Section 3 Upper Limb Injections
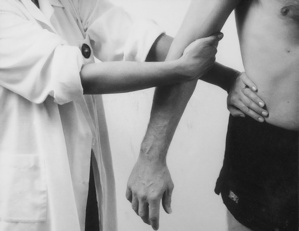
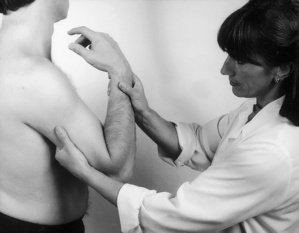
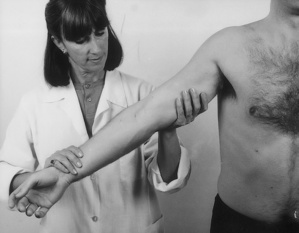
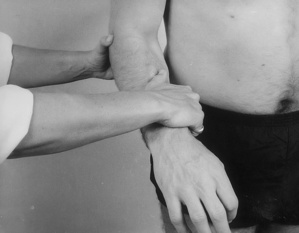
Examination of the upper limb
| Shoulder tests | |
| Active flexion above head | Resisted abduction |
| Passive flexion with overpressure | Resisted lateral rotation |
| Active abduction to ear for painful arc | Resisted medial rotation |
| Passive lateral rotation | Resisted elbow flexion |
| Passive abduction | Resisted elbow extension |
| Passive medial rotation | Resisted adduction |
| Impingement/lag/stability/proprioception tests | |
| Shoulder capsular pattern: most loss of lateral rotation, less of abduction, least of medial rotation | |
| Elbow tests | |
| Passive flexion | Resisted flexion |
| Passive extension | Resisted extension |
| Passive pronation | Resisted pronation |
| Passive supination | Resisted supination |
| Resisted wrist flexion | |
| Resisted wrist extension | |
| Elbow capsular pattern: more loss of flexion than extension | |
| Wrist tests | |
| Passive pronation | Resisted extension |
| Passive supination | Resisted flexion |
| Passive extension | Resisted radial deviation |
| Passive flexion | Resisted ulnar deviation |
| Passive radial deviation | |
| Passive ulnar deviation | |
| Wrist capsular pattern: equal loss of flexion and extension | |
| Finger tests | |
| Passive thumb extension | Passive finger extension |
| Resisted thumb abduction | Passive finger flexion |
| Resisted thumb adduction | Resisted finger abduction |
| Resisted thumb extension | Resisted finger adduction |
| Resisted thumb flexion | |
| Finger capsular patterns: Loss of: | |
| Thumb: extension & abduction | |
| Metacarpophalangeal joints: extension and radial deviation | |
| Interphalangeal joints: flexion | |
| Distal phalangeal joints: extension | |
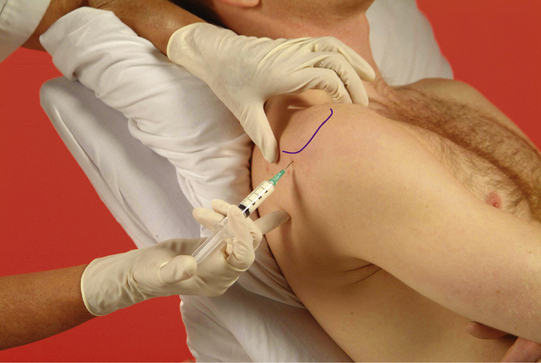
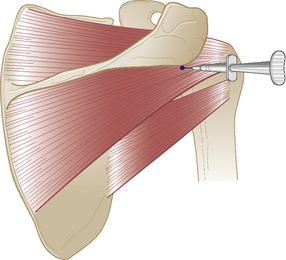
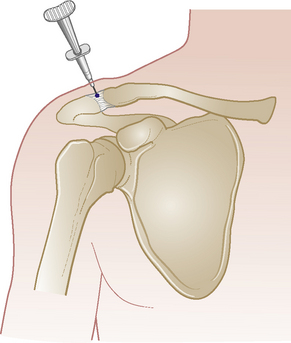
Glenohumeral joint
Acute or chronic capsulitis – ‘frozen shoulder’
Causes and findings
• Trauma, osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, idiopathic or secondary to neurological disease, diabetes, stroke, etc
• Pain in deltoid area, possibly radiating down to hand in severe cases, aggravated by arm movements and lying on shoulder
Technique
• Insert needle directly below angle and pass anteriorly obliquely towards coracoid process until needle gently touches intra-articular cartilage
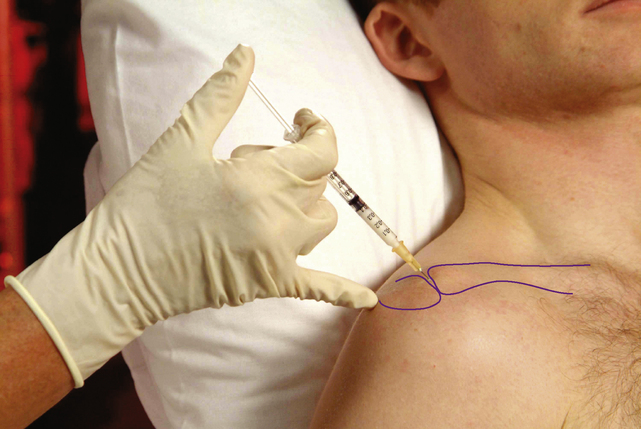
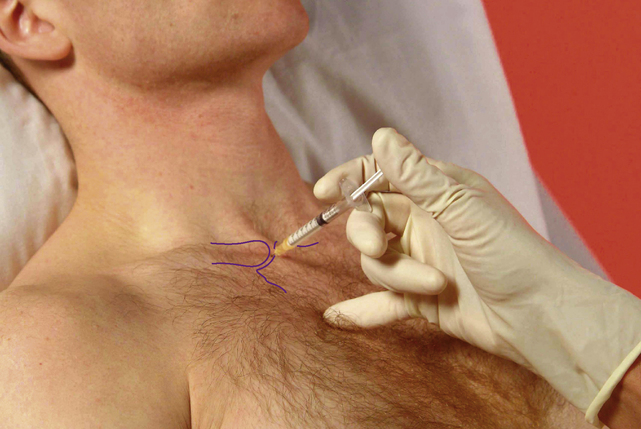
Acromioclavicular joint
Subacromial bursa
Chronic bursitis
Causes and findings
• Painful: passive elevation and medial rotation more than lateral rotation. Resisted abduction and lateral rotation, often on release of resistance – these two tests often appear weak due to muscle inhibition. Possible arc, ‘muddle’ of signs, with resisted tests less painful when tested under distraction