracic artery
Collaterals
• The anterior intercostal arteries perforate the intercostal muscle and pectoralis major at the third, fourth, and fifth intercostal spaces. These branches then reach the mammary gland, becoming the medial mammary arteries.
• Posterior branches go to the thymus and the pericardium.
• Lateral branches, which form the anterior arteries, are distributed in pairs in each intercostal space.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree